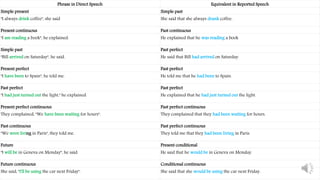
- Reported speech is used to report what other people have said by changing the tense and pronouns. For example, "I am tired" would become "She said that she was tired."
- Tenses in reported speech are typically one step back from the original tense. For example, present simple becomes past simple.
- Reported questions use verbs like "ask" and change the question structure, but maintain normal word order. For example, "Where does Peter live?" becomes "She asked him where Peter lived."
- The reporting verbs used can be more descriptive than just "say", like admit, reveal, or suggest.