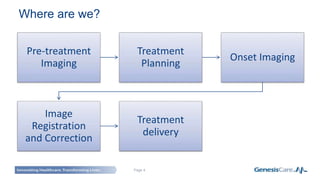
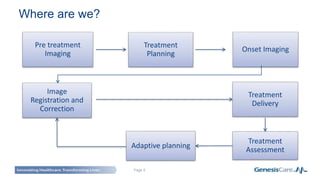
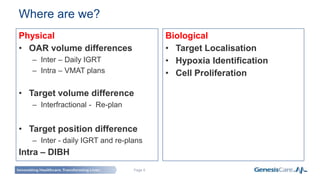
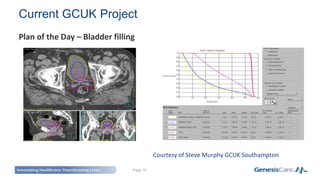
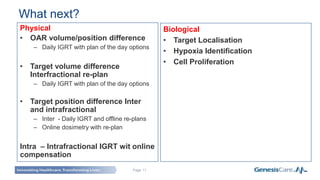
Adaptive radiotherapy is a process that modifies the treatment plan based on systematic monitoring of treatment variations to improve radiation treatment. It customizes the treatment dose and field margins for each individual patient based on changes in target and organ-at-risk volumes and target position between and during fractions to safely escalate the dose. Current projects at GenesisCare UK are exploring using daily onboard imaging with plan of the day options and offline replanning to adapt for interfractional changes and intrafractional guidance with online compensation.