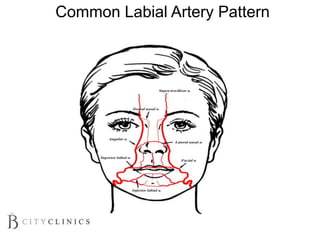
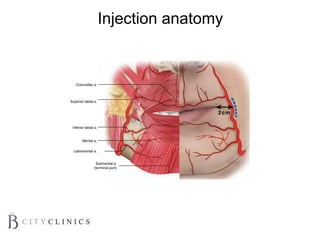
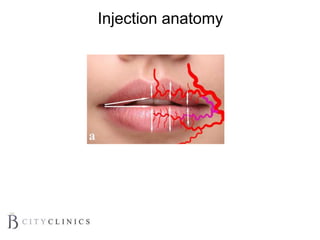
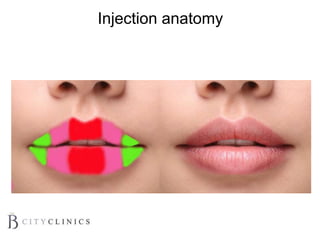
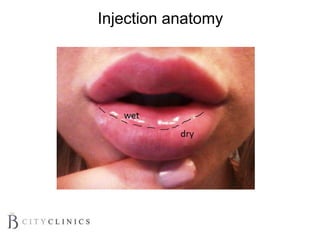
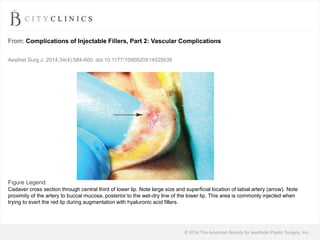
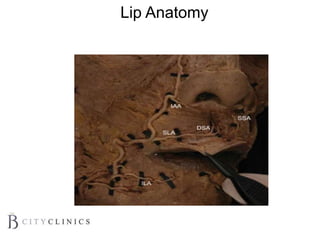
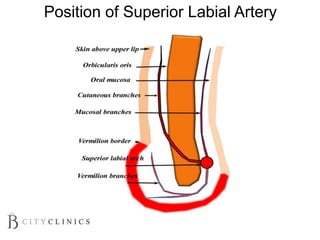
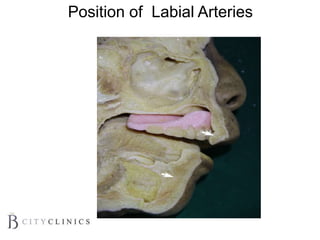
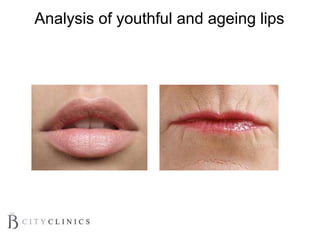
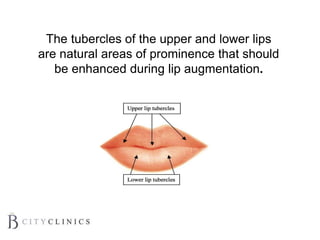
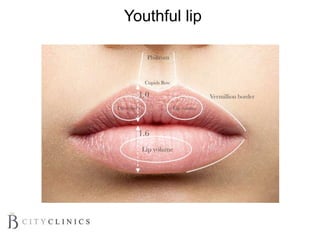
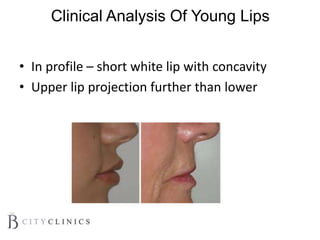
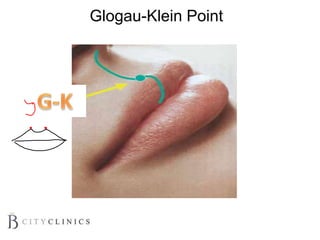
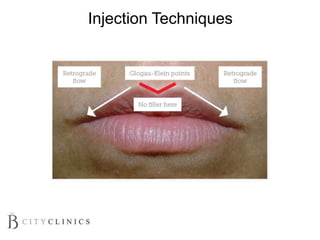
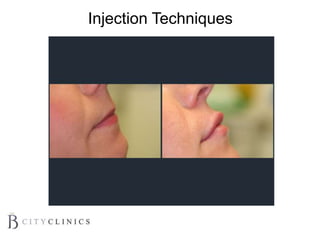
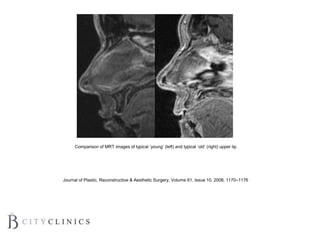
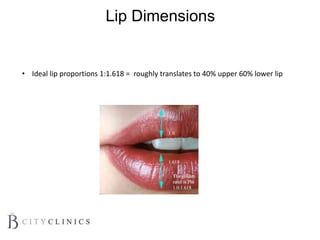
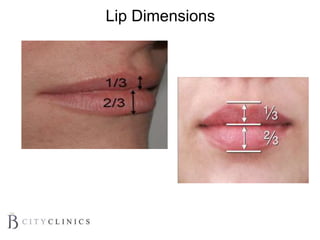
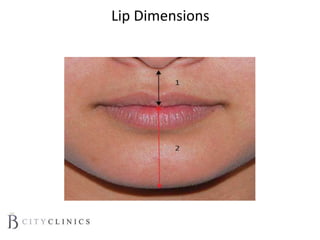
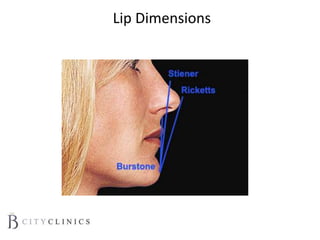
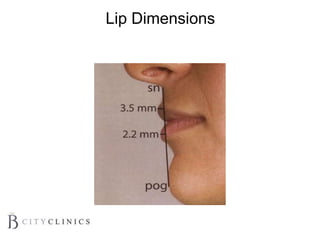
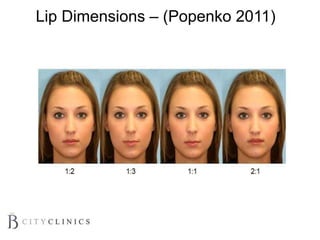
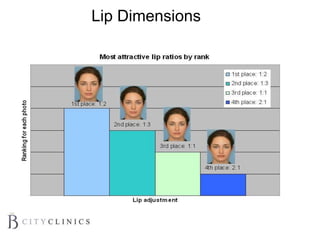
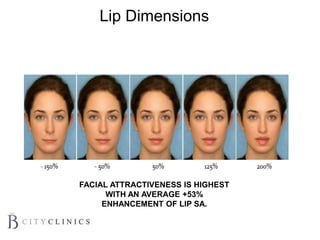
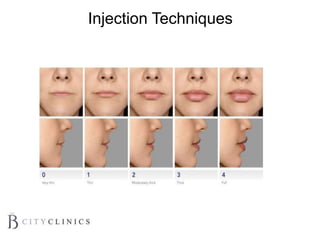
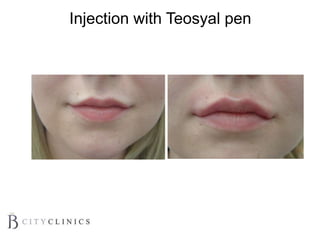
This document provides information on lip augmentation using the Teosyal pen. It begins with an introduction to the speaker's qualifications and objectives of the presentation. It then covers anatomy of the lips, how lips age, factors to consider for lip augmentation, and techniques for injection. The main technique discussed is using the Teosyal pen, which offers precise, homogeneous delivery of hyaluronic acid filler for lip augmentation in a minimally invasive manner. Key advantages include less pain on injection and quicker recovery time compared to manual injection techniques.