This document is a lab manual for the course "Analysis and Design of Algorithms" at Amity University Haryana. It contains 11 experiments on algorithms including binary search, merge sort, quicksort, knapsack problem, and graph algorithms like Kruskal, Prim's, BFS and DFS. The introduction provides an overview of algorithm design and analysis. The experiments provide code snippets in C/C++ to implement the given algorithms.



![AMITY UNIVERSITY HARYANA, ASET ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF ALGORITHMS
- 6 -
Experiment No. 1
Write a program to perform binary search*/
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int a[10],sc,mid,qq=0;
int temp;
clrscr();
cout<<"enter the values"<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
{
cin>>a[i];
}
for(int ctr=0;ctr<10;ctr++){
for(int i=0;i<9;i++)
{
if(a[i+1]<a[i])
{
temp=a[i];
a[i]=a[i+1];
a[i+1]=temp;
}
}}
cout<<"The value in the array is"<<endl;
for(int qtr=0;qtr<10;qtr++)
{
cout<<a[qtr]<<"t";
}
cout<<"Enter the value to be searched"<<endl;
cin>>sc;
mid=5;
if(sc>=a[mid]){
for(int ztr=mid;ztr<10;ztr++)
{
if(sc==a[ztr])
{qq=1;
cout<<"Value found at"<<ztr+1<<endl;
break;
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adalabmanual-220215100317/85/Ada-lab-manual-6-320.jpg)
![AMITY UNIVERSITY HARYANA, ASET ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF ALGORITHMS
- 7 -
else
{
for(int qtr=0;qtr<mid;qtr++)
{if(sc==a[qtr]){qq=1;
cout<<"Value found at"<<qtr+1<<endl;
break;
}
}
if(qq==0){cout<<"Value not found"<<endl;}
}
getch();
}
Output:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adalabmanual-220215100317/85/Ada-lab-manual-7-320.jpg)
![AMITY UNIVERSITY HARYANA, ASET ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF ALGORITHMS
- 8 -
Experiment No. 2
Write a program to perform merge sort */
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void merge(int [],int ,int ,int );
void part(int [],int ,int );
void main()
{
int arr[30];
int i,size;
clrscr();
printf("Enter total no. of elements : ");
scanf("%d",&size);
for(i=0; i<size; i++)
{
scanf("%d",&arr[i]);
}
part(arr,0,size-1);
printf("ntSorted elements arenn");
for(i=0; i<size; i++)
printf("%d ",arr[i]);
getch();
}
void part(int arr[],int min,int max)
{
int mid;
if(min<max)
{
mid=(min+max)/2;
part(arr,min,mid);
part(arr,mid+1,max);
merge(arr,min,mid,max);
}
}
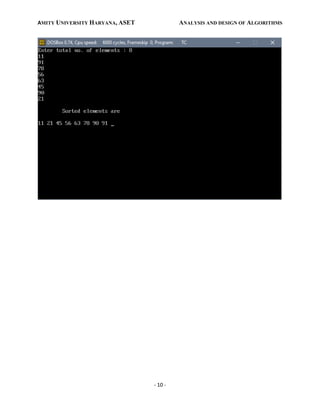
void merge(int arr[],int min,int mid,int max)
{
int tmp[30];
int i,j,k,m;
j=min;
m=mid+1;
for(i=min; j<=mid && m<=max ; i++)
{](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adalabmanual-220215100317/85/Ada-lab-manual-8-320.jpg)
![AMITY UNIVERSITY HARYANA, ASET ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF ALGORITHMS
- 9 -
if(arr[j]<=arr[m])
{
tmp[i]=arr[j];
j++;
}
else
{
tmp[i]=arr[m];
m++;
}
}
if(j>mid)
{
for(k=m; k<=max; k++)
{
tmp[i]=arr[k];
i++;}
}
else
{ for(k=j; k<=mid; k++)
{ tmp[i]=arr[k];
i++;
}
}
for(k=min; k<=max; k++)
arr[k]=tmp[k];
}
Output:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adalabmanual-220215100317/85/Ada-lab-manual-9-320.jpg)
![AMITY UNIVERSITY HARYANA, ASET ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF ALGORITHMS
- 11 -
Experiment No.-3
/*Write a program to perform quick sort*/
#include<stdio.h>
void quicksort(int [10],int,int);
int main()
{
int x[20],size,i;
printf("Enter size of the array: ");
scanf("%d",&size);
printf("Enter %d elements: ",size);
for(i=0;i<size;i++)
scanf("%d",&x[i]);
quicksort(x,0,size-1);
printf("Sorted elements: ");
for(i=0;i<size;i++)
printf(" %d",x[i]);
return 0;
}
void quicksort(int x[10],int first,int last)
{
int pivot,j,temp,i;
if(first<last)
{
pivot=first;
i=first;
j=last;
while(i<j)
{
while(x[i]<=x[pivot]&&i<last)
i++;
while(x[j]>x[pivot])
j--;
if(i<j)
{
temp=x[i];
x[i]=x[j];
x[j]=temp;
}
}
temp=x[pivot];
x[pivot]=x[j];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adalabmanual-220215100317/85/Ada-lab-manual-11-320.jpg)
![AMITY UNIVERSITY HARYANA, ASET ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF ALGORITHMS
- 12 -
x[j]=temp;
quicksort(x,first,j-1);
quicksort(x,j+1,last);
}
}
Output:-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adalabmanual-220215100317/85/Ada-lab-manual-12-320.jpg)
![AMITY UNIVERSITY HARYANA, ASET ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF ALGORITHMS
- 13 -
Experiment No.-4
/*Write a program to perform insertion sort*/
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int n, array[1000], c, d, t;
printf("Enter number of elementsn");
scanf("%d", &n);
printf("Enter %d integersn", n);
for (c = 0; c < n; c++) {
scanf("%d", &array[c]);
}
for (c = 1 ; c <= n - 1; c++) {
d = c;
while ( d > 0 && array[d] < array[d-1]) {
t = array[d];
array[d] = array[d-1];
array[d-1] = t;
d--;
}
}
printf("Sorted list in ascending order:n");
for (c = 0; c <= n - 1; c++) {
printf("%dn", array[c]);
}
return 0;
}
Output:-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adalabmanual-220215100317/85/Ada-lab-manual-13-320.jpg)
![AMITY UNIVERSITY HARYANA, ASET ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF ALGORITHMS
- 14 -
Experiment No.-5
/*Write a program for knapsack 01*/
#include<stdio.h>
int max(int a, int b) { return (a > b)? a : b; }
int knapSack(int W, int wt[], int val[], int n)
{
if (n == 0 || W == 0)
return 0;
if (wt[n-1] > W)
return knapSack(W, wt, val, n-1);
else return max( val[n-1] + knapSack(W-wt[n-1], wt, val, n-1),
knapSack(W, wt, val, n-1)
);
}
int main()
{
int val[] = {60, 100, 120};
int wt[] = {10, 20, 30};
int W = 50;
int n = sizeof(val)/sizeof(val[0]);
printf("%d", knapSack(W, wt, val, n));
return 0;
}
Output:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adalabmanual-220215100317/85/Ada-lab-manual-14-320.jpg)
![AMITY UNIVERSITY HARYANA, ASET ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF ALGORITHMS
- 15 -
Experiment No.-6
/*Write a program for cross multiplication using dynamic
programming*/
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int n, array[1000], c, d, t;
printf("Enter number of elementsn");
scanf("%d", &n);
printf("Enter %d integersn", n);
for (c = 0; c < n; c++) {
scanf("%d", &array[c]);
}
for (c = 1 ; c <= n - 1; c++) {
d = c;
while ( d > 0 && array[d] < array[d-1]) {
t = array[d];
array[d] = array[d-1];
array[d-1] = t;
d--;
}
}
printf("Sorted list in ascending order:n");
for (c = 0; c <= n - 1; c++) {
printf("%dn", array[c]);
}
return 0;
}
Output:-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adalabmanual-220215100317/85/Ada-lab-manual-15-320.jpg)
![AMITY UNIVERSITY HARYANA, ASET ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF ALGORITHMS
- 16 -
Experiment No.-7
/*Write a program for implementing kruskal algorithm*/
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int i,j,k,a,b,u,v,n,ne=1;
int min,mincost=0,cost[9][9],parent[9];
int find(int);
int uni(int,int);
void main()
{
clrscr();
printf("nntImplementation of Kruskal's algorithmnn");
printf("nEnter the no. of verticesn");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("nEnter the cost adjacency matrixn");
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(j=1;j<=n;j++)
{
scanf("%d",&cost[i][j]);
if(cost[i][j]==0)
cost[i][j]=999;
}
}
printf("nThe edges of Minimum Cost Spanning Tree arenn");
while(ne<n)
{
for(i=1,min=999;i<=n;i++)
{
for(j=1;j<=n;j++)
{
if(cost[i][j]<min)
{
min=cost[i][j];
a=u=i;
b=v=j;
}
}
}
u=find(u);
v=find(v);
if(uni(u,v))
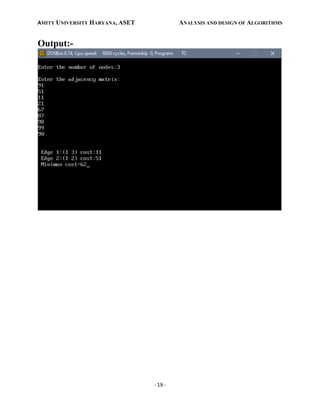
{](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adalabmanual-220215100317/85/Ada-lab-manual-16-320.jpg)
![AMITY UNIVERSITY HARYANA, ASET ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF ALGORITHMS
- 17 -
printf("n%d edge (%d,%d) =%dn",ne++,a,b,min);
mincost +=min;
}
cost[a][b]=cost[b][a]=999;
}
printf("ntMinimum cost = %dn",mincost);
getch();
}
int find(int i)
{
while(parent[i])
i=parent[i];
return i;
}
int uni(int i,int j)
{
if(i!=j)
{
parent[j]=i;
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
Output:-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adalabmanual-220215100317/85/Ada-lab-manual-17-320.jpg)
![AMITY UNIVERSITY HARYANA, ASET ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF ALGORITHMS
- 18 -
Experiment No.-8
/*Write a program for implementing prims algorithm*/
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
int a,b,u,v,n,i,j,ne=1;
int visited[10]={0},min,mincost=0,cost[10][10];
void main()
{
clrscr();
printf("nEnter the number of nodes:");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("nEnter the adjacency matrix:n");
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(j=1;j<=n;j++)
{
scanf("%d",&cost[i][j]);
if(cost[i][j]==0)
cost[i][j]=999;
}
visited[1]=1;
printf("n");
while(ne < n)
{
for(i=1,min=999;i<=n;i++)
for(j=1;j<=n;j++)
if(cost[i][j]< min)
if(visited[i]!=0)
{
min=cost[i][j];
a=u=i;
b=v=j;
}
if(visited[u]==0 || visited[v]==0)
{
printf("n Edge %d:(%d %d) cost:%d",ne++,a,b,min);
mincost+=min;
visited[b]=1;
}
cost[a][b]=cost[b][a]=999;
}
printf("n Minimun cost=%d",mincost);
getch();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adalabmanual-220215100317/85/Ada-lab-manual-18-320.jpg)
![AMITY UNIVERSITY HARYANA, ASET ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF ALGORITHMS
- 20 -
Experiment No.-9
/*Write a program for implementing BFS algorithm*/
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
int a[20][20],q[20],visited[20],n,i,j,f=0,r=-1;
void bfs(int v)
{
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
if(a[v][i] && !visited[i])
q[++r]=i;
if(f<=r)
{
visited[q[f]]=1;
bfs(q[f++]);
}
}
int main()
{
int v;
printf("n Enter the number of vertices:");
scanf("%d",&n);
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
q[i]=0;
visited[i]=0;
}
printf("n Enter graph data in matrix form:n");
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(j=1;j<=n;j++)
scanf("%d",&a[i][j]);
printf("n Enter the starting vertex:");
scanf("%d",&v);
bfs(v);
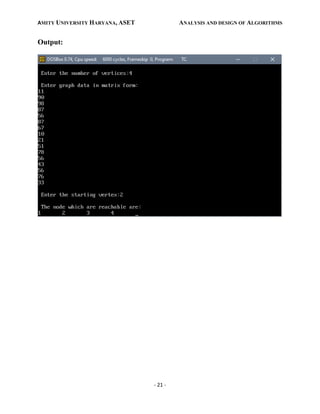
printf("n The node which are reachable are:n");
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
if(visited[i])
printf("%dt",i);
else
printf("n Bfs is not possible");
getch();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adalabmanual-220215100317/85/Ada-lab-manual-20-320.jpg)
![AMITY UNIVERSITY HARYANA, ASET ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF ALGORITHMS
- 22 -
Experiment.-10
/*Write a program for implementing DFS algorithm*/
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void DFS(int);
int G[10][10],visited[10],n;
void main()
{
int i,j;
clrscr();
printf("Enter number of vertices:");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("nEnter adjecency matrix of the graph:");
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
scanf("%d",&G[i][j]);
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
visited[i]=0;
DFS(0);
getch();
}
void DFS(int i)
{
int j;
printf("n%d",i);
visited[i]=1;
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
if(!visited[j]&&G[i][j]==1)
DFS(j);
}
Output](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adalabmanual-220215100317/85/Ada-lab-manual-22-320.jpg)
![AMITY UNIVERSITY HARYANA, ASET ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF ALGORITHMS
- 23 -
Experiment No.-11
/*Write a program for implementing LCS algorithm*/
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
int max(int a, int b);
int lcs( char *X, char *Y, int m, int n )
{
if (m == 0 || n == 0)
return 0;
if (X[m-1] == Y[n-1])
return 1 + lcs(X, Y, m-1, n-1);
else
return max(lcs(X, Y, m, n-1), lcs(X, Y, m-1, n));
}
int max(int a, int b)
{
return (a > b)? a : b;
}
int main()
{
char X[] = "AVGTAB";
char Y[] = "GNTXAYB";
int m = strlen(X);
int n = strlen(Y);
clrscr();
printf("Length of LCS is %dn", lcs( X, Y, m, n ) );
getch();
return 0;
}
Output:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adalabmanual-220215100317/85/Ada-lab-manual-23-320.jpg)