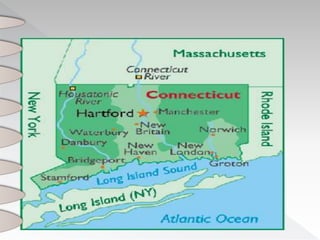
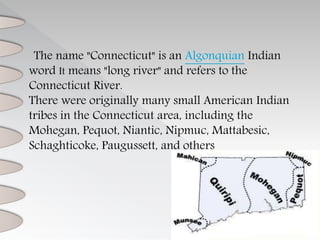
Connecticut was originally inhabited by several Native American tribes like the Mohegan and Pequot. Early European settlers included the Dutch in 1614 and English colonists from Plymouth in 1633. In 1636, Reverend Thomas Hooker led a group from Massachusetts to found Hartford. The three settlements of Hartford, Windsor, and Wethersfield united in 1639 to form the Connecticut colony with a set of basic laws called the Fundamental Orders, establishing one of the first democratic governments in North America. The economy was based around productive agriculture along the Connecticut River valley and trade of surplus crops, livestock, wood, and furs. Congregationalism became the official and dominant religion.