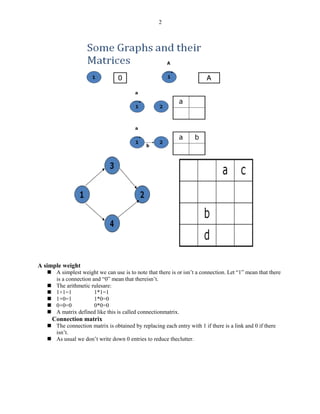
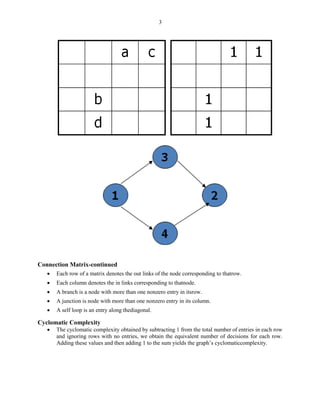
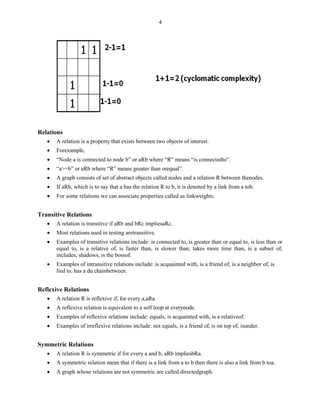
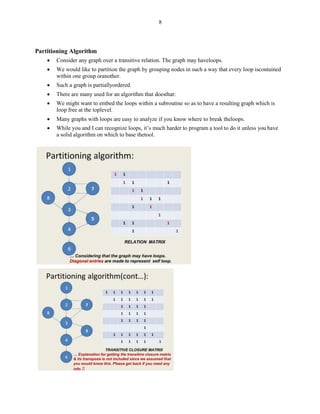
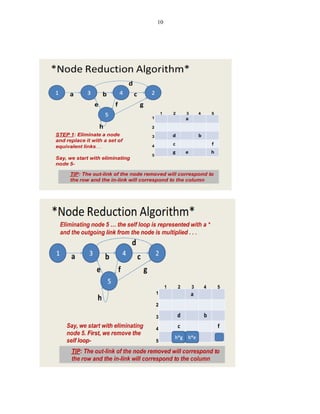
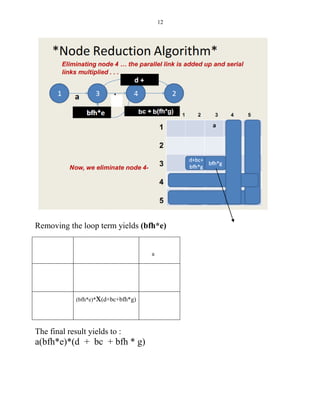
This document discusses representing graphs as matrices and using matrix operations to analyze graphs. It begins by explaining that graphs can be difficult to analyze by tracing paths visually, so representing them as matrices allows using more reliable matrix operations. The key algorithms covered include matrix multiplication to find paths between nodes, partitioning graphs to make them loop-free, and collapsing to find paths between any two nodes. The rest of the document defines graph matrices and different types of relations between nodes that can be represented with weights in the matrices. It provides examples of how to perform operations like taking powers of the matrix to find all paths between nodes up to a certain length. Finally, it discusses an algorithm for partitioning graphs to group nodes such that all loops are within the