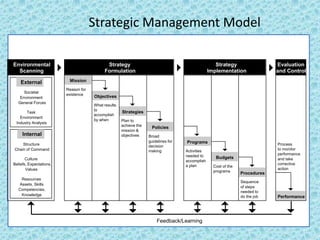
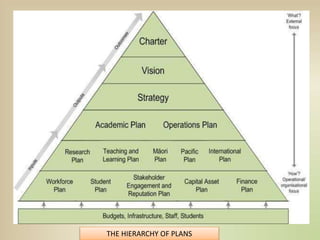
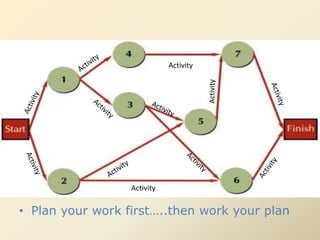
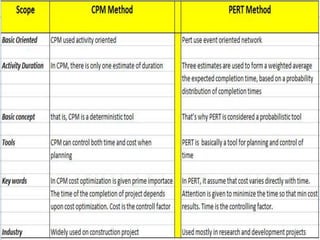
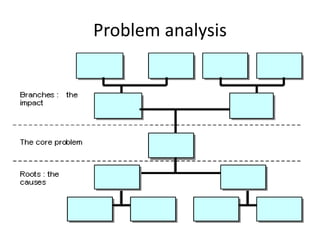
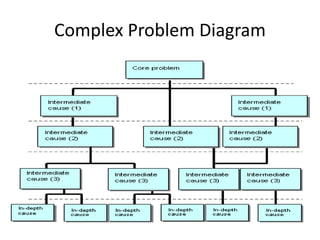
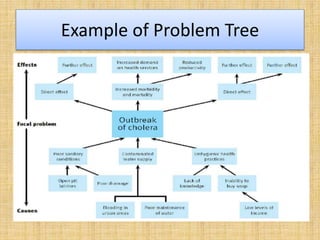
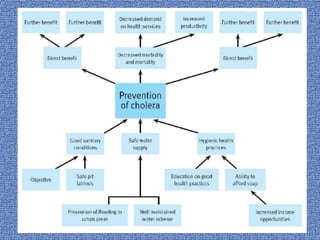
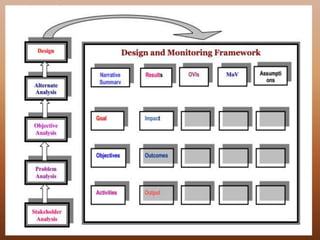
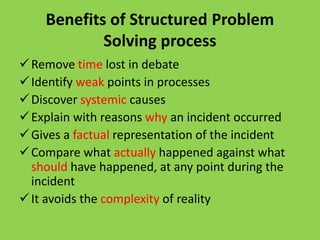
This document discusses goal oriented project planning (GOPP) for effective problem solving. It provides an introduction and outline of GOPP concepts, principles, and steps. GOPP is a participatory planning tool used in project management to define goals and objectives, analyze problems, and design action plans. The key principles of GOPP include planning logically and documenting it, involving stakeholders in the planning process, and determining goals before measures to achieve them. The main steps involve analyzing the project context, stakeholders, problems, objectives, activities, resources, and risks. GOPP aims to improve project design and ensure plans are relevant to those implementing them. It is an effective tool for problem definition and solution.