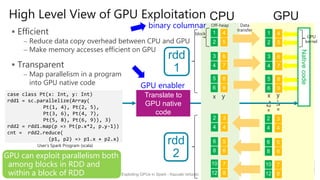
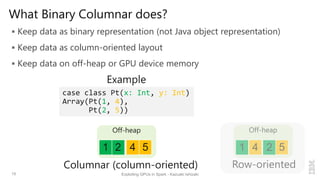
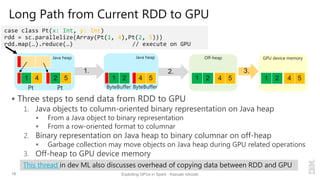
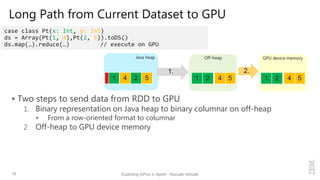
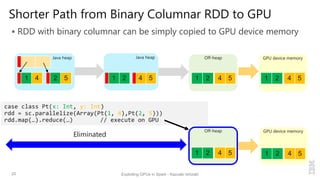
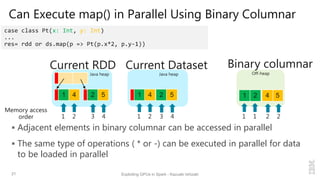
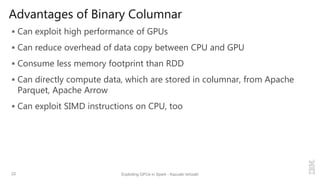
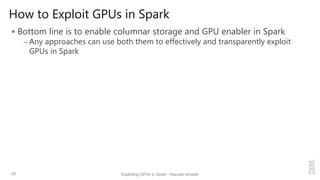
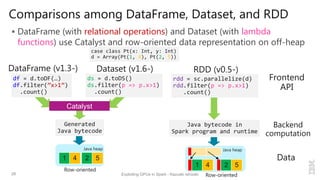
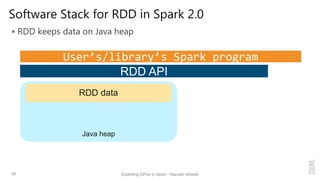
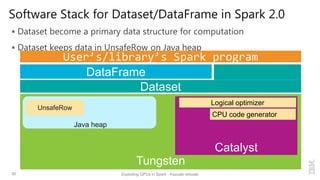
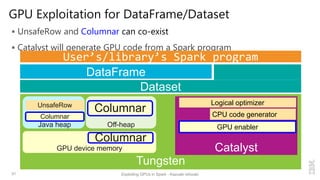
Kazuaki Ishizaki is a research staff member at IBM Research - Tokyo who is interested in compiler optimizations, language runtimes, and parallel processing. He has worked on the Java virtual machine and just-in-time compiler for over 20 years. His message is that Spark can utilize GPUs to accelerate computation-heavy applications in a transparent way. He proposes new binary columnar and GPU enabler components that would efficiently store and handle data on GPUs without requiring changes to Spark programs. This could be implemented either through a Spark plugin for RDDs or by enhancing the Catalyst optimizer in Spark to generate GPU code.
















![Exploit GPUs for RDD
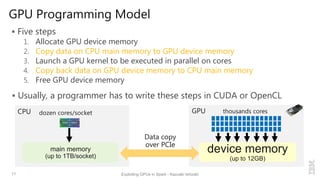
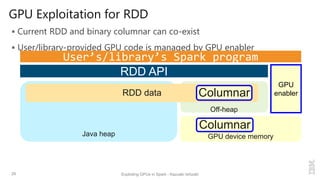
Execute user-provided GPU kernels from map()/reduce() functions
– GPU memory managements and data copy are automatically handled
Generate GPU native code for simple map()/reduce() methods
– “spark.gpu.codegen=true” in spark-defaults.conf
32 Exploiting GPUs in Spark - Kazuaki Ishizaki
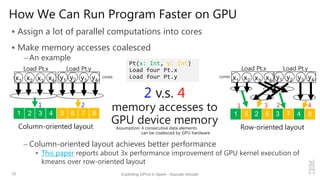
rdd1 = sc.parallelize(1 to n, 2).convert(ColumnFormat) // rdd1 uses binary columnar RDD
sum = rdd1.map(i => i * 2)
.reduce((x, y) => (x + y))
// CUDA
__global__ void sample_map(int *inX, int *inY, int *outX, int *outY, long size) {
long ix = threadIdx.x + blockIdx.x * blockDim.x;
if (size <= ix) return;
outX[ix] = inX[ix] * 2;
outY[ix] = inY[ix] – 1;
}
// Spark
mapFunction = new CUDAFunction(“sample_map", // CUDA method name
Array("this.x", "this.y"), // input object has two fields
Array("this.x“, “this.y”), // output object has two fields
this.getClass.getResource("/sample.ptx")) // ptx is generated by CUDA complier
rdd1 = sc.parallelize(…).convert(ColumnFormat) // rdd1 uses binary columnar RDD
rdd2 = rdd1.mapExtFunc(p => Pt(p.x*2, p.y-1), mapFunction)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/advancedapachesparkmeetup20160407spark-gpuishizaki-160413084404/85/Exploiting-GPUs-in-Spark-32-320.jpg)
![How to Use Exploitation of GPUs for RDD
Easy to install by one-liner and to run by one-liner
– on x86_64, mac, and ppc64le with CUDA 7.0 or later with any JVM such as IBM
JDK or OpenJDK
Run script for AWS EC2 is available, which support spot instances33 Exploiting GPUs in Spark - Kazuaki Ishizaki
$ wget https://s3.amazonaws.com/spark-gpu-public/spark-gpu-latest-bin-hadoop2.4.tgz &&
tar xf spark-gpu-latest-bin-hadoop2.4.tgz && cd spark-gpu
$ LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/usr/local/cuda/lib64 MASTER='local[2]' ./bin/run-example SparkGPULR 8 3200 32 5
…
numSlices=8, N=3200, D=32, ITERATIONS=5
On iteration 1
On iteration 2
On iteration 3
On iteration 4
On iteration 5
Elapsed time: 431 ms
$
Available at http://kiszk.github.io/spark-gpu/
• 3 contributors
• Private communications
with other developers](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/advancedapachesparkmeetup20160407spark-gpuishizaki-160413084404/85/Exploiting-GPUs-in-Spark-33-320.jpg)
![Achieved 3.15x Performance Improvement by GPU
Ran naïve implementation of logistic regression
Achieved 3.15x performance improvement of logistic regression over
without GPU on a 16-core IvyBridge box with an NVIDIA K40 GPU card
– We have rooms to improve performance
34 Exploiting GPUs in Spark - Kazuaki Ishizaki
Details are available at https://github.com/kiszk/spark-gpu/wiki/Benchmark
Program parameters
N=1,000,000 (# of points), D=400 (# of features), ITERATIONS=5
Slices=128 (without GPU), 16 (with GPU)
MASTER=local[8] (without and with GPU)
Hardware and software
Machine: nx360 M4, 2 sockets 8-core Intel Xeon E5-2667 3.3GHz, 256GB memory, one NVIDIA K40m card
OS: RedHat 6.6, CUDA: 7.0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/advancedapachesparkmeetup20160407spark-gpuishizaki-160413084404/85/Exploiting-GPUs-in-Spark-34-320.jpg)


