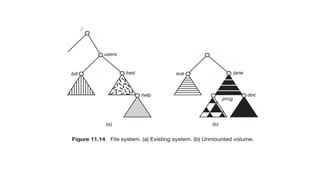
There are three main ways to access files in a computer: sequential access, direct access, and index access. Sequential access reads files in order from beginning to end, direct access allows reading or writing any block directly by number, and index access uses pointers in an index to access records. A file system must be mounted before files can be accessed, with mount points typically being empty directories where the file system attaches within the overall file structure.