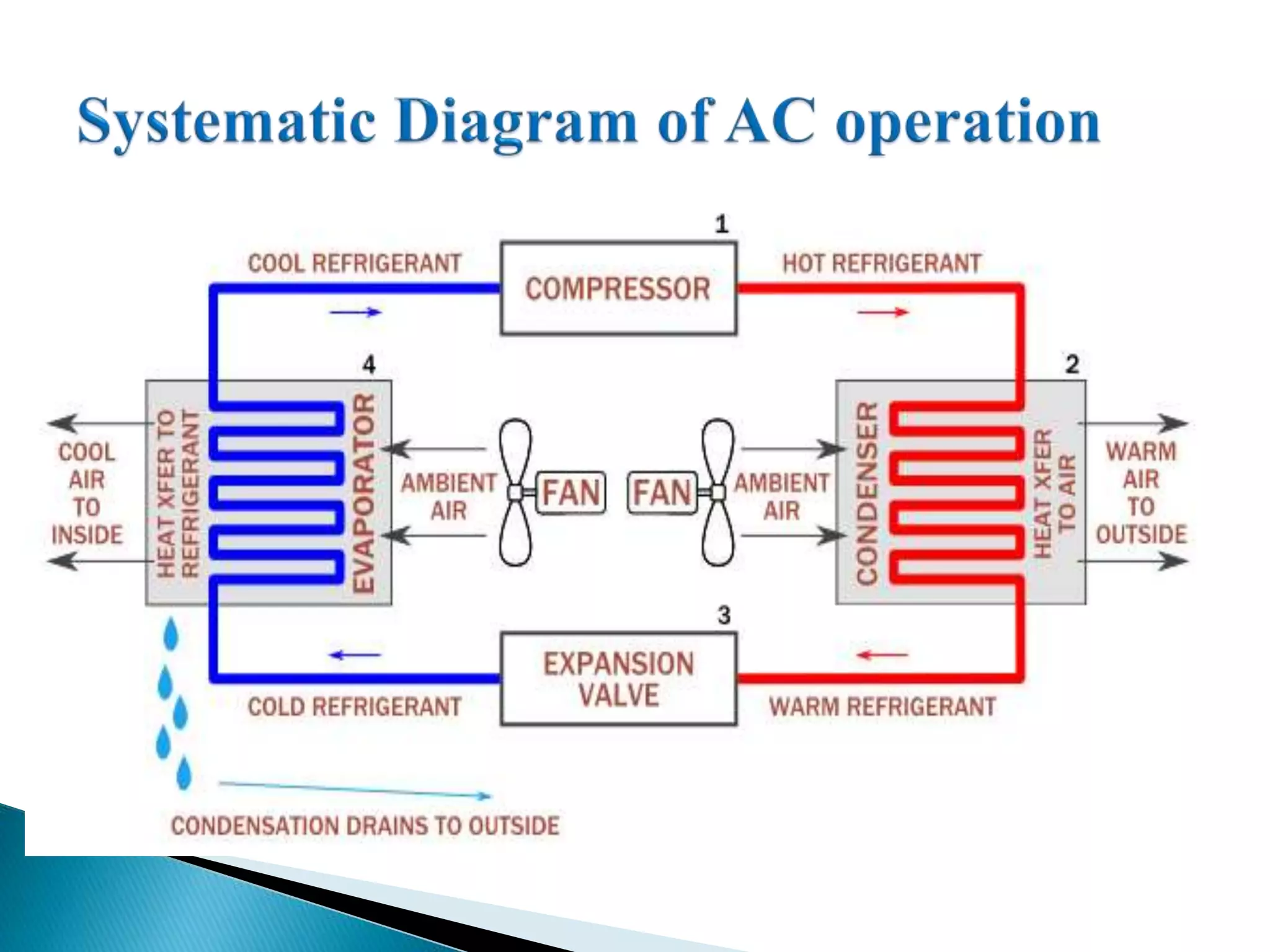
The document summarizes the history and operation of air conditioning systems. It discusses how the first modern air conditioning system was invented in 1902 by Willis Carrier to solve a humidity problem. It explains that air conditioners and refrigerators work in a similar way using a refrigerant to transfer heat from the inside to outside air. It also outlines the key components of an air conditioning system including the compressor, condenser, evaporator, blower, and thermostat. Finally, it discusses factors that determine the proper sizing of an air conditioner like home size, insulation, and heat loads.