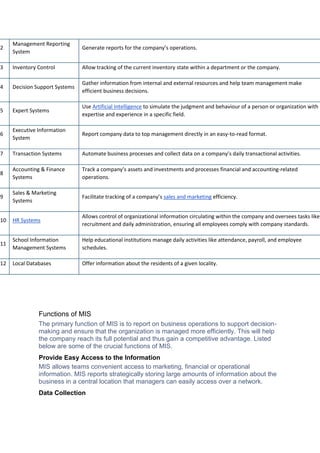
The document outlines the significance and operation of transaction processing systems (TPS) and management information systems (MIS) in businesses. It details TPS components including inputs, outputs, storage, and processing systems, while also emphasizing the importance of MIS for managerial decision-making and performance tracking. Additionally, it discusses decision support systems (DSS) as tools for real-time data analysis to aid decision-making processes across various organizational sectors.