The document discusses the calculation of element addresses in 1D and 2D arrays. It provides formulas for finding addresses based on base addresses, element sizes, and indices, with examples illustrating both row-major and column-major order representations. Additionally, it emphasizes the organization of arrays in contiguous memory locations and includes resources for further practice.


![Calculation of Address in 1D Array:
• To find the address of an element in a 1D array following
formula is used:
• Address of Array[i] = B + S*(i L.B.)
−
• Where:
• i = index of an element to be searched.
• B = Base address i.e. address of the first element of
arrays/address of the array
• S = size of the data type stored in an array
• L.B. = lower bound(i.e. index of the first element of
the Array), if a lower bound is not given consider it
as 0.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/addresscalculationarrays-241116182244-d94faaa0/85/Address_Calculation_Arrays-pptx-3-320.jpg)
![Calculation of Address in 1D Array:
• Example: Given the base address of an array A[1300 …………1900]
as 1020 and the size of each element is 2 bytes in the memory, find
the address of A[1700].
• Given data is :
• Base address (B) = 1020
• Lower bound (LB) = 1300
• Size of each element (S) = 2 bytes
• Index of element (not value) = 1700
• Formula used:
• Address of A[Index] = B + S * (Index – LB)
• Address of A[1700] = 1020 + 2 * (1700 – 1300)
= 1020 + 2 * (400)
= 1020 + 800
• Address of A[1700] = 1820](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/addresscalculationarrays-241116182244-d94faaa0/85/Address_Calculation_Arrays-pptx-4-320.jpg)

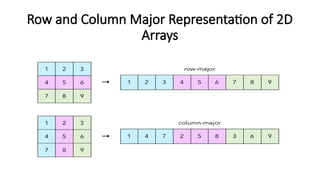
![Row Major Representation of 2D
Arrays:
• To calculate the address of an element stored in a 2D Array
in Row Major Order following formula is used:
• Address of Array[i][j] = B + S*[C*(i L.R.) + (j
− −
L.C.)]
• Where:
• i = row subset of an element whose address is to be
found
• j = column subset of an element whose address is to
be found
• B = Base address i.e. address of the first element of
arrays/address of an array
• S = size of the data type stored in an array
• C = total number of columns in an Array](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/addresscalculationarrays-241116182244-d94faaa0/85/Address_Calculation_Arrays-pptx-7-320.jpg)
![How to find address using Row Major Order?
Example :- Given an array, arr[1………10][1………15] with base
value 100 and the size of each element is 1 Byte in memory.
Find the address of arr[8][6] with the help of row-major order.
• Given :
• Base address B = 100
• Size of one element of S = 1 Bytes
• Row index of an element whose address to be found I = 8
• Column index an element whose address to be found J = 6
• Lower Limit of row/start row index of matrix LR = 1
• Lower Limit of column/start column index of matrix = 1
• Number of column given in the matrix
• C = Upper Bound – Lower Bound + 1
• = 15 – 1 + 1
• = 15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/addresscalculationarrays-241116182244-d94faaa0/85/Address_Calculation_Arrays-pptx-8-320.jpg)
![How to find address using Row Major Order?
Formula: Address of A[I][J] = B + S * ((I – LR) * C + (J – LC))
Solution:
Address of A[8][6] = 100 + 1 * ((8 – 1) * 15 + (6 – 1))
= 100 + 1 * ((7) * 15 + (5))
= 100 + 1 * (110)
Address of A[I][J] = 210](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/addresscalculationarrays-241116182244-d94faaa0/85/Address_Calculation_Arrays-pptx-9-320.jpg)
![Column Major Representation of 2D
Arrays:
• To calculate the address of an element stored in a 2D Array in
Column Major Order following formula is used:
• Address of Array[i][j] = B + S*[R*(j L.C.) + (i L.R.)]
− −
• Where
• i = row subset of an element whose address is to be found
• j = column subset of an element whose address is to be found
• B = Base address i.e. address of the first element of
arrays/address of the array
• S = size of the data type stored in an array
• R = total number of rows in an Array
• L.C. = start column index
• L.R. = start row index](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/addresscalculationarrays-241116182244-d94faaa0/85/Address_Calculation_Arrays-pptx-10-320.jpg)
![How to find address using Column Major Order?
• Example :- Given an array arr[1………10][1………15] with a base value of 100 and
the size of each element is 1 Byte in memory find the address of arr[8][6] with the
help of column-major order.
• Given Date is :
• Base address B = 100
• size of one element in any array S = 1 Bytes
• Row index of an element whose address to be found I = 8
• Column index of an element whose address to be found J = 6
• Lower Limit of row/start row index of matrix LR = 1
• Lower Limit of column/start column index of matrix = 1
• Number of Rows given in the matrix
• R = Upper Bound – Lower Bound + 1
= 10 – 1 + 1
= 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/addresscalculationarrays-241116182244-d94faaa0/85/Address_Calculation_Arrays-pptx-11-320.jpg)
![How to find address using Column Major Order?
• Formula:
• Address of A[I][J] = B + S * ((J – LC) * R + (I – LR))
• Address of A[8][6] = 100 + 1 * ((6 – 1) * 10 + (8 – 1))
= 100 + 1 * ((5) * 10 + (7))
= 100 + 1 * (57)
• Address of A[I][J] = 157](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/addresscalculationarrays-241116182244-d94faaa0/85/Address_Calculation_Arrays-pptx-12-320.jpg)

