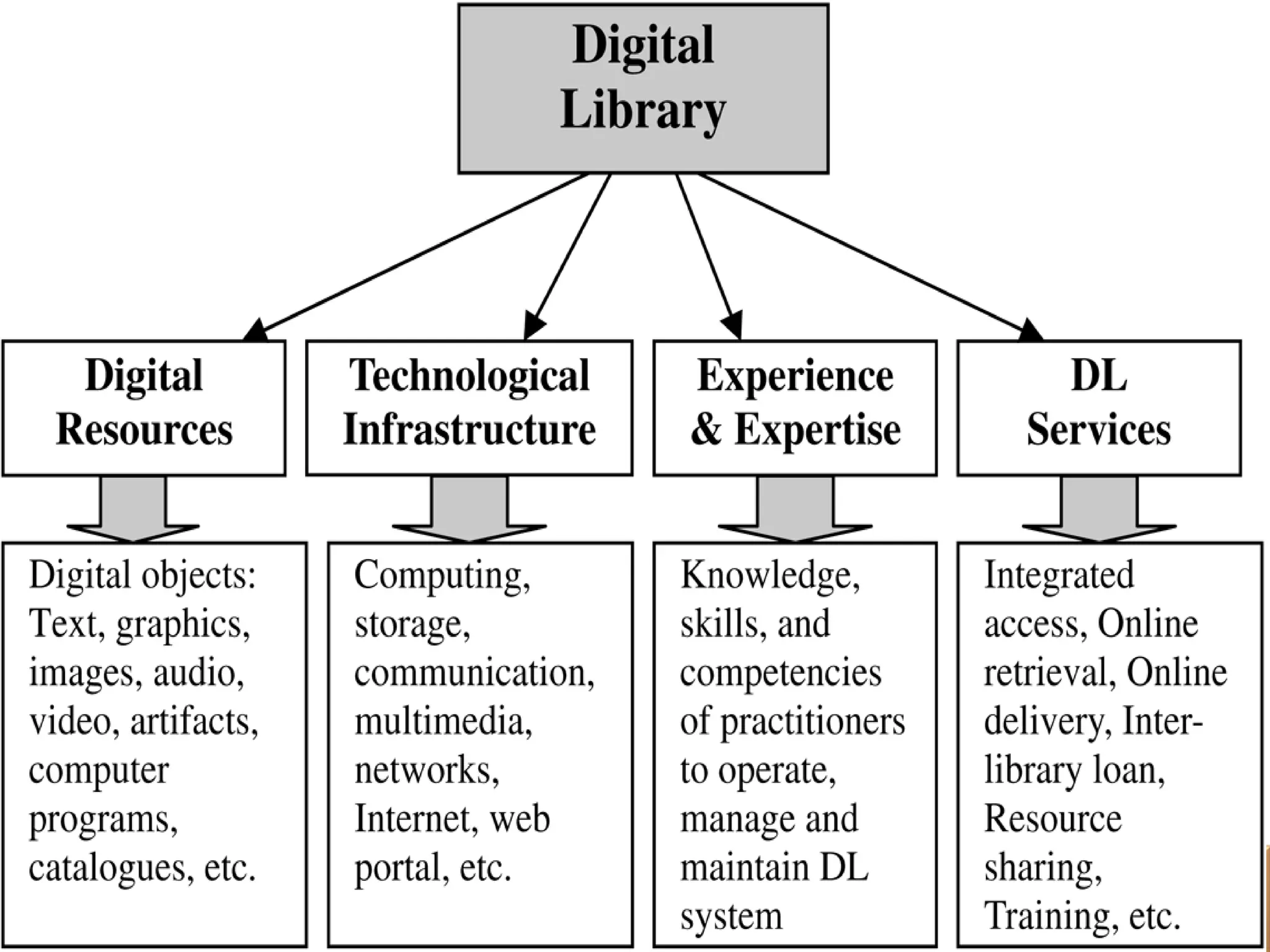
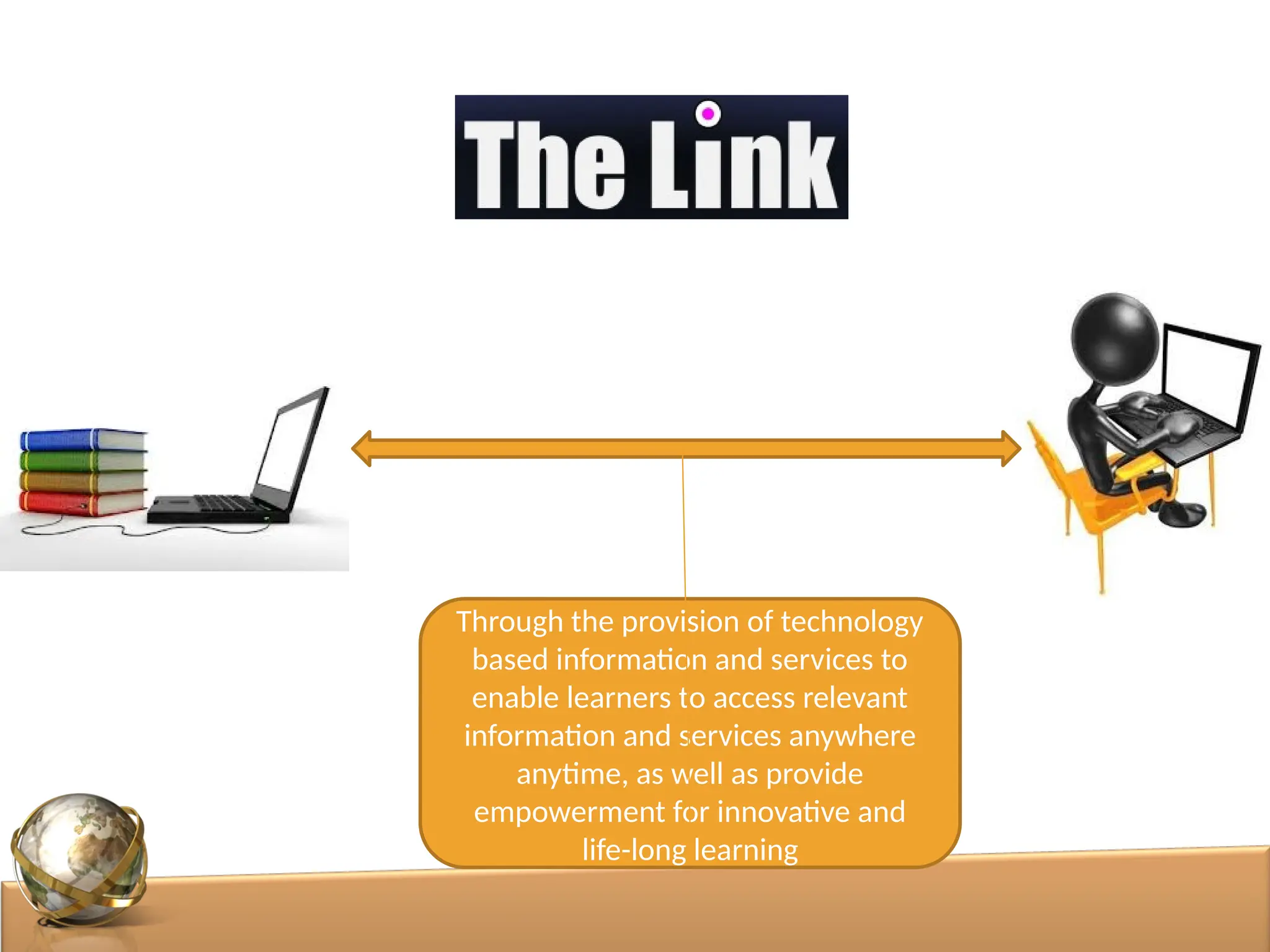
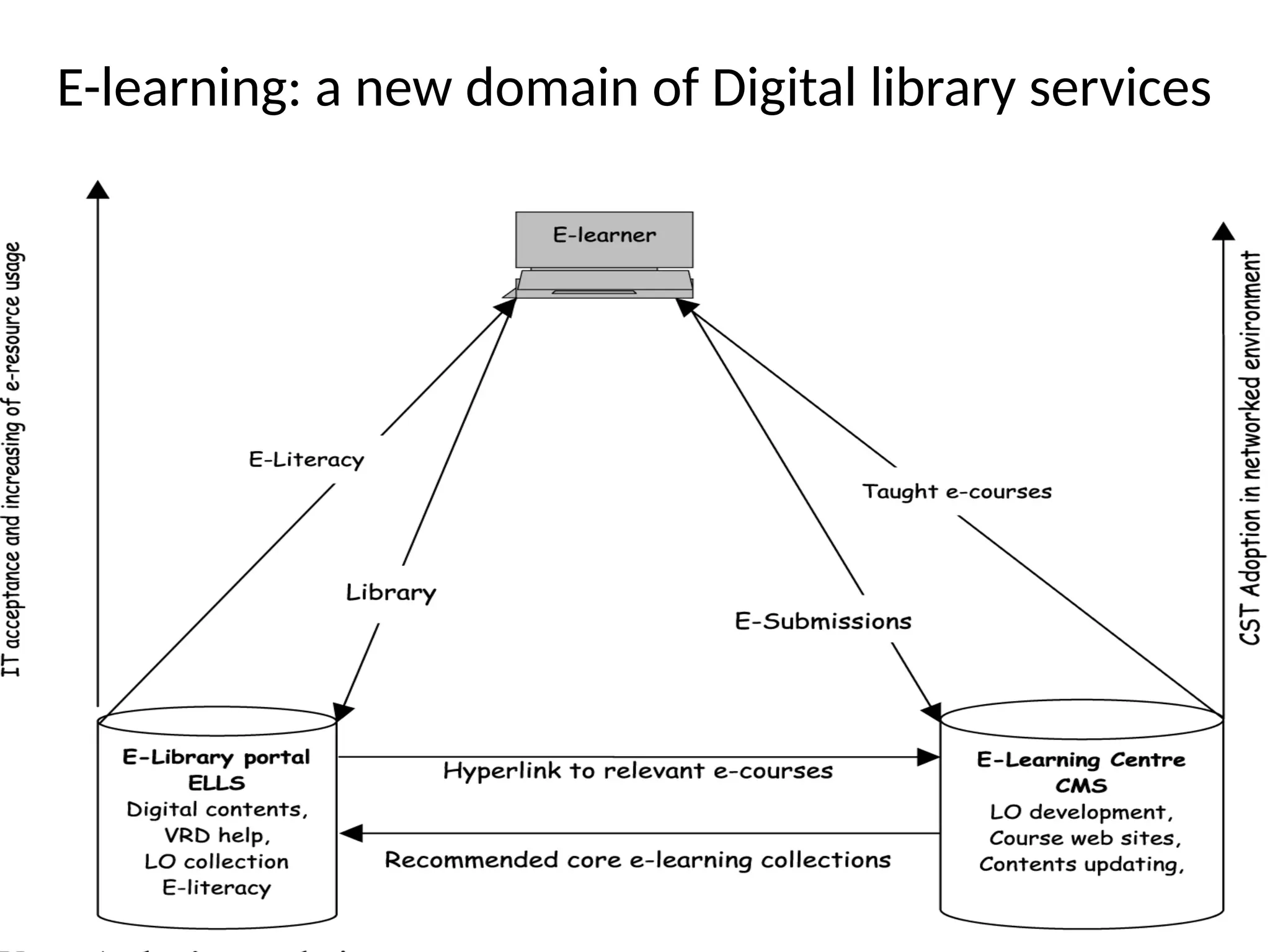
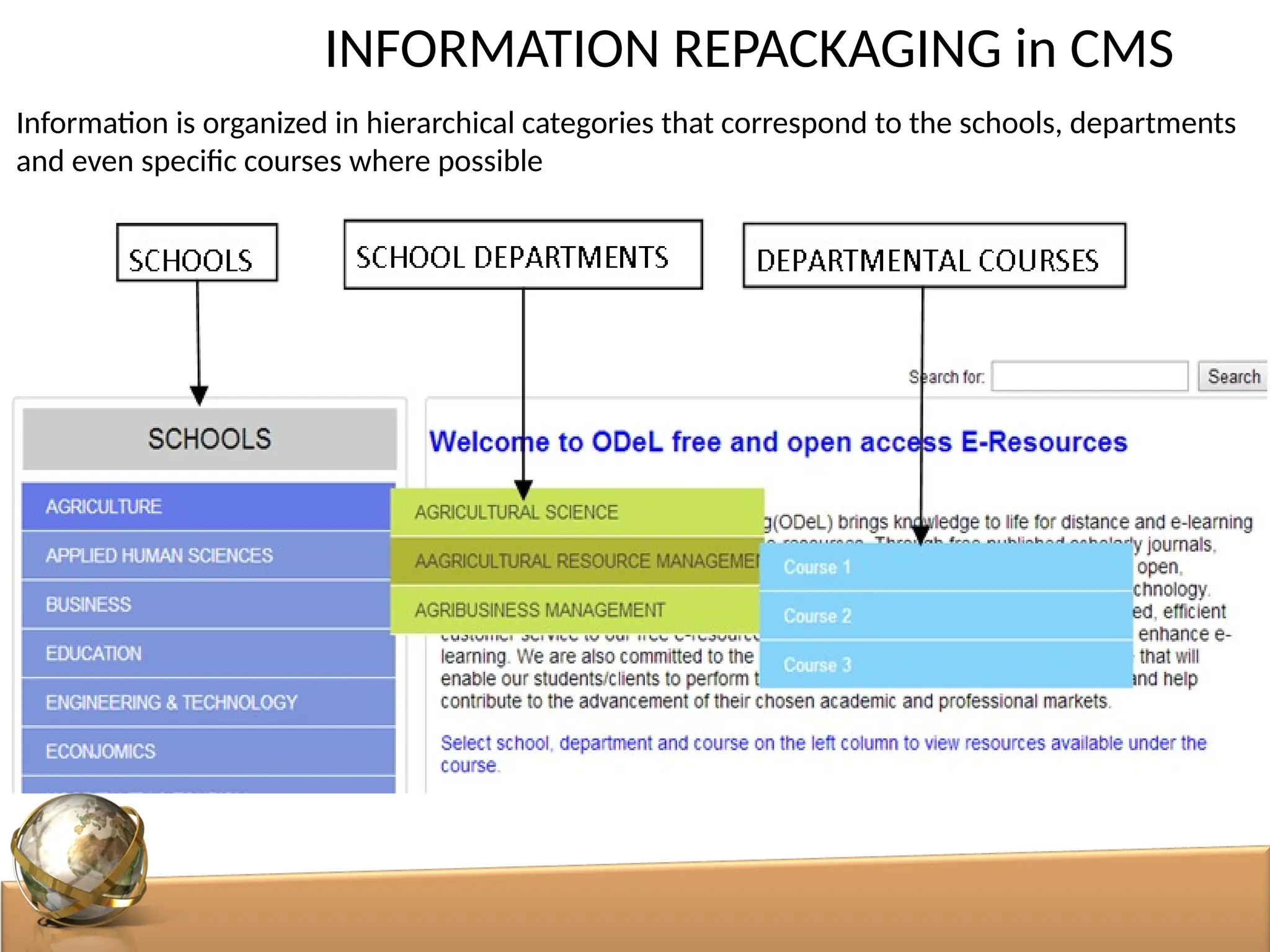
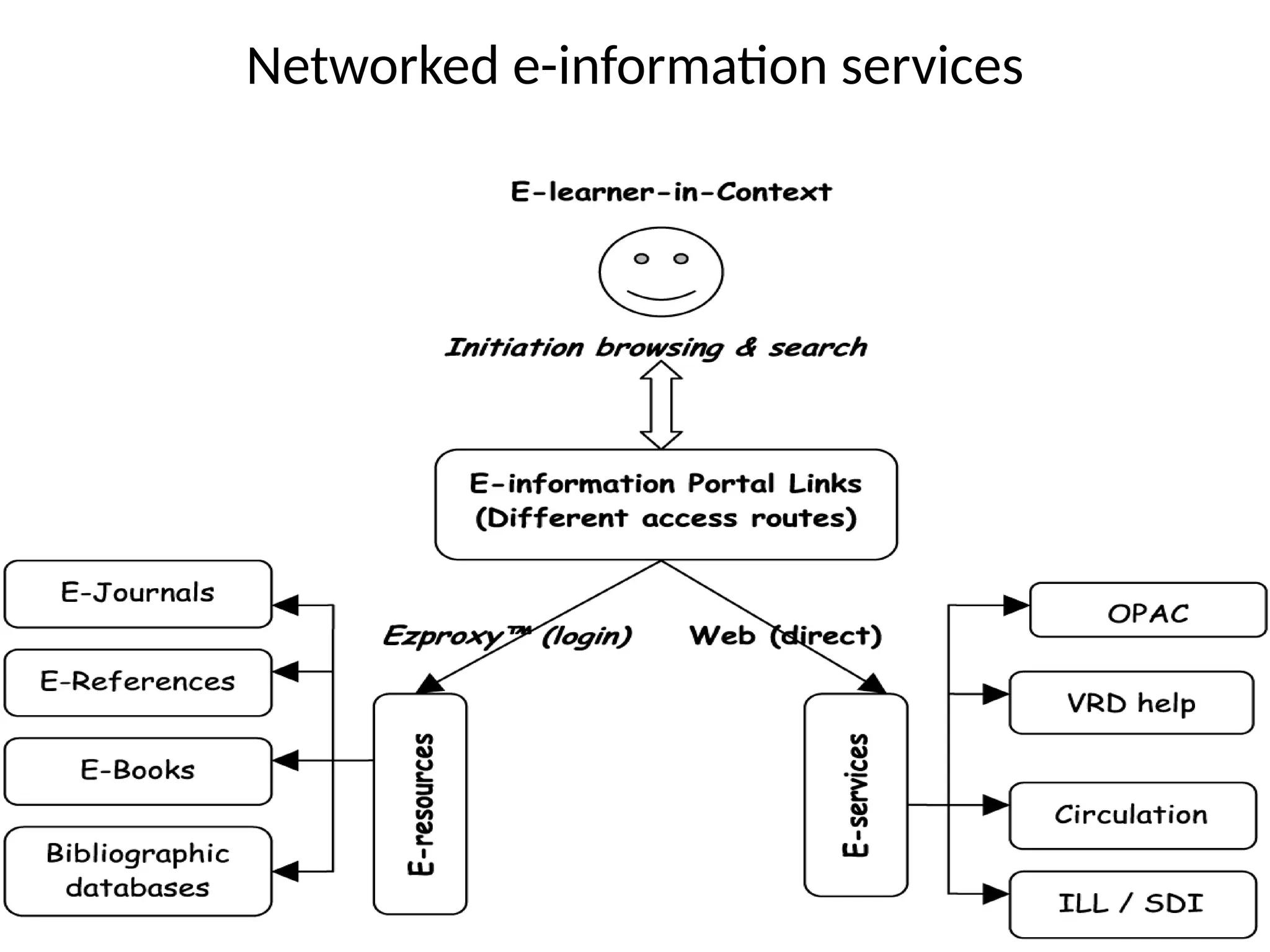
The document discusses the role of digital libraries in supporting e-learning and distance education, emphasizing the need for innovative academic programs and effective use of technologies. It outlines various functional roles of digital libraries and e-learning institutions, describing how they can enhance learning experiences through integrated resources and services. Challenges such as lack of collaboration and copyright issues are identified, along with recommendations for developing e-learning oriented collections and formalizing partnerships between faculty and support departments.