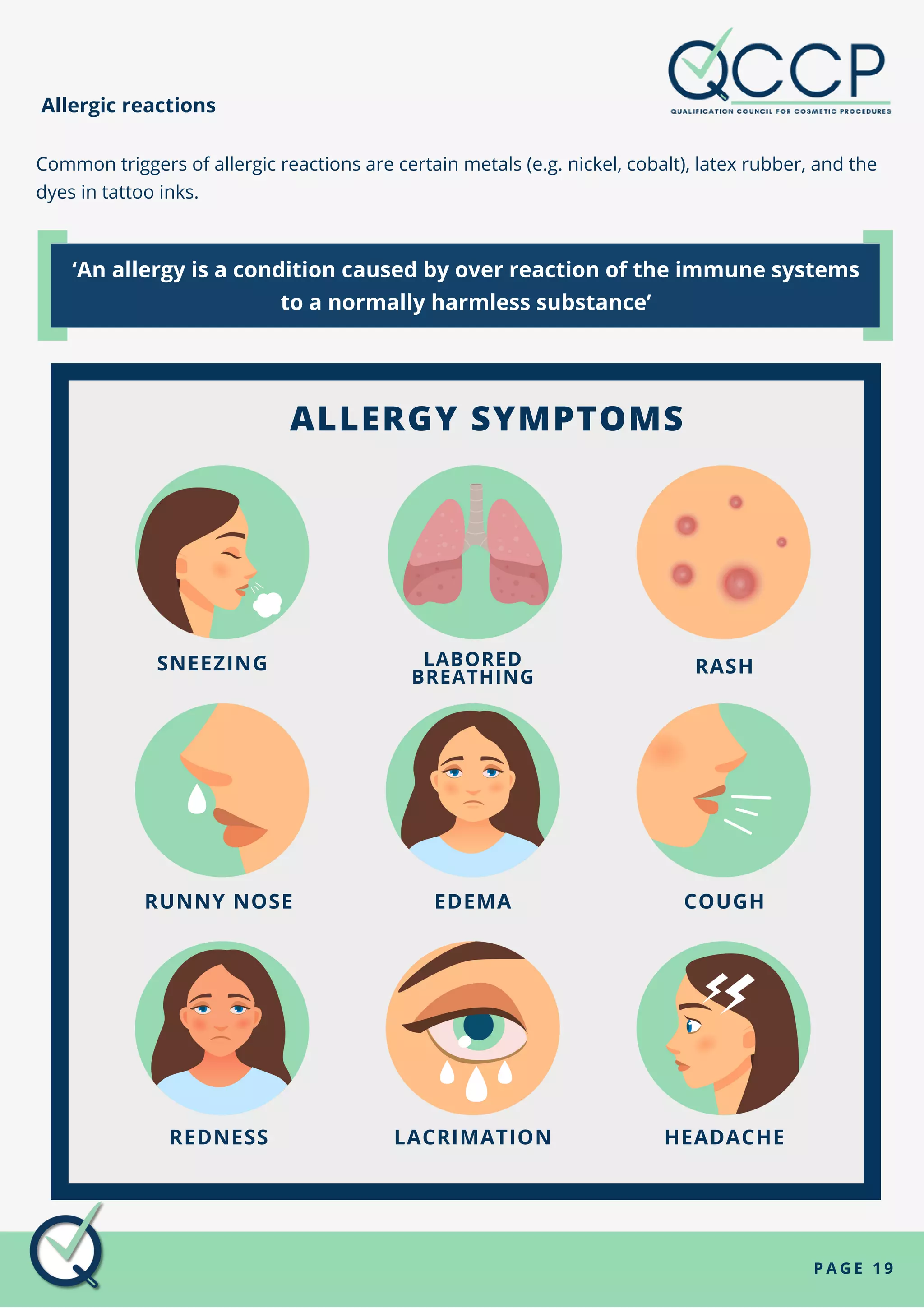
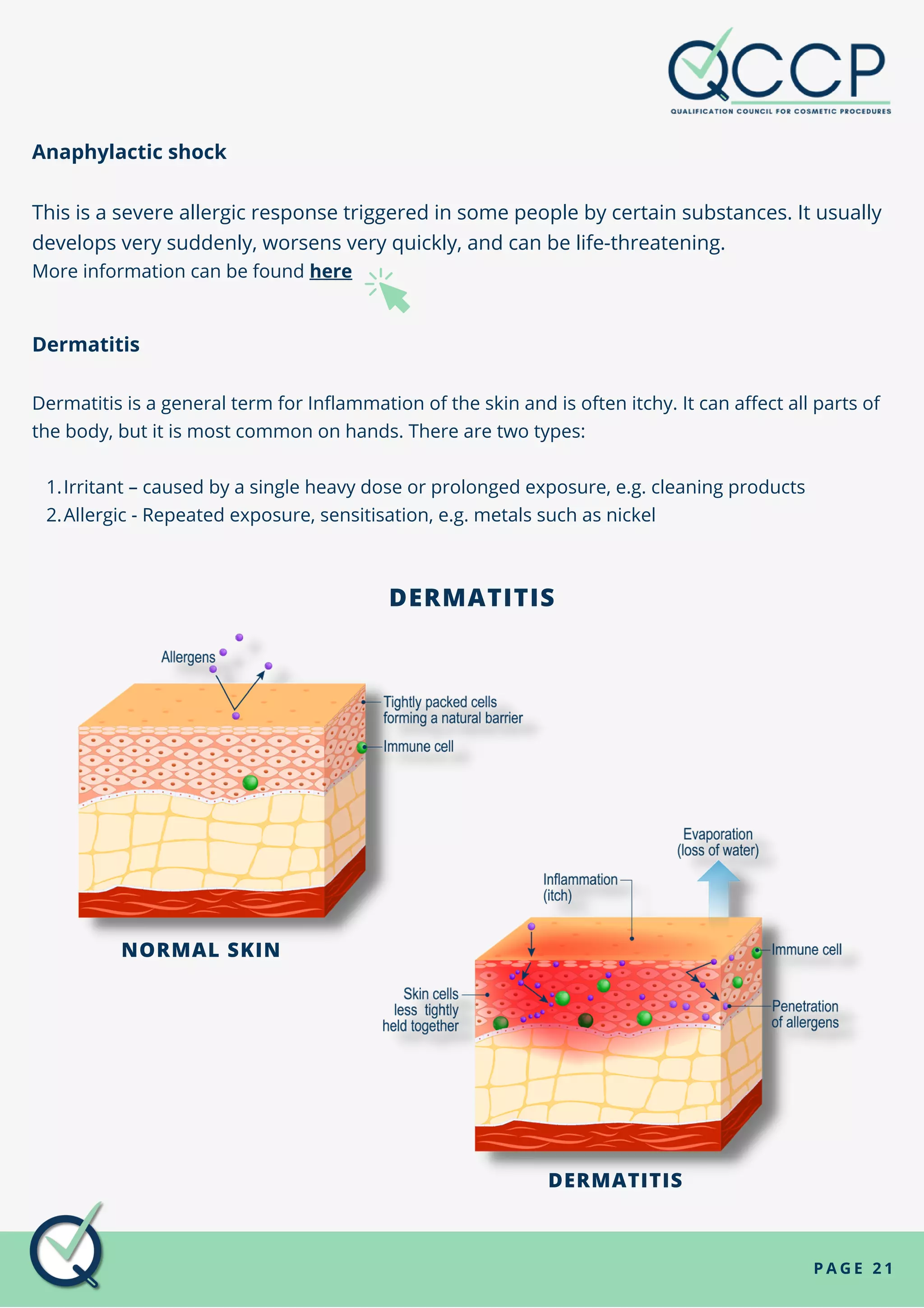
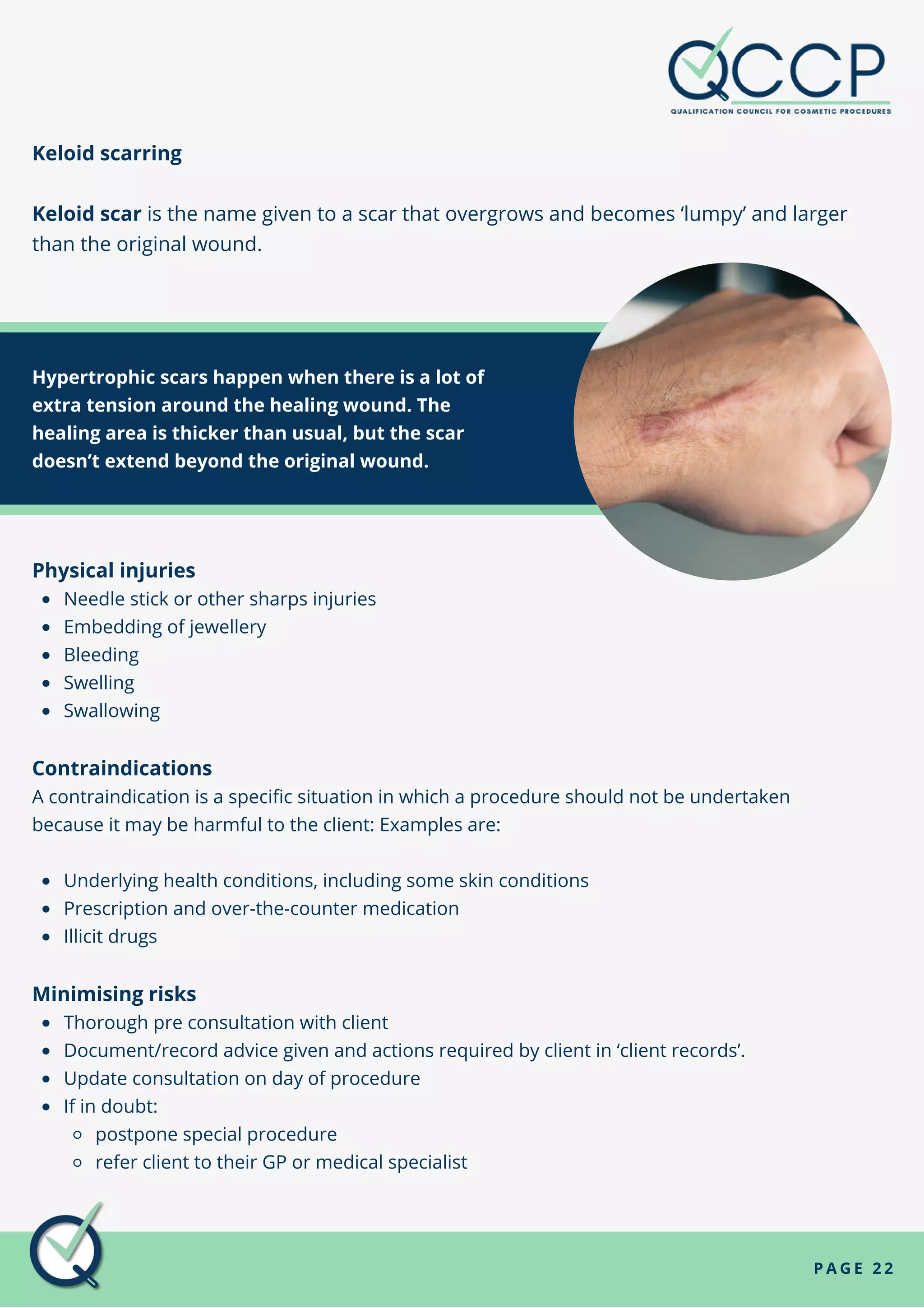
Allergic reactions, keloid and hypertrophic scars, and physical injuries are common non-infectious hazards. Allergic reactions can be triggered by metals, latex, and tattoo inks, and cause symptoms like sneezing, coughing, rashes, and headaches. Keloid scars occur when a wound overgrows and becomes lumpy, while hypertrophic scars involve extra tension around a healing wound. Non-infectious hazards are not spread between people and can be caused by genetics, lifestyle, and environment.