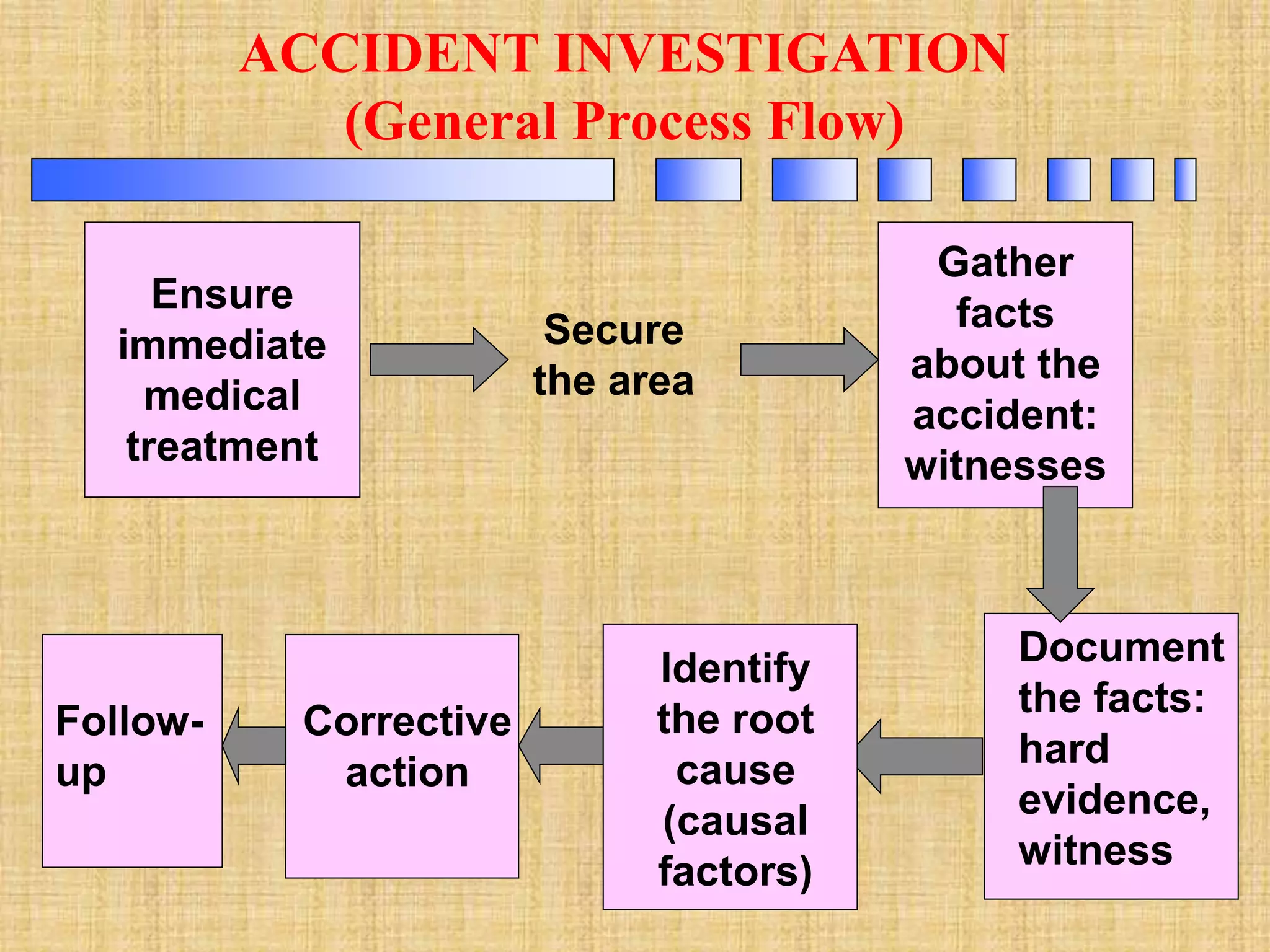
This document provides an overview of accident investigation procedures. It discusses the purpose of investigations as preventing recurrence, complying with policies, and maintaining employee awareness. The key steps in conducting an investigation are to: immediately secure the accident scene and ensure treatment of injured; gather information from witnesses, physical evidence, and records; analyze the facts to identify direct and root causes; and make recommendations for corrective actions and follow up. Accident investigations aim to understand why unsafe acts or conditions were present in order to prevent future accidents.