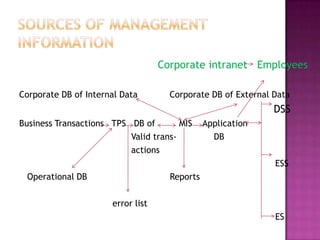
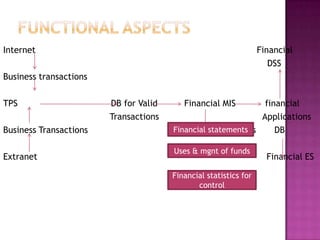
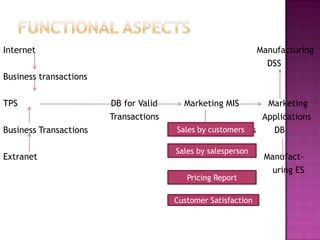
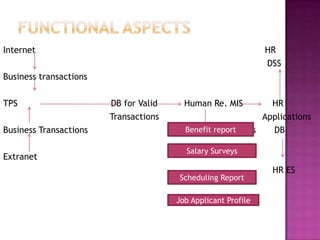
An MIS integrates data from various departments and provides operations and management with required information for decision making and daily operations. The document then provides examples of different types of MIS like financial MIS, marketing MIS, human resources MIS, and manufacturing MIS. It describes the purpose, inputs, and outputs of each system.