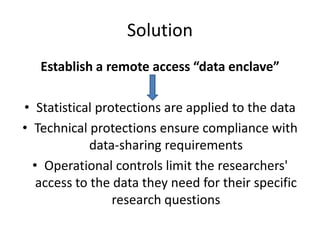
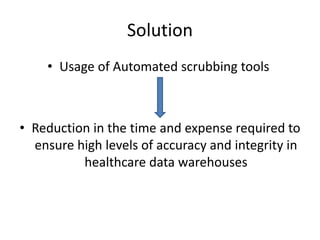
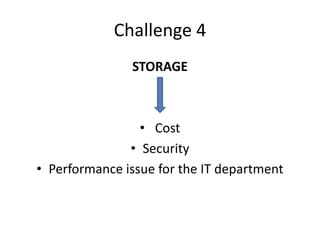
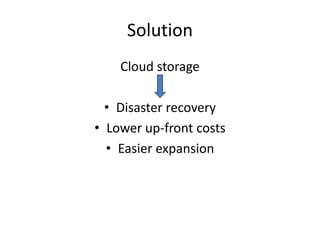
The document discusses the challenges and solutions related to accessing health data and information, highlighting issues such as legislative privacy protections, data capture, cleaning, security, and stewardship. It proposes various solutions, including establishing data enclaves, improving electronic health record usability, utilizing automated cleaning tools, and implementing robust security measures. Ultimately, it emphasizes the need for commitment and resources to overcome these barriers and improve healthcare analytics.


















![References
• https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2965886/
• https://healthitanalytics.com/news/top-10-challenges-of-big-data-
analytics-in-healthcare
• https://www.healthit.gov/video/how-use-safer-
guides#:~:text=The%20SAFER%20Guides%20are%20designed,Syste
m%20Configuration%2C%20System%20Interfaces%2C%20Patient
• Abowd J, Lane J. New Approaches to Confidentiality Protection:
Synthetic Data, Remote Access and Research Data Centers. In:
Domingo-Ferrer J, Torra V, editors. Privacy in Statistical
Databases. Berlin: Springer-Verlag; 2004. pp. 282–289. [Google
Scholar]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/accesstohealthdataandinformationchallenges-210902155355/85/Access-to-health-data-and-information-challenges-24-320.jpg)
