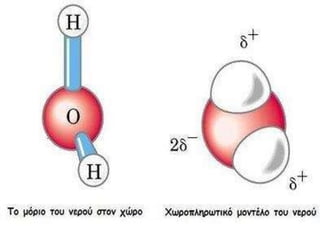
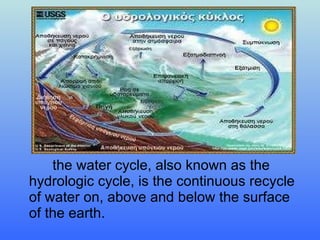
Water is a crucial chemical compound made of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom, existing in solid, liquid, and gaseous states. The water cycle continuously recycles water on Earth, while purification processes, including pre-chlorination and filtration, are necessary to make water safe for drinking. Wastewater is collected and treated at a municipal plant to ensure environmental safety.