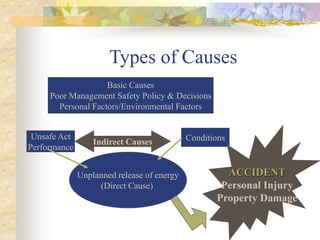
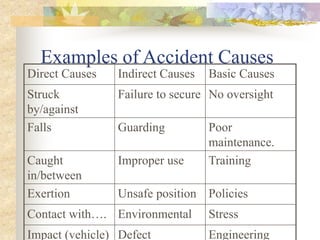
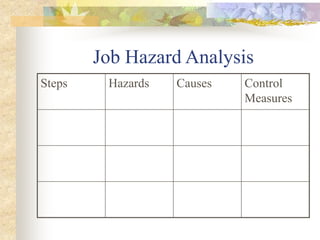
The document outlines the objectives and processes of accident investigation, emphasizing the need to determine causes, document events, and implement preventative measures. It details the types of consequences from accidents, ranging from personal injury to financial losses, and discusses basic and indirect causes of accidents. Guidelines for conducting investigations, including interviewing witnesses and analyzing data, are provided to promote safety and reduce future incidents.