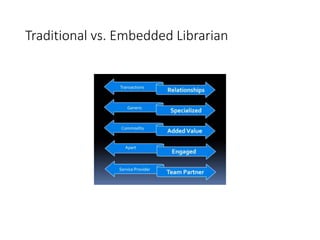
The document discusses the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats faced by academic libraries in the digital age, emphasizing the importance of adapting to changing information delivery models. It highlights challenges such as flat budgets and growing online programs while presenting opportunities like new reference models and embedded librarianship. The document also covers library statistics and trends in e-book usage, providing a comprehensive overview of how libraries can meet the evolving needs of users.