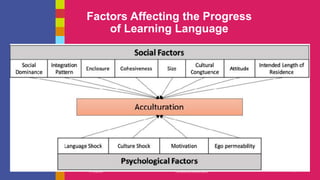
The document discusses John Schumann's acculturation theory of second language acquisition from 1978. The theory proposes that social and psychological factors influence how quickly learners acquire a new language. These factors include things like social dominance between cultures, language community size, attitudes between groups, and an individual's motivation and comfort with the new culture. While influential, the theory has also received some criticism for not clearly specifying how factors combine to predict outcomes and for not finding clear links between acculturation factors and proficiency in some studies. Supporters argue it provides insights into research and teaching approaches.