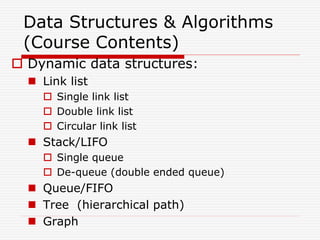
The document provides an overview of data structures and algorithms. It defines key terms like data, information, structures, and data structures. It discusses one-dimensional and two-dimensional arrays, including how they are represented in memory in row-major and column-major order. The document also covers topics like algorithms, different types of data structures, operations that can be performed on data, and the difference between static and dynamic data structures.

![ Data Structure: collection of data
elements in an organized form with some
basic operations/specifications. i.e. array
is a basic data structure
int list[10];
Data Structures & Algorithms
(Basic Concepts)
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
101 103 105 107 109 111 113 115 117 119
Memory
Address
LB UB](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1stlecture-230309014257-247eb7e3/85/1st-lecture-ppt-3-320.jpg)
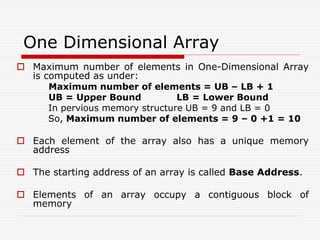
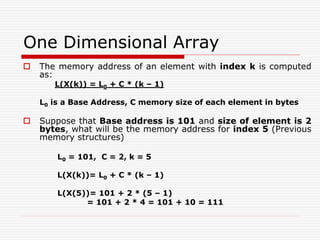
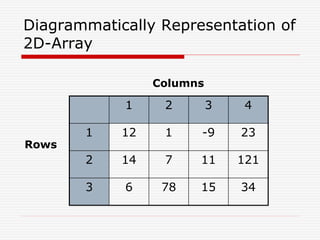
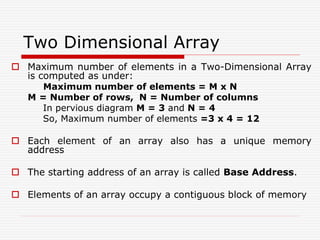
![Row-Major Order
The memory address of an element with index i (row) and j
(Col) is computed as:
L(X[i][j]) = L0 + [(i – 1) * N + (j – 1)] * d
L0 is a Base Address, d memory size of each element in
byte
i is a row, j is a col and N is total number of columns of an
array
Suppose that Base address is 502 and size of each
element is 2 bytes, what will be the memory address for
position x[2][2] (Previous diagram)
L0 = 502, d = 2, i = 2, j = 2, N = 4
L(X[i][j]) = L0 + [(i – 1) * N + (j – 1)] * d
L(X[2][2]) = 502 + [(2 – 1) * 4 + (2 – 1)] * 2
= 502 + [4 + 1] * 2 = 502 + 5 * 2 = 502 + 10 = 512](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1stlecture-230309014257-247eb7e3/85/1st-lecture-ppt-9-320.jpg)
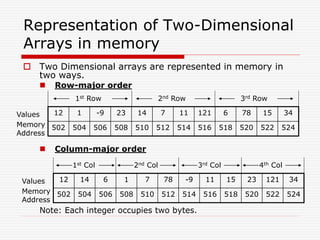
![Col-Major Order
The memory address of an element with index i (row) and j
(Col) is computed as:
L(X[i][j]) = L0 + [(i – 1) + (j – 1) * M] * d
L0 is a Base Address, d memory size of each element in byte
i is a row, j is a col and M is total number of rows of an array
Suppose that Base address is 502 and size of element is 2
bytes, what will be the memory address for position x[2][2]
(Previous diagram)
L0 = 502, d = 2, i = 2, j = 2, M = 3
L(X[i][j]) = L0 + [(i – 1) + (j – 1) * M] * d
L(X[2][2]) = 502 + [(2 – 1) + (2 – 1) * 3] * 2
= 502 + [1 + 3] * 2 = 502 + 4 * 2 = 502 + 8 = 510](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1stlecture-230309014257-247eb7e3/85/1st-lecture-ppt-10-320.jpg)








![Static Data Structure Vs Dynamic
Data Structure (Comparison)
In SDS, size is fixed and memory is allocated at compile time. In
DDS, size is variable and memory is allocated at run time. In
C++ new operator is used to allocate memory at run time to
pointer to object and delete operator is used to deallocate the
memory. int *Px; Px = new int; int num; Px=# delete
Px; int list[size]; const int size =10;
In SDS, elements are directly accessed but in case of searching
of DDS, it is much slower.
In SDS, only its data part occupies 2 byte memory but in DDS, it
data part as well as its link part also occupies 2+2 bytes memory.
In SDS, memory is allocated in consecutive way, but in DDS
memory is allocated in non-consecutive way.
In SDS, insertion or deletion of any element is too much slow, bu
in DDS insertion or deletion is too much fast.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1stlecture-230309014257-247eb7e3/85/1st-lecture-ppt-22-320.jpg)
