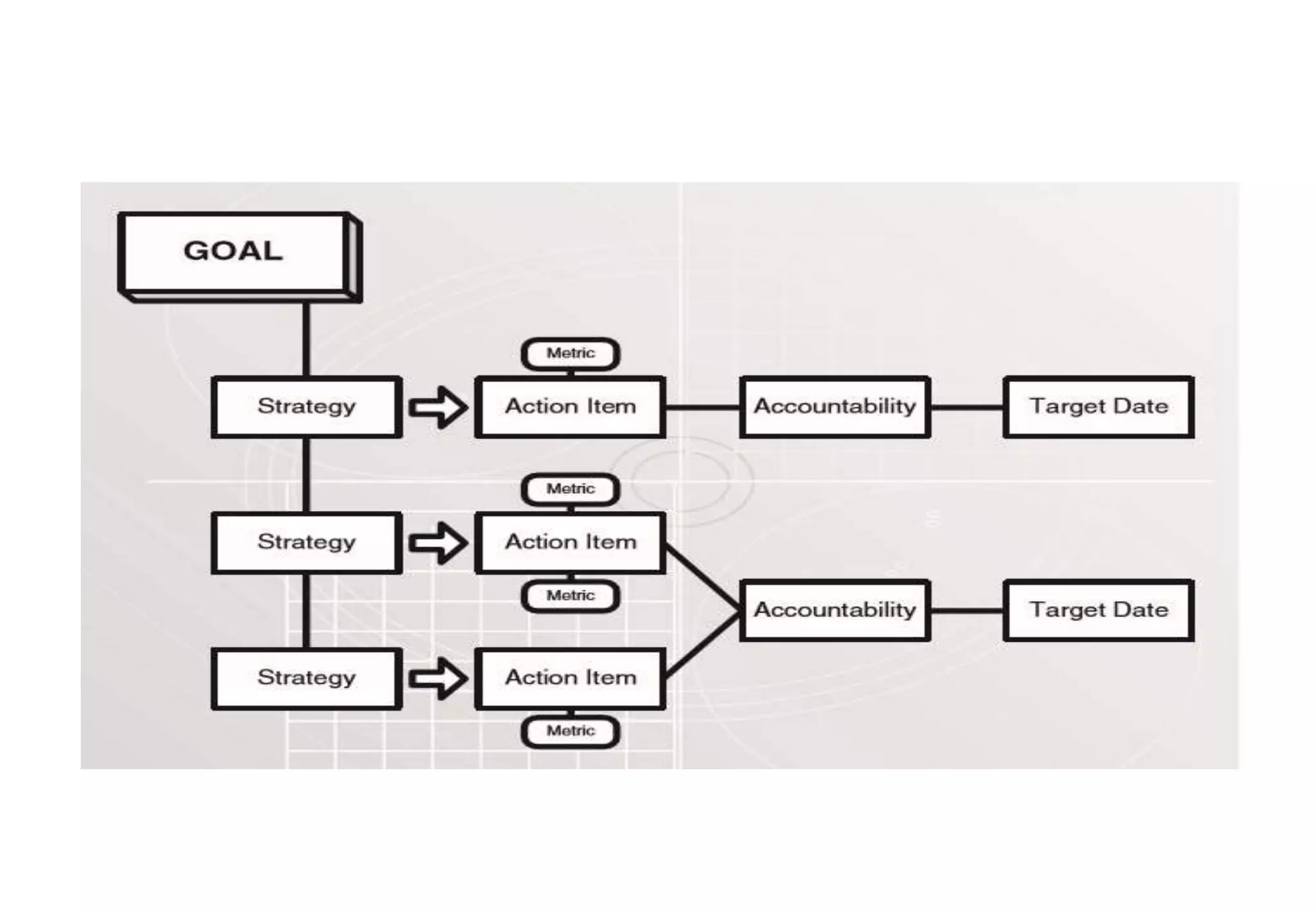
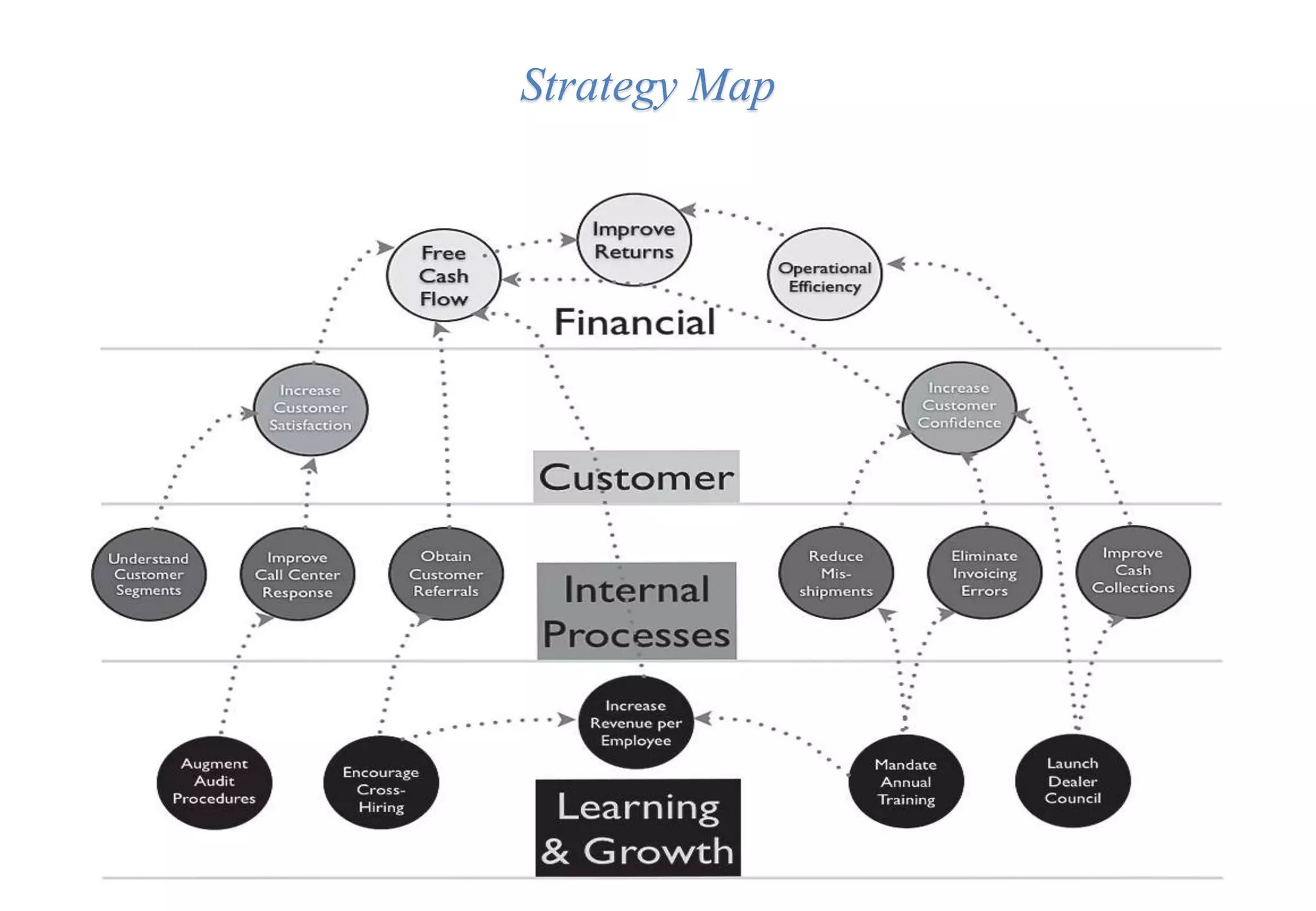
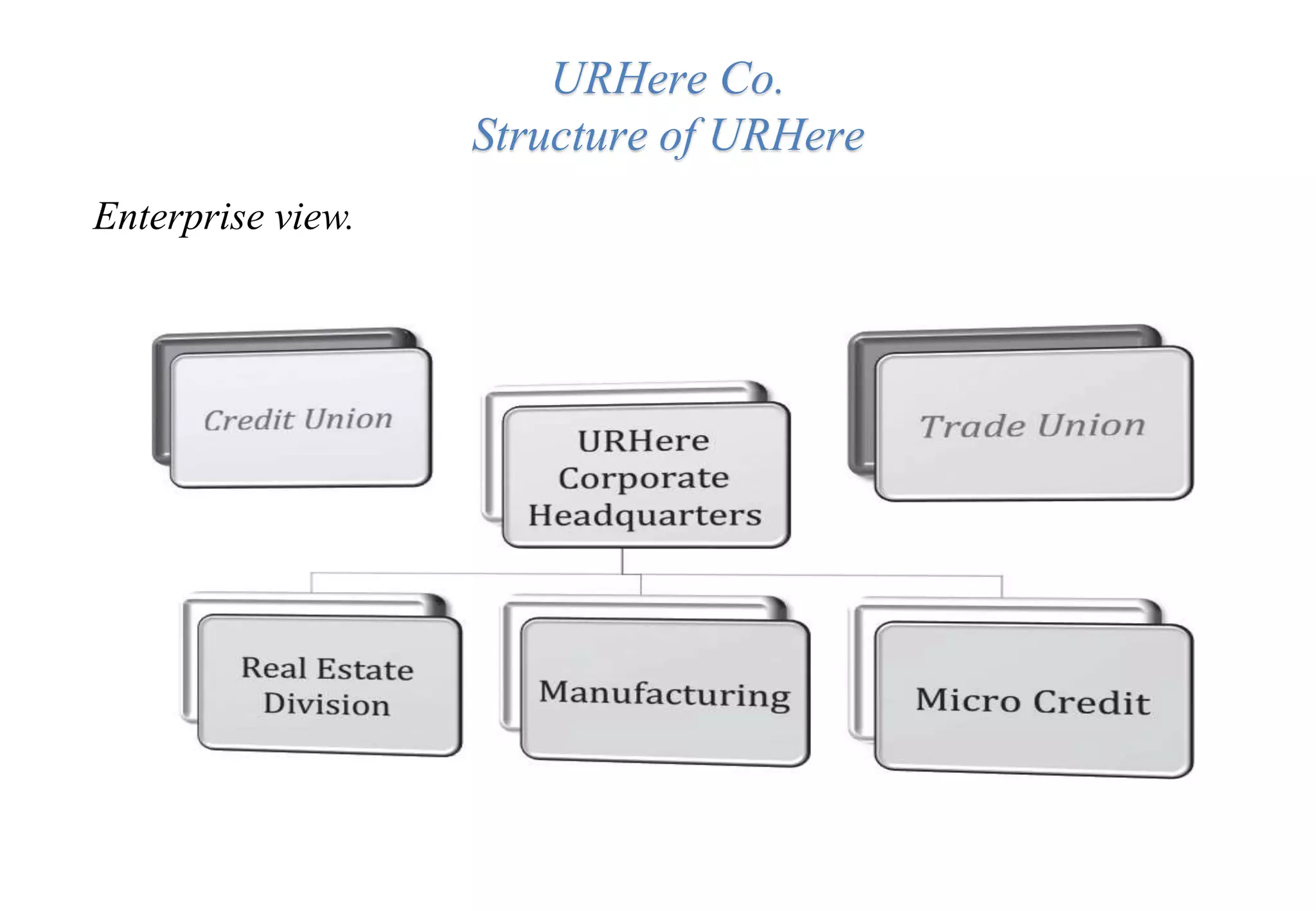
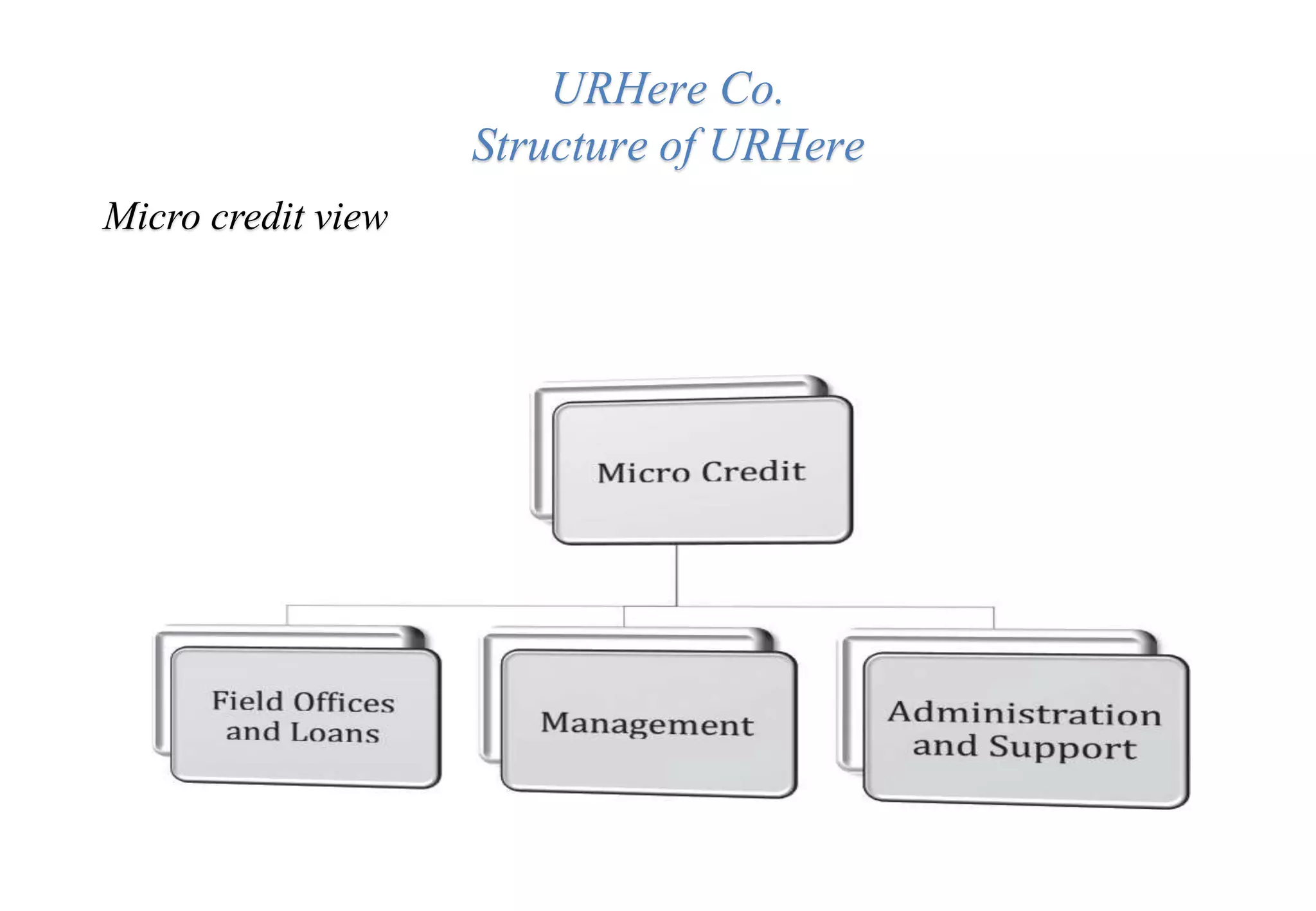
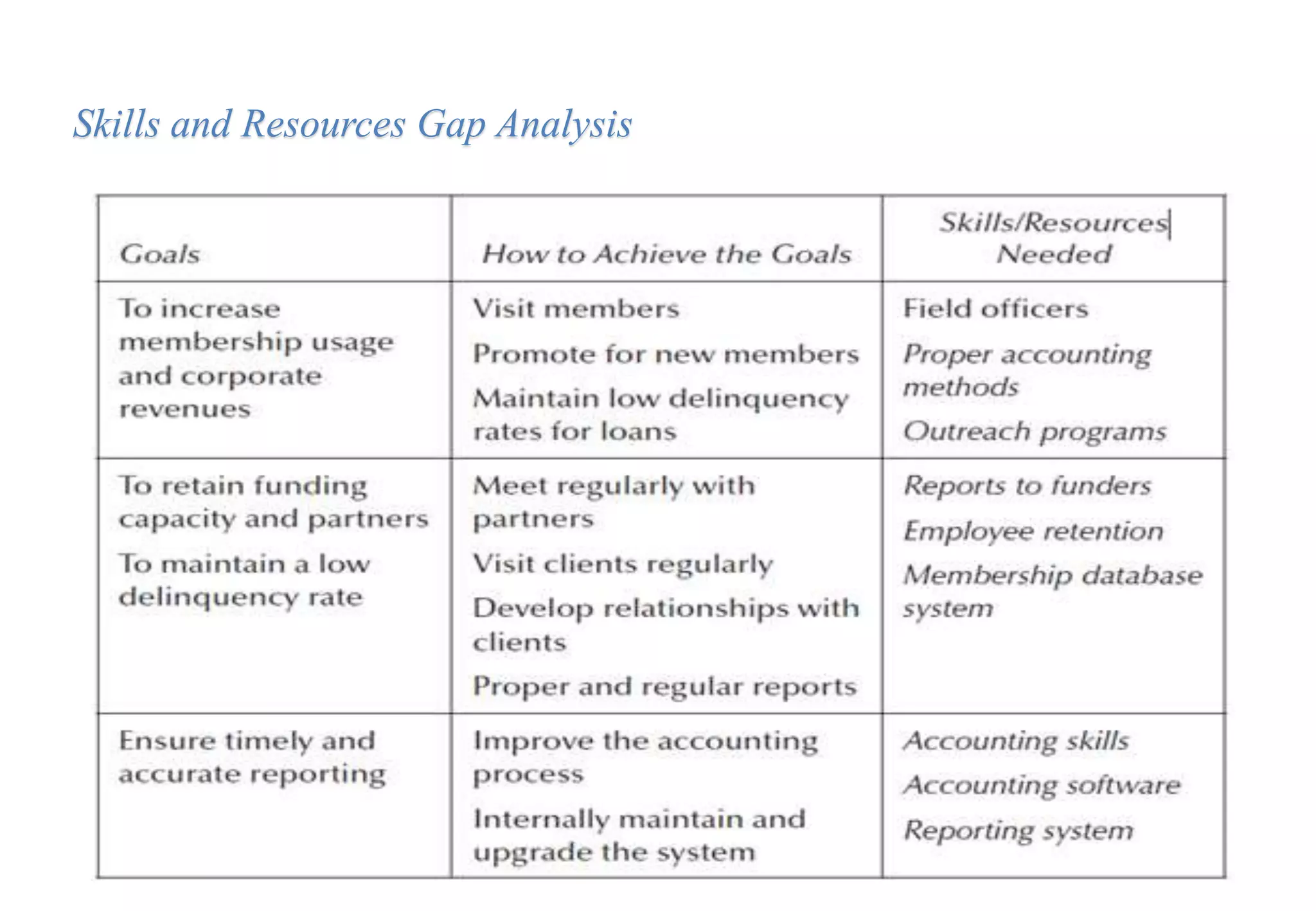
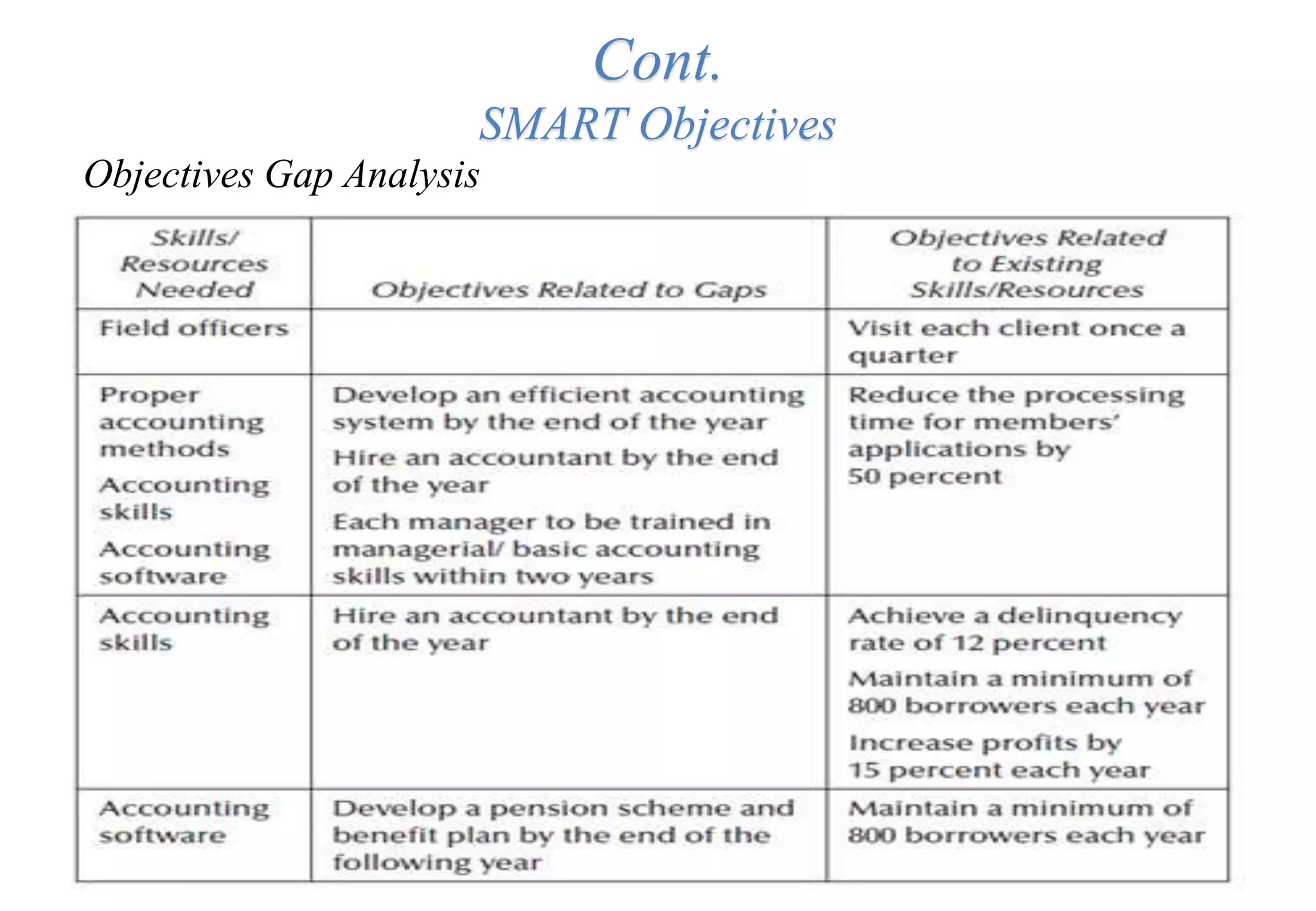
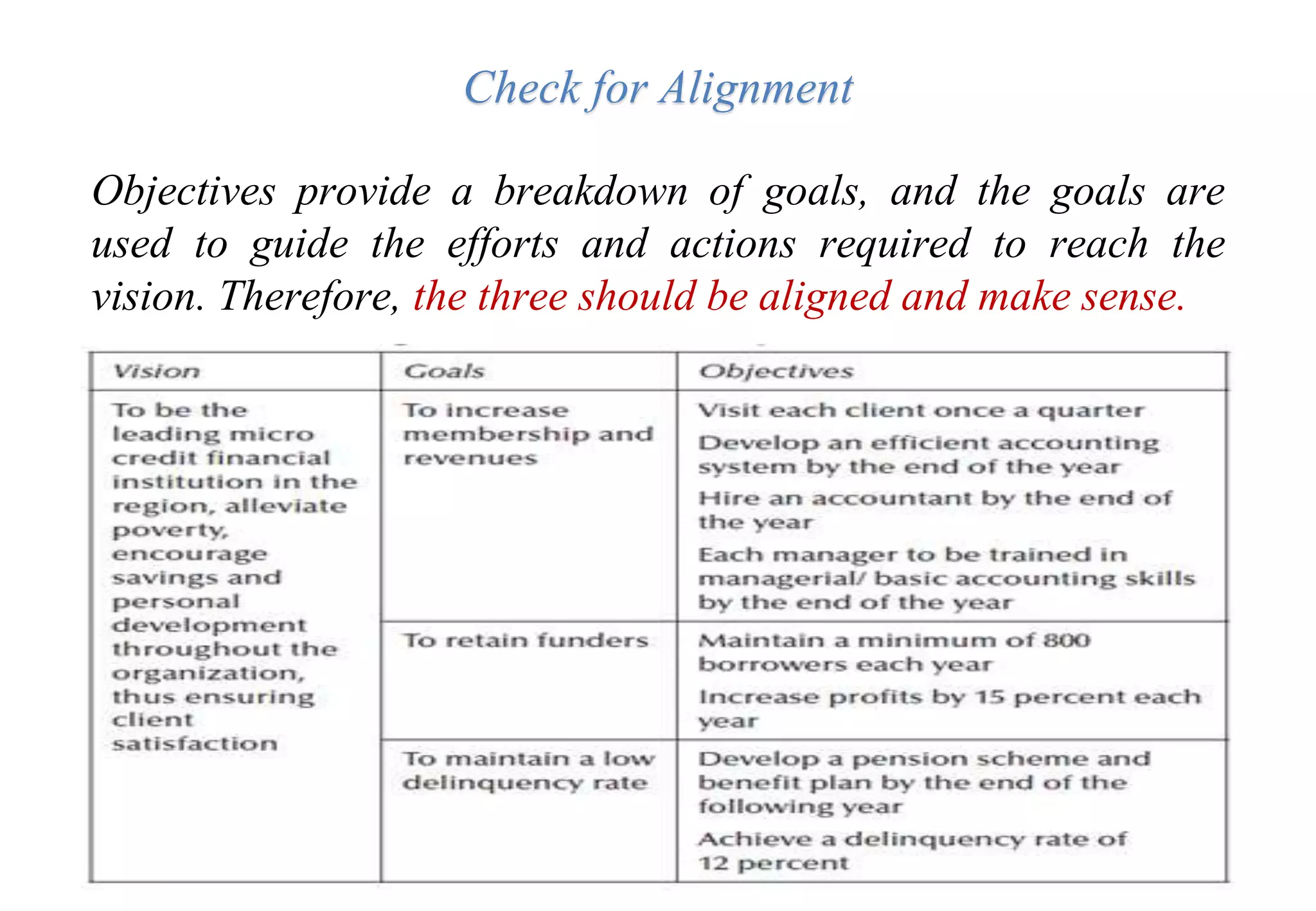
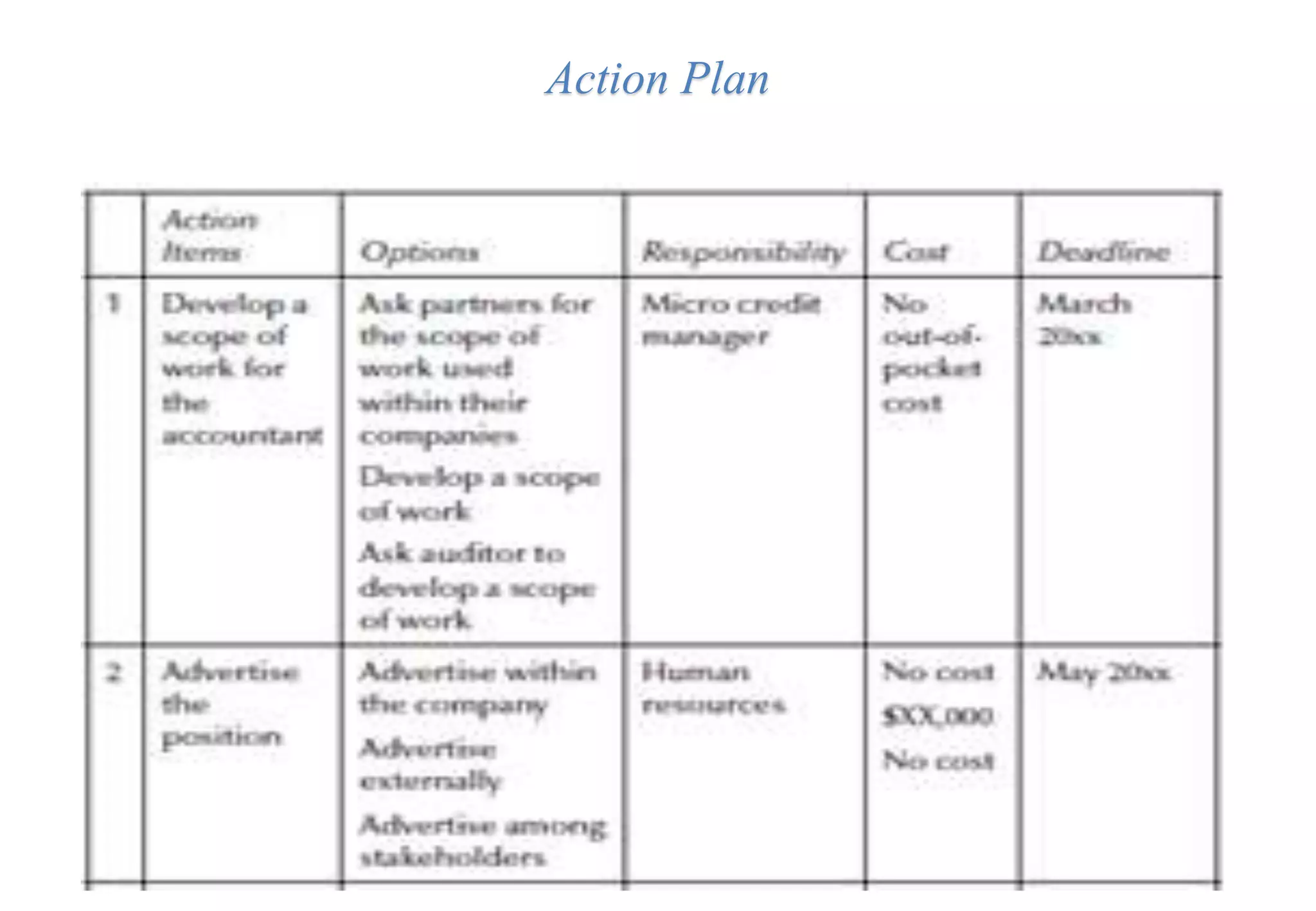
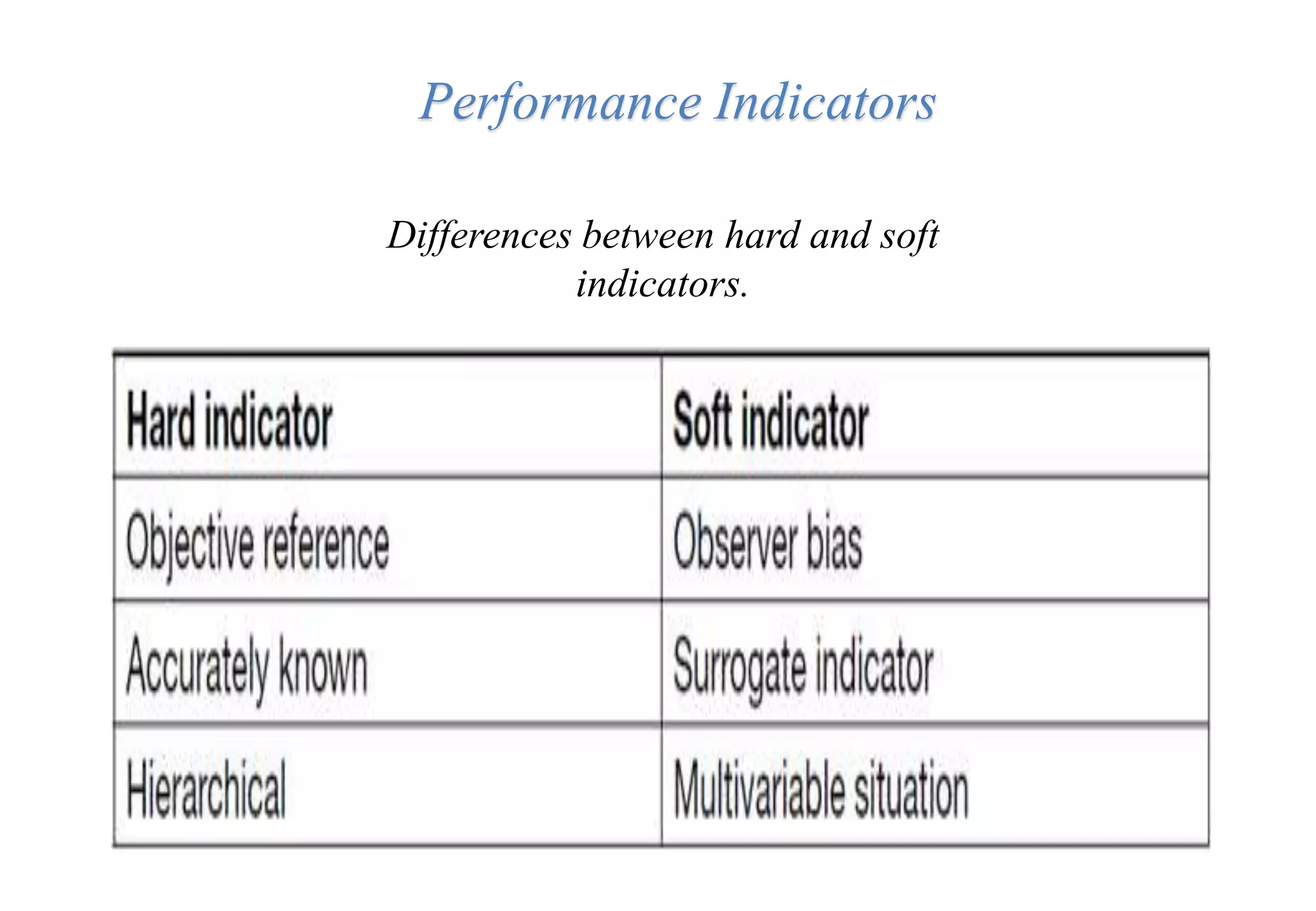
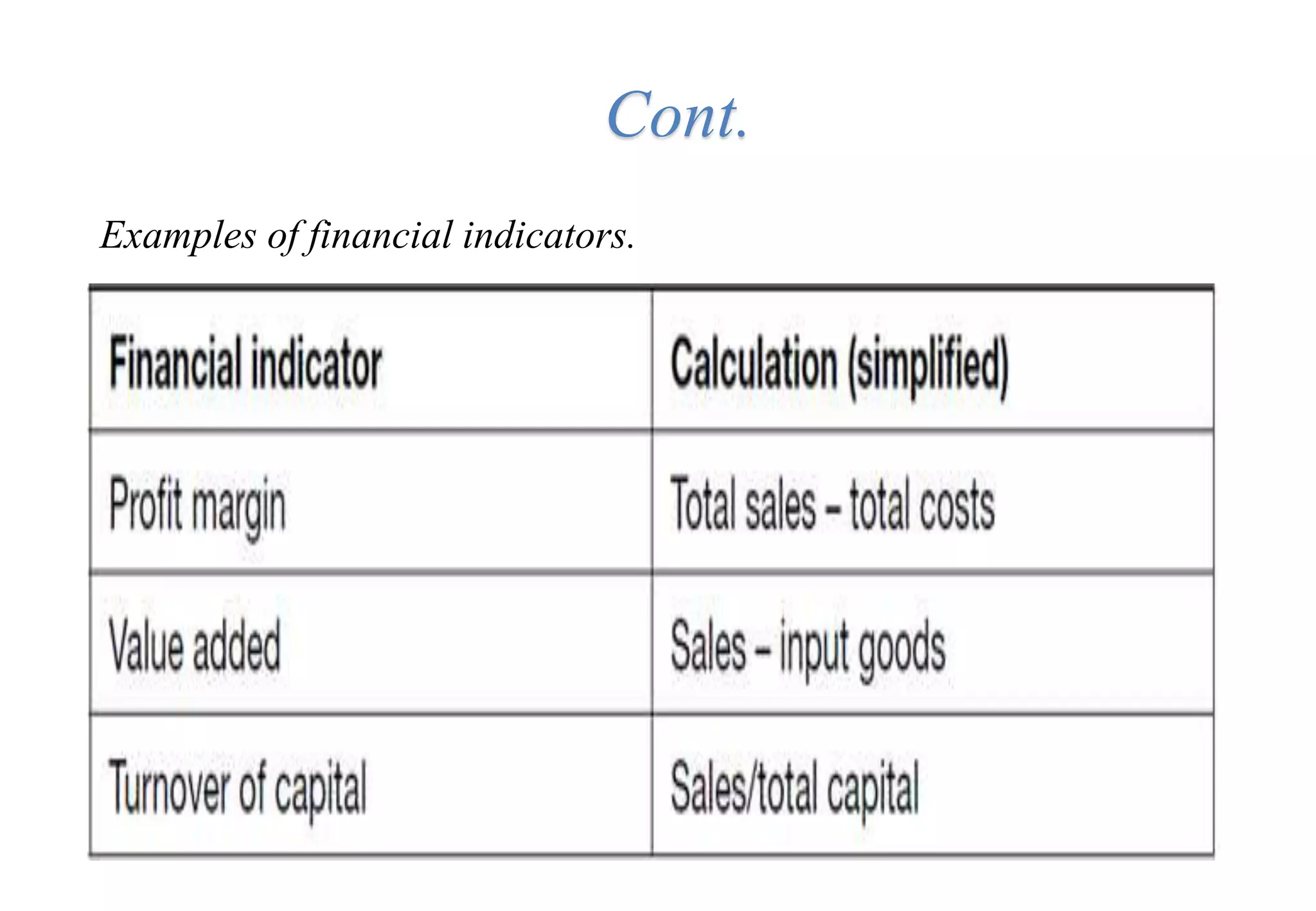
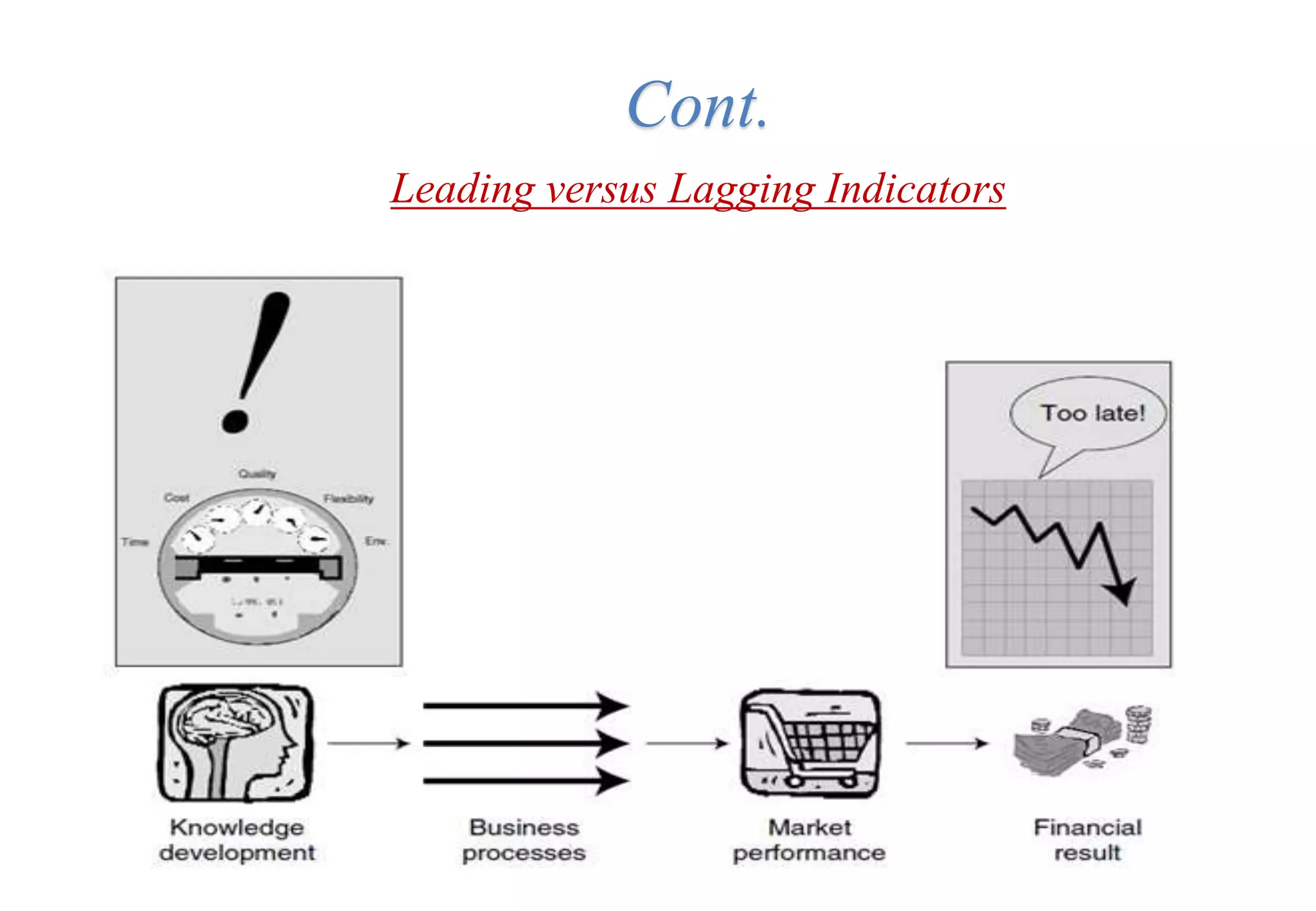
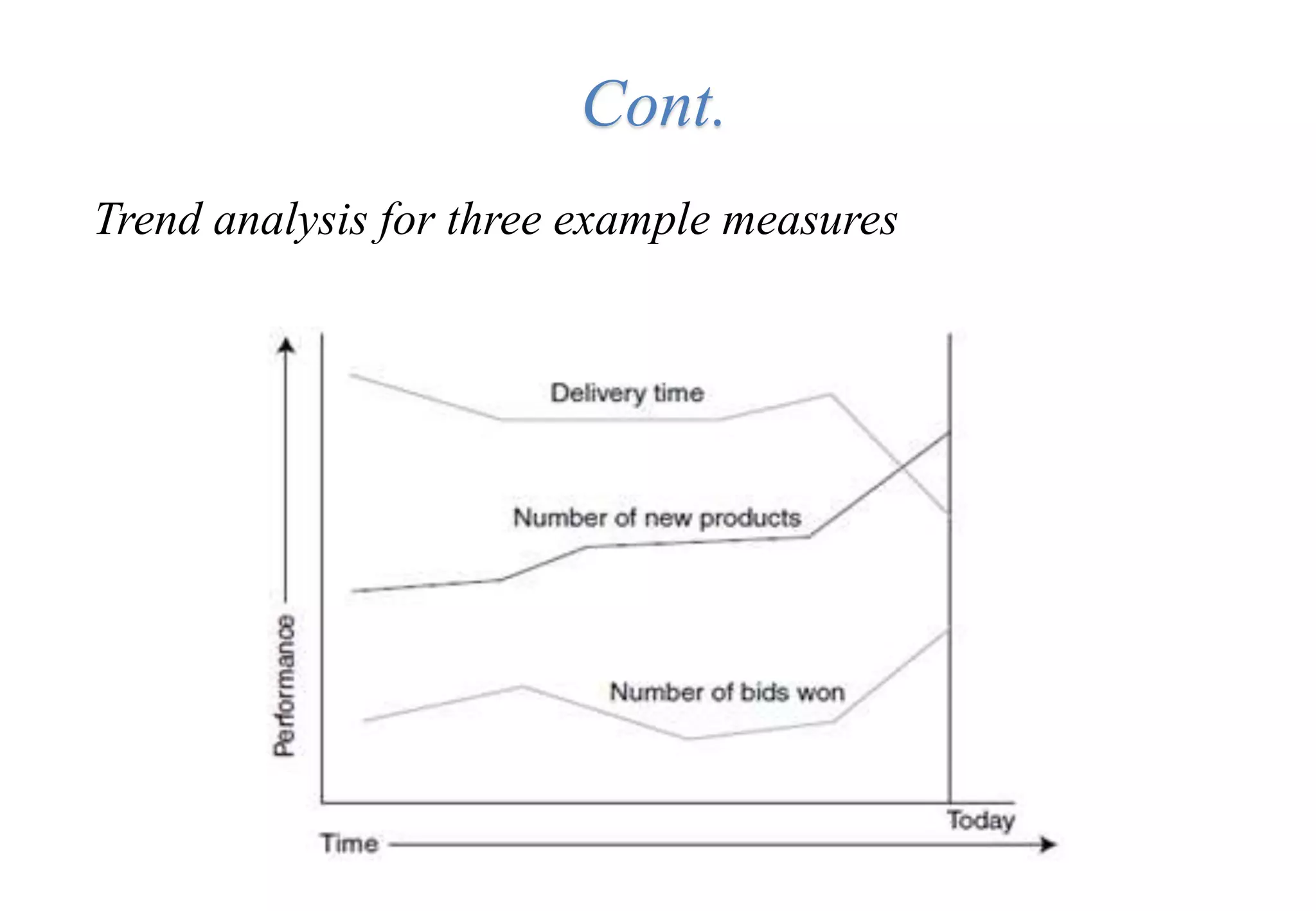
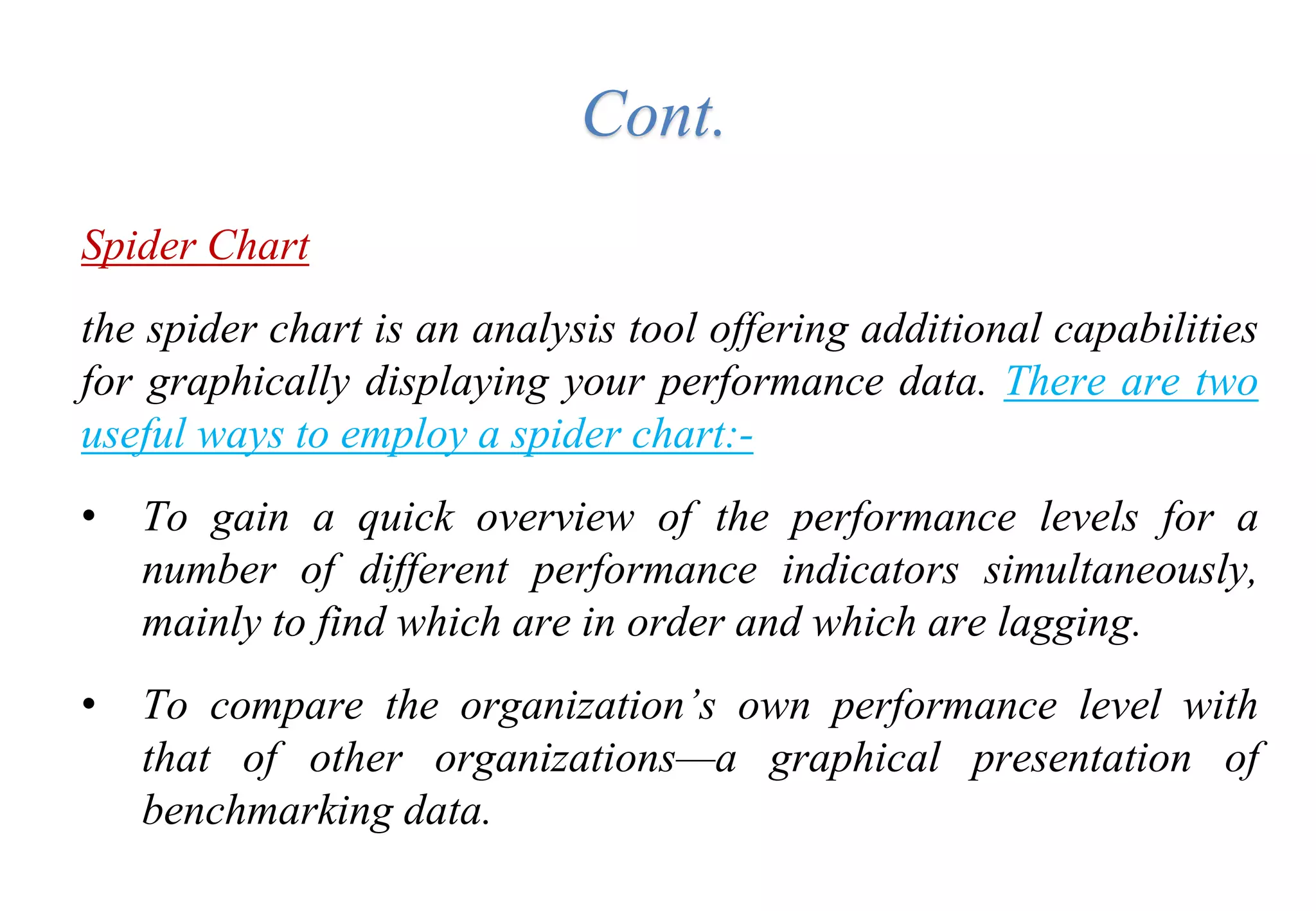
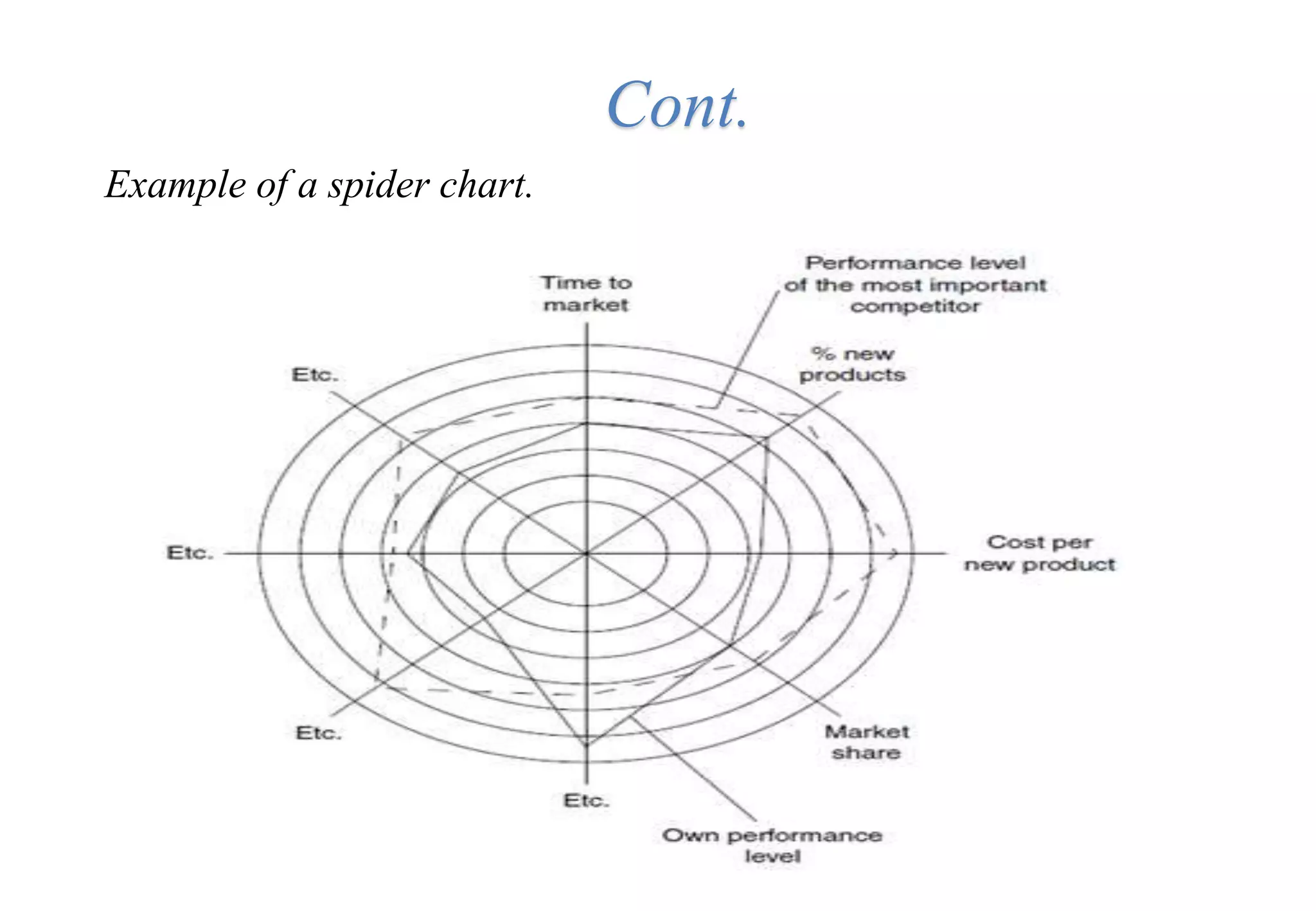
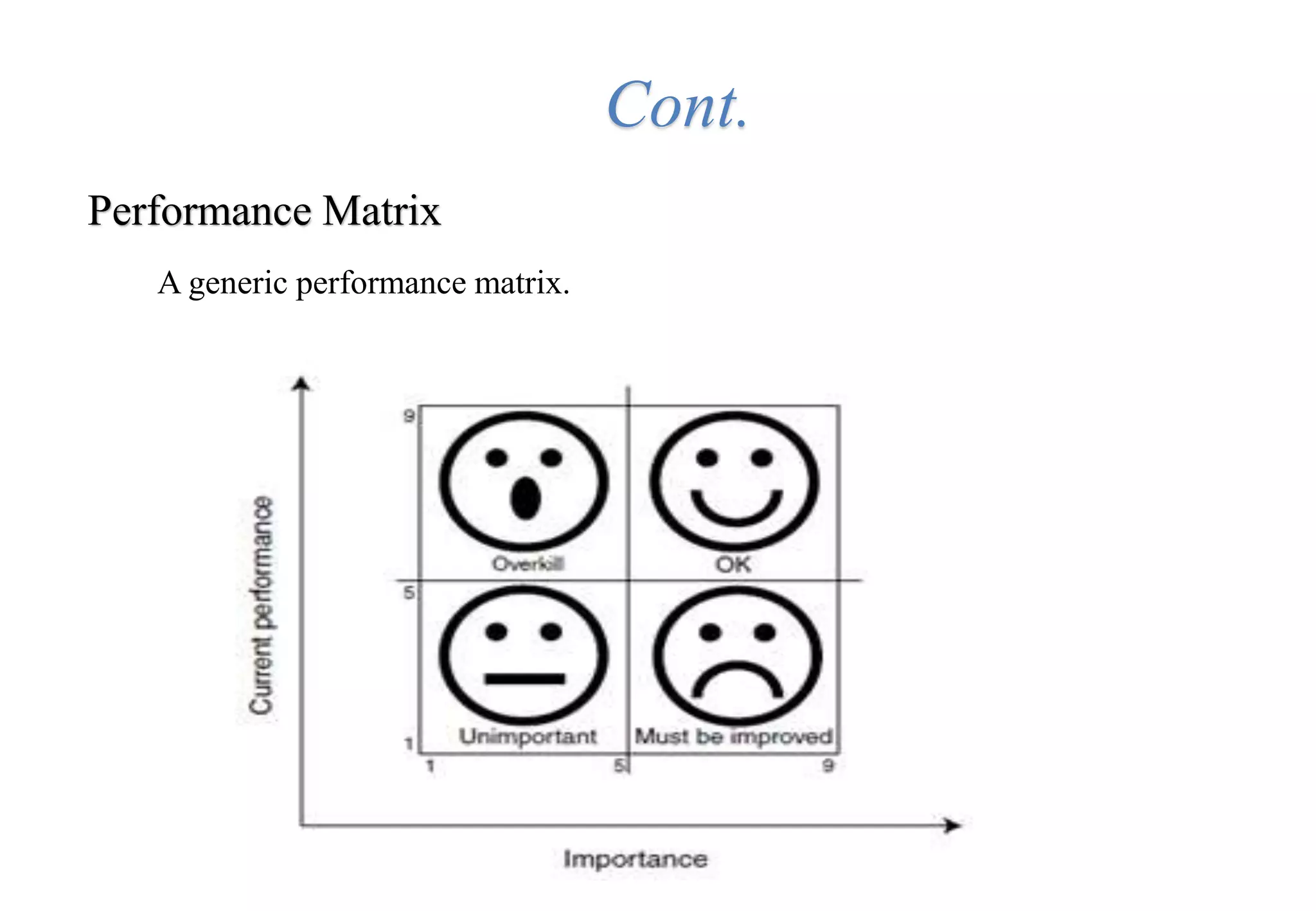
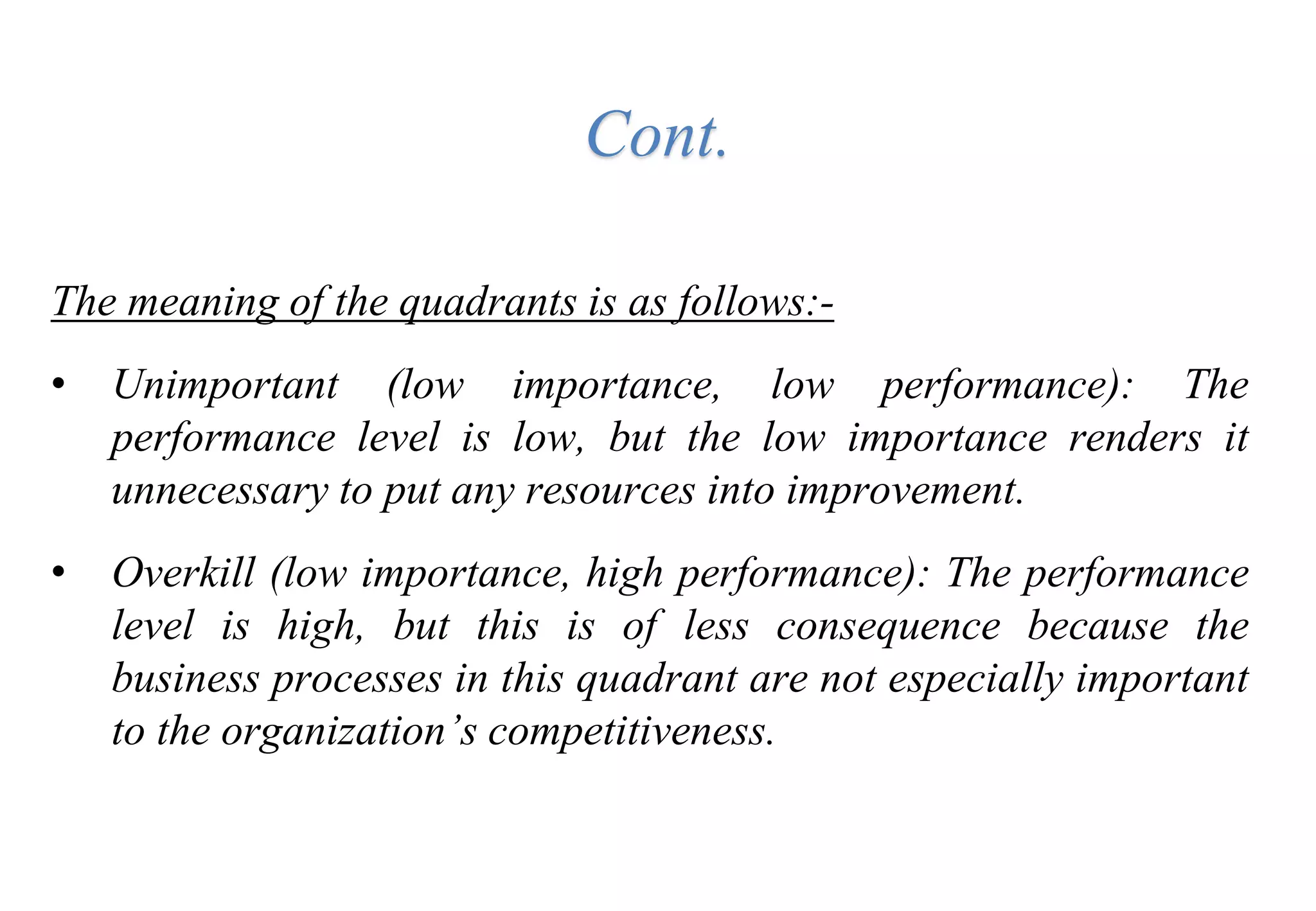
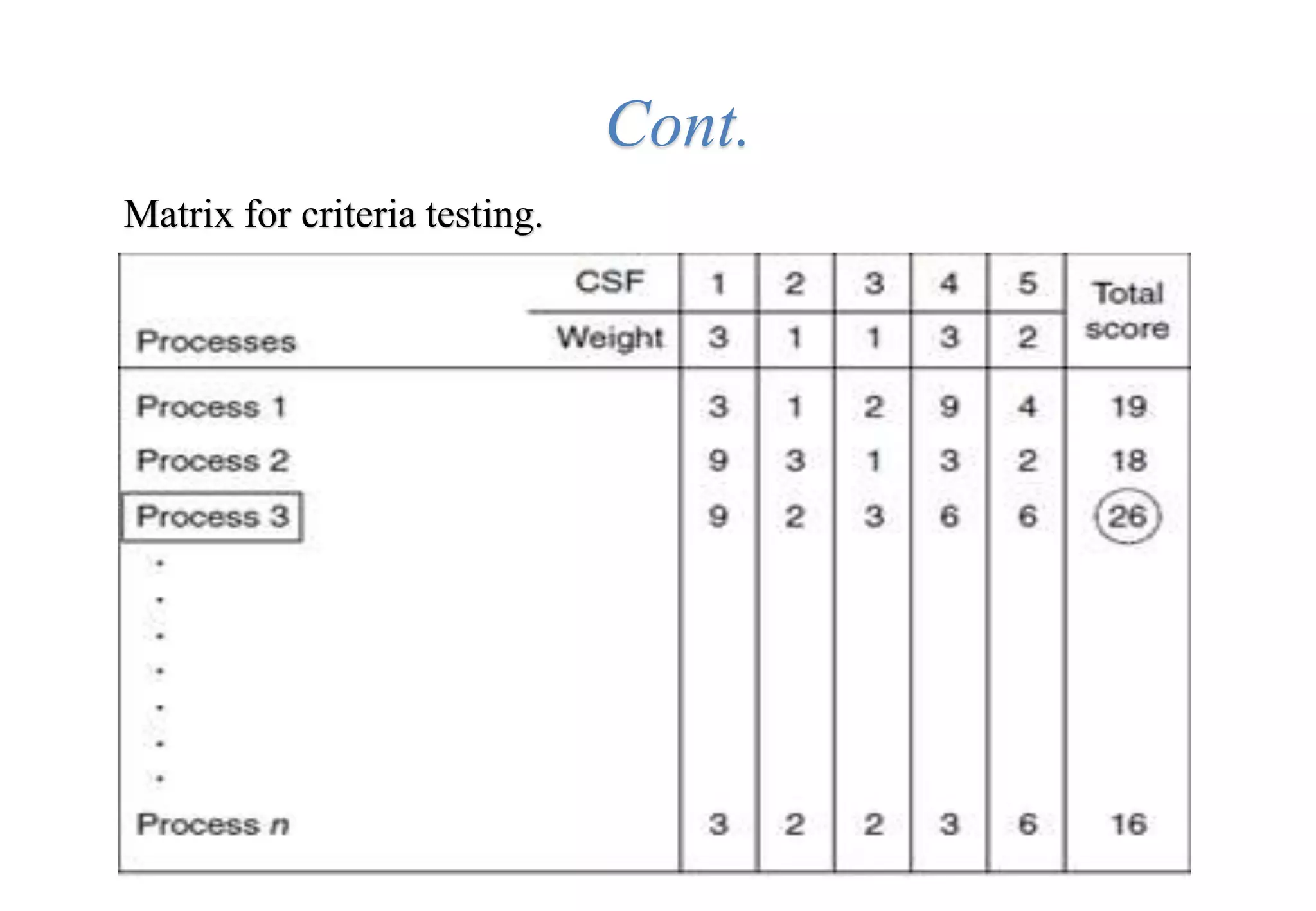
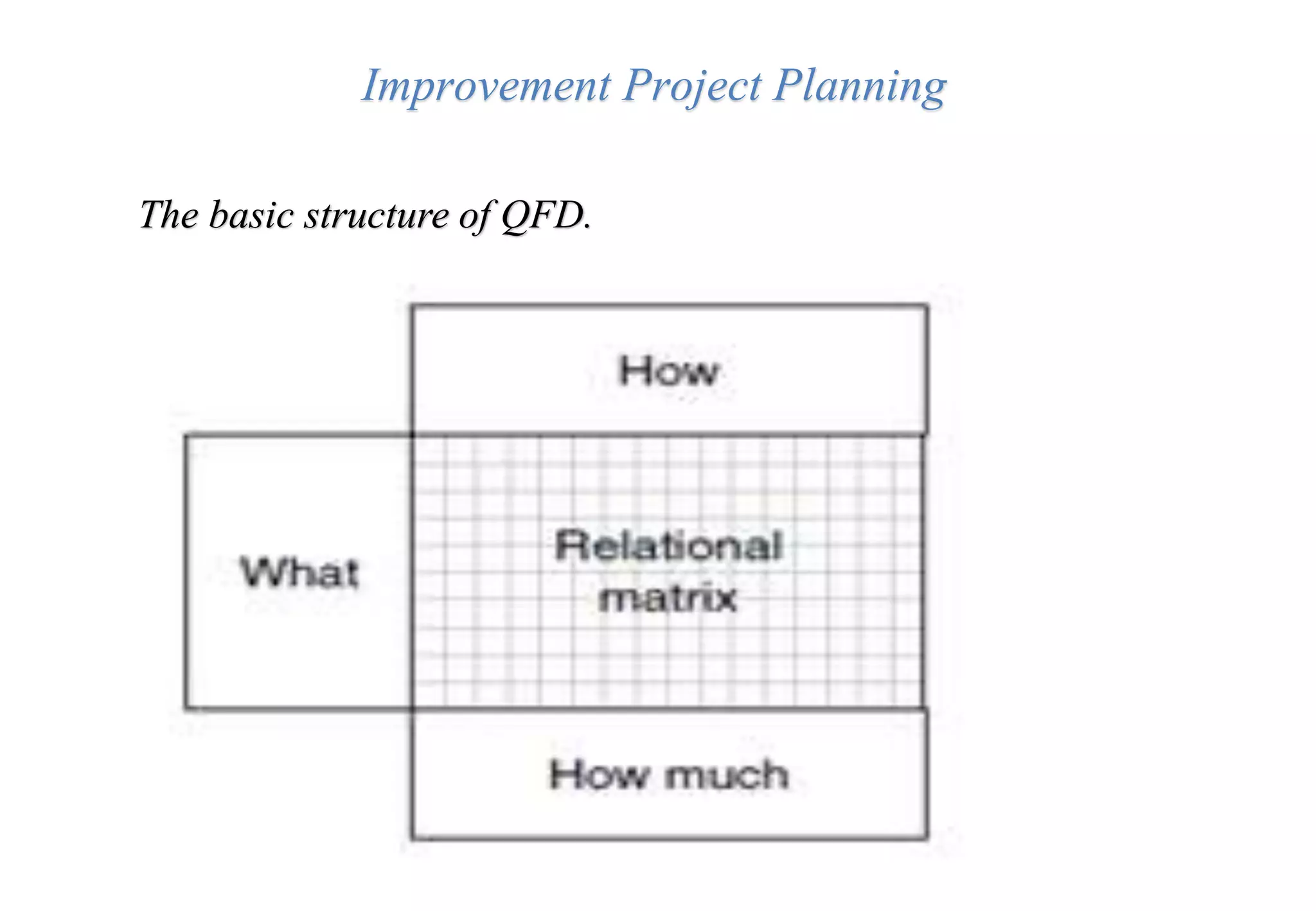
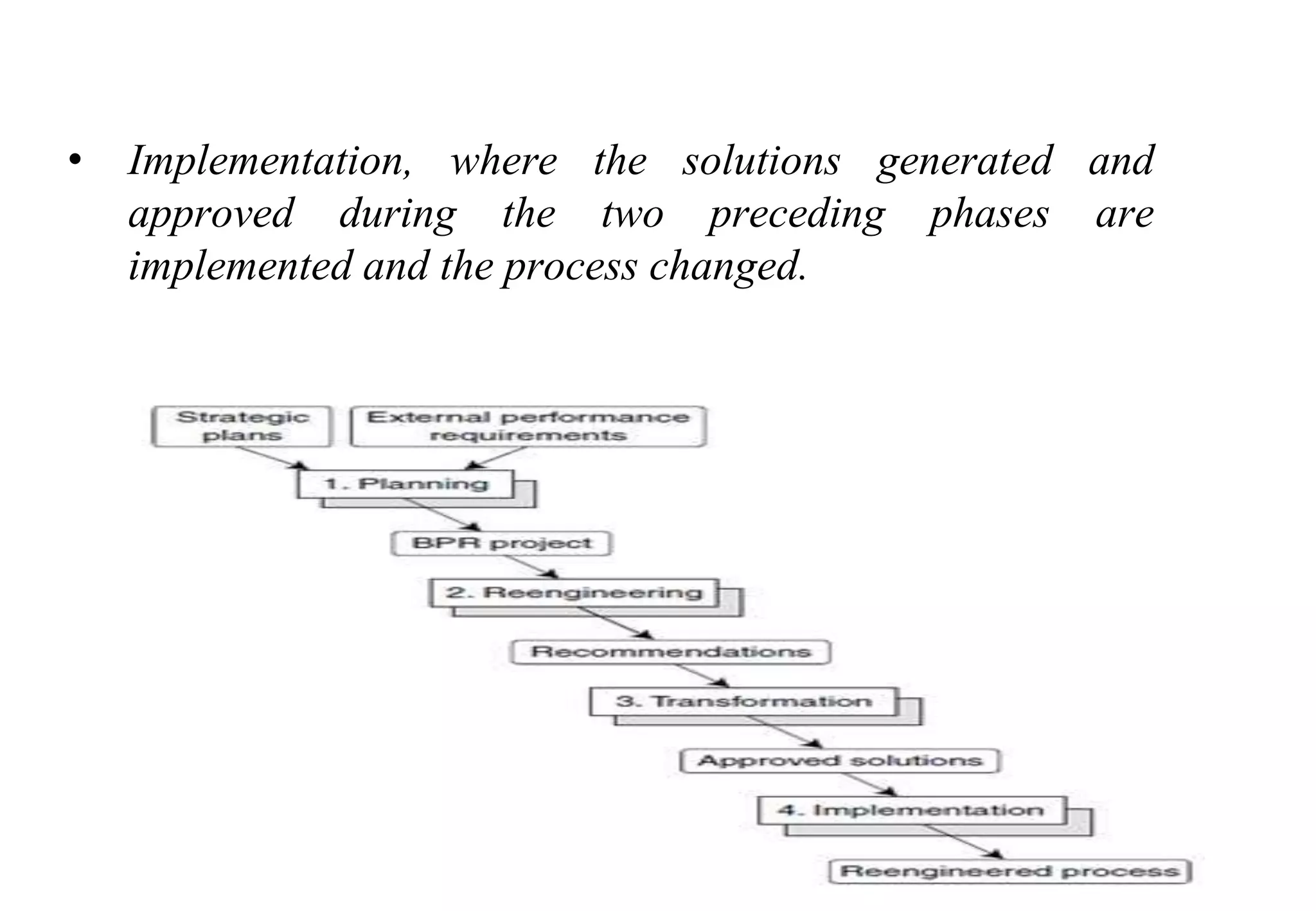
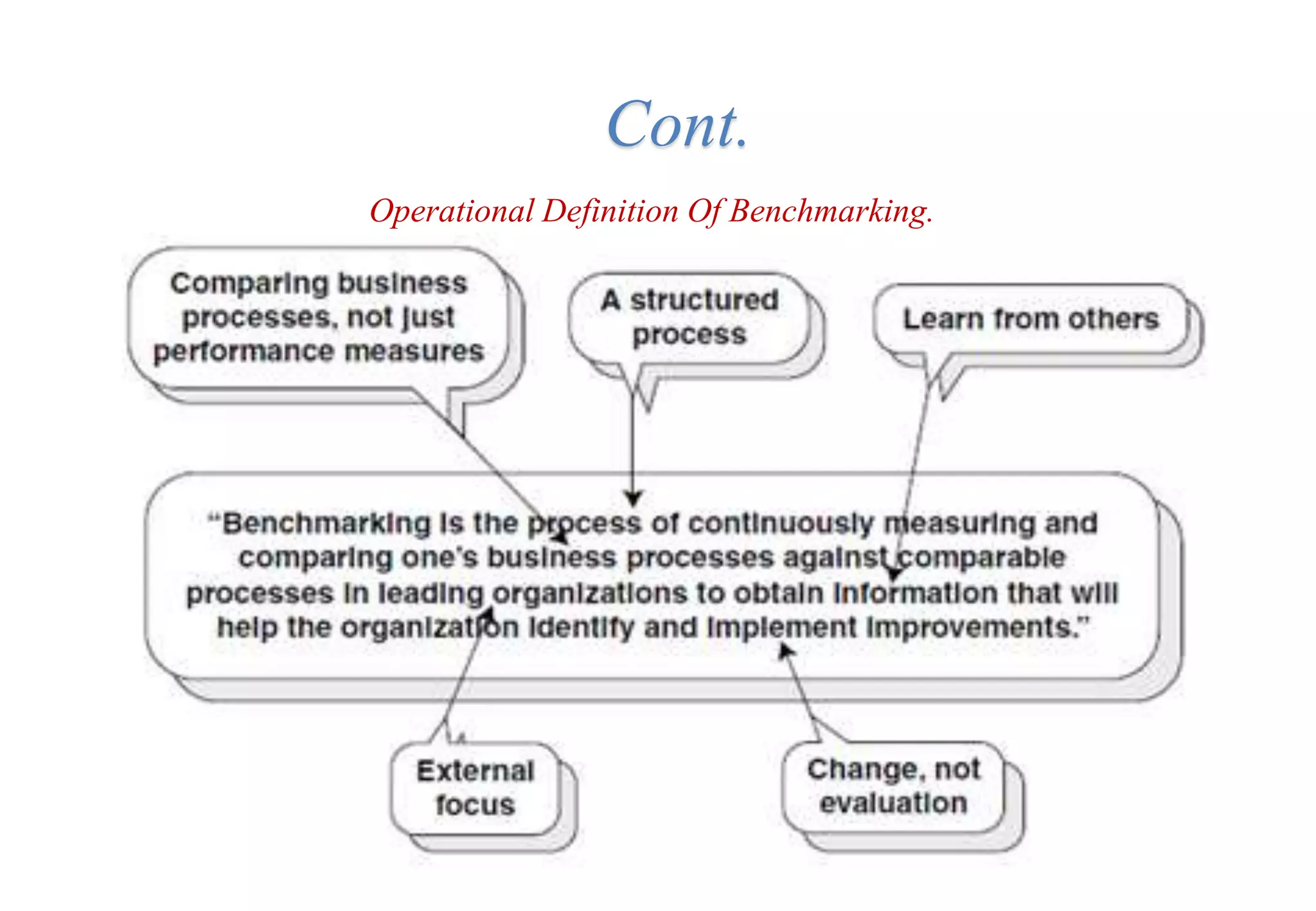
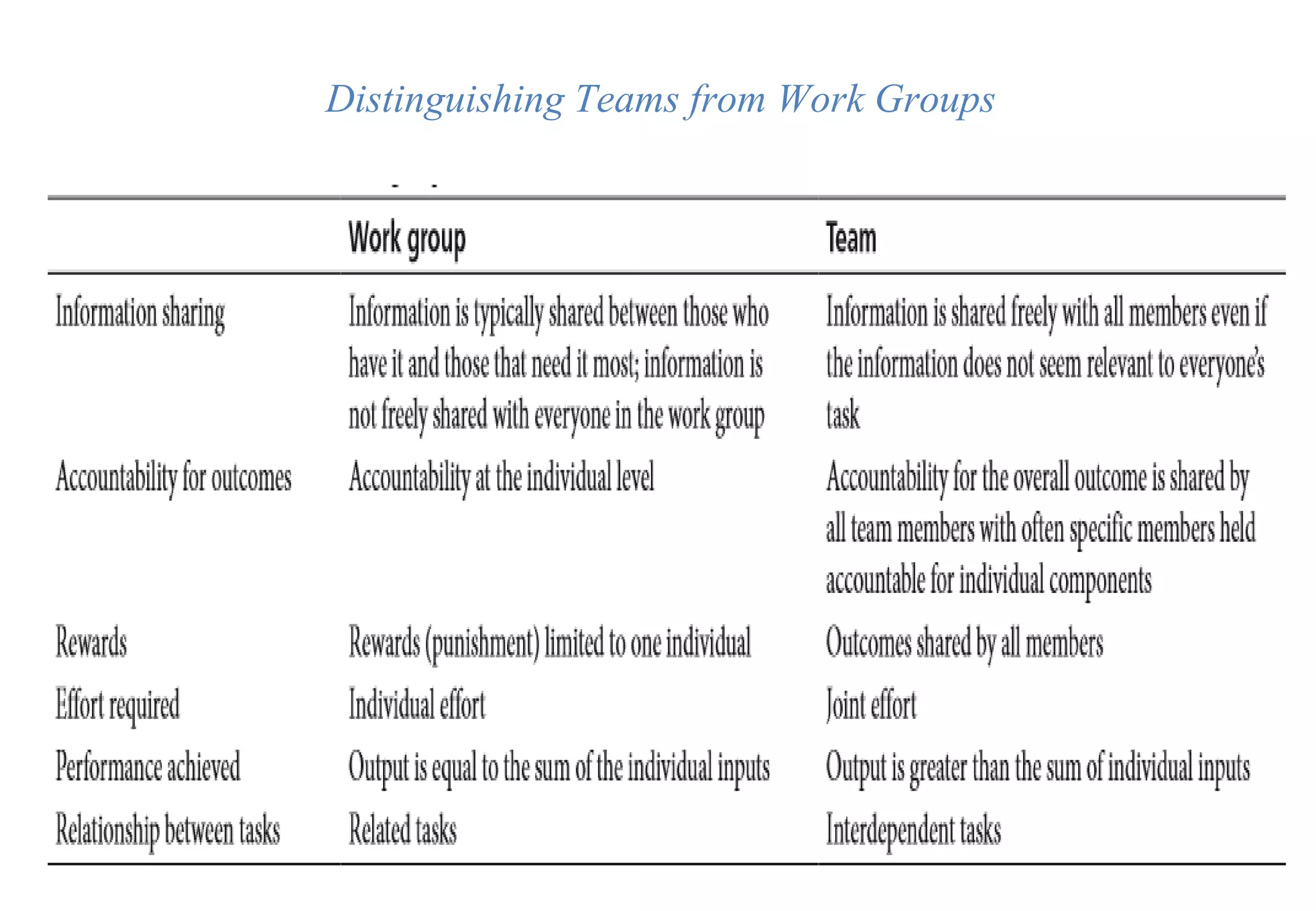
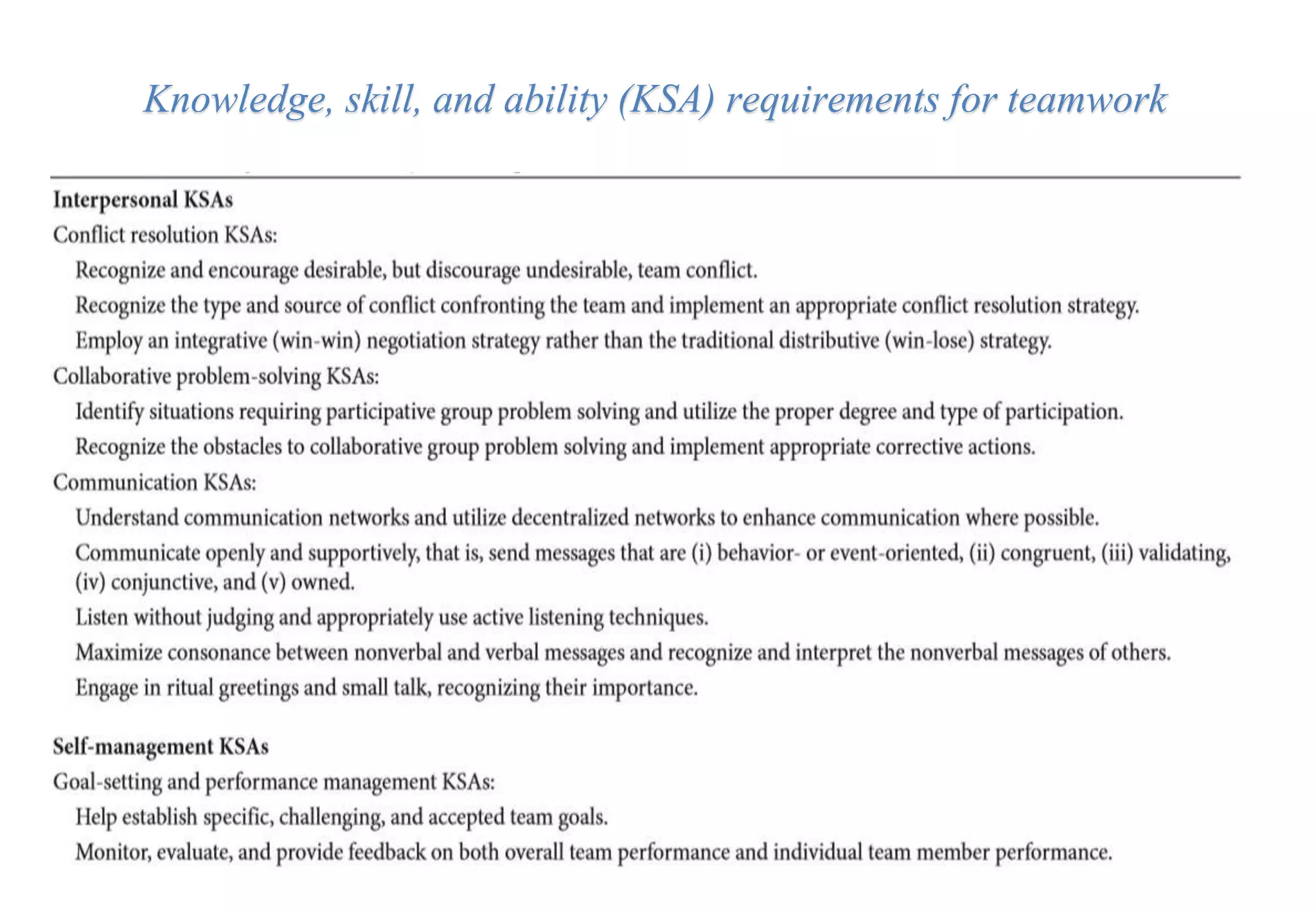
A laboratory manager's responsibilities include directing daily operations, anticipating potential problems, and balancing responsibilities. An effective manager is a strategist who looks to the future and identifies opportunities, a problem solver who addresses differences between plans and reality, and a teacher who guides others. Strategic planning involves selecting a planning group, performing an environmental analysis, identifying strengths/weaknesses/opportunities/threats, setting goals and strategies, prioritizing goals, assigning accountabilities, and measuring progress regularly. Organizing the laboratory optimally through structures, workflows, staffing, and time management is key to accomplishing objectives efficiently.