ABG.pptx
•Download as PPTX, PDF•
0 likes•19 views
ARTERIAL BLOOD GAS ANALYSIS DEALS WITH STUDY OF VARIOUS RESPIRATORY AND METABOLIC DISTURBANCES AND THEIR TREATMENT.
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
Blood gas analyser & blood gas analysis with clinical significancee

A comprehensive presentation on Blood Gas Analyzer and Blood Gas Analysis for self- learning undergraduate medical ,dental, ,pharmacology and biotechnology students . Laboratory determination of blood gas analysis –Micro method & technical errors involved are described.
Blood sample collection for blood gas analysis is illustrated.
Principle & Important components of Blood gas Analyzer are presented in lucid language.
Polari graphic method for PO₂ Measurement using pO₂ electrode is explained. Integral parts of pO₂ electrode ie platinum electrode, silver /silver chloride reference electrode & their working (reaction at electrode) is presented here.
Design of pCO2, & pH electrodes along with their working principles are elucidated for perusal of technologist.
Typical reference ranges in blood gas analysis are mentioned and are useful to classify acid base imbalance. Nomogram of acid base disorder is illustrated for clinical applications.
Laboratory determination of blood gas analysis along with its standardization is presented step wise. The Henderson’s Hassel Balch equation pursuing interrelation of TCO₂, Bicarbonate, Carbonic acid, PCO ₂, & p H is presented for manual calculation of certain parameters.
Google images are used for impact of subject on self-learners.
Arterial blood gas analysis and interpretation

The document discusses arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis, which measures pH, oxygen, and carbon dioxide levels in arterial blood to assess acid-base balance, oxygenation, and respiratory function. ABG provides values for pH, pO2, pCO2, HCO3, and other electrolytes that can indicate acid-base disorders. The document reviews the physiology of acid-base balance, components of ABG analysis, indications, contraindications, procedure steps, and interpretation of ABG results.
Abg analysis

ABG is a examination procedure test used for oxygen assessment of the body and its metabolismthis ppt can be used by the nursing students for the evaluation of the ABG report and its interpretation for better ventilatory management and for study and learning regarding abg analysis by gnm and bsc nursing students
ABG (Emergency Medicine)

The document discusses acid-base physiology and regulation. It covers 3 key topics:
1) Chemical buffering systems help resist changes in pH, with the HCO3-/CO2 system being the most important extracellular buffer.
2) Pulmonary regulation finely controls CO2 levels through respiration, helping normalize pH.
3) The kidneys play a major role in long-term pH regulation by adjusting HCO3- reabsorption and excretion over hours to days.
ABGs test and errors in chemistry LAB.pptx

The document discusses arterial blood gas (ABG) tests. ABGs are used to monitor acid-base imbalances by measuring oxygen, carbon dioxide, pH and bicarbonate levels in arterial blood. Kidneys and lungs work to maintain pH levels through compensatory mechanisms like regulating bicarbonate reabsorption or excretion. ABG tests are recommended for conditions affecting breathing or the kidneys. The procedure involves drawing arterial blood, usually from the radial or femoral artery, and analyzing it using an ABG machine with electrodes that measure levels of oxygen, carbon dioxide, pH and bicarbonate. Normal ranges for these values are provided along with interpretations of potential acid-base imbalances.
ARTERIAL BLOOD GAS.pptx

This document discusses arterial blood gas analysis (ABG). An ABG test measures pH, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and bicarbonate levels in arterial blood and is useful for diagnosing respiratory, circulatory, and metabolic conditions. It describes how an ABG is performed by puncturing an artery to draw blood into a heparinized syringe. The results are used to assess lung function and acid-base balance. Common acid-base imbalances like respiratory acidosis and metabolic alkalosis are also summarized.
Arterial blood gas analysis in clinical practice (2)

This document provides information about arterial blood gases (ABGs), including what an ABG is, the components that are measured, normal ranges, reasons for ordering an ABG, how to interpret ABG results, and types of acid-base imbalances. An ABG is a blood test that measures pH, oxygen, and carbon dioxide levels to help diagnose respiratory and metabolic conditions. The document outlines the steps to interpret an ABG and explains various acid-base disorders like respiratory acidosis, metabolic alkalosis, and mixed disorders. Compensation mechanisms of the lungs and kidneys in response to acid-base imbalances are also discussed.
Abg short seminar

This document provides information about arterial blood gases (ABGs), including what parameters are measured in an ABG, which artery is commonly used for sampling, cautions when obtaining an ABG, and conditions that can invalidate or modify ABG results. It also outlines the six step approach to evaluating acid-base disorders based on an ABG result, including identifying if the primary disturbance is respiratory or metabolic, ruling out combined disorders, checking the anion gap in metabolic acidosis, and calculating the delta anion gap. An illustrative case is provided where the ABG results indicate a mixed metabolic acidosis and respiratory acidosis based on application of the six step approach.
Recommended
Blood gas analyser & blood gas analysis with clinical significancee

A comprehensive presentation on Blood Gas Analyzer and Blood Gas Analysis for self- learning undergraduate medical ,dental, ,pharmacology and biotechnology students . Laboratory determination of blood gas analysis –Micro method & technical errors involved are described.
Blood sample collection for blood gas analysis is illustrated.
Principle & Important components of Blood gas Analyzer are presented in lucid language.
Polari graphic method for PO₂ Measurement using pO₂ electrode is explained. Integral parts of pO₂ electrode ie platinum electrode, silver /silver chloride reference electrode & their working (reaction at electrode) is presented here.
Design of pCO2, & pH electrodes along with their working principles are elucidated for perusal of technologist.
Typical reference ranges in blood gas analysis are mentioned and are useful to classify acid base imbalance. Nomogram of acid base disorder is illustrated for clinical applications.
Laboratory determination of blood gas analysis along with its standardization is presented step wise. The Henderson’s Hassel Balch equation pursuing interrelation of TCO₂, Bicarbonate, Carbonic acid, PCO ₂, & p H is presented for manual calculation of certain parameters.
Google images are used for impact of subject on self-learners.
Arterial blood gas analysis and interpretation

The document discusses arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis, which measures pH, oxygen, and carbon dioxide levels in arterial blood to assess acid-base balance, oxygenation, and respiratory function. ABG provides values for pH, pO2, pCO2, HCO3, and other electrolytes that can indicate acid-base disorders. The document reviews the physiology of acid-base balance, components of ABG analysis, indications, contraindications, procedure steps, and interpretation of ABG results.
Abg analysis

ABG is a examination procedure test used for oxygen assessment of the body and its metabolismthis ppt can be used by the nursing students for the evaluation of the ABG report and its interpretation for better ventilatory management and for study and learning regarding abg analysis by gnm and bsc nursing students
ABG (Emergency Medicine)

The document discusses acid-base physiology and regulation. It covers 3 key topics:
1) Chemical buffering systems help resist changes in pH, with the HCO3-/CO2 system being the most important extracellular buffer.
2) Pulmonary regulation finely controls CO2 levels through respiration, helping normalize pH.
3) The kidneys play a major role in long-term pH regulation by adjusting HCO3- reabsorption and excretion over hours to days.
ABGs test and errors in chemistry LAB.pptx

The document discusses arterial blood gas (ABG) tests. ABGs are used to monitor acid-base imbalances by measuring oxygen, carbon dioxide, pH and bicarbonate levels in arterial blood. Kidneys and lungs work to maintain pH levels through compensatory mechanisms like regulating bicarbonate reabsorption or excretion. ABG tests are recommended for conditions affecting breathing or the kidneys. The procedure involves drawing arterial blood, usually from the radial or femoral artery, and analyzing it using an ABG machine with electrodes that measure levels of oxygen, carbon dioxide, pH and bicarbonate. Normal ranges for these values are provided along with interpretations of potential acid-base imbalances.
ARTERIAL BLOOD GAS.pptx

This document discusses arterial blood gas analysis (ABG). An ABG test measures pH, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and bicarbonate levels in arterial blood and is useful for diagnosing respiratory, circulatory, and metabolic conditions. It describes how an ABG is performed by puncturing an artery to draw blood into a heparinized syringe. The results are used to assess lung function and acid-base balance. Common acid-base imbalances like respiratory acidosis and metabolic alkalosis are also summarized.
Arterial blood gas analysis in clinical practice (2)

This document provides information about arterial blood gases (ABGs), including what an ABG is, the components that are measured, normal ranges, reasons for ordering an ABG, how to interpret ABG results, and types of acid-base imbalances. An ABG is a blood test that measures pH, oxygen, and carbon dioxide levels to help diagnose respiratory and metabolic conditions. The document outlines the steps to interpret an ABG and explains various acid-base disorders like respiratory acidosis, metabolic alkalosis, and mixed disorders. Compensation mechanisms of the lungs and kidneys in response to acid-base imbalances are also discussed.
Abg short seminar

This document provides information about arterial blood gases (ABGs), including what parameters are measured in an ABG, which artery is commonly used for sampling, cautions when obtaining an ABG, and conditions that can invalidate or modify ABG results. It also outlines the six step approach to evaluating acid-base disorders based on an ABG result, including identifying if the primary disturbance is respiratory or metabolic, ruling out combined disorders, checking the anion gap in metabolic acidosis, and calculating the delta anion gap. An illustrative case is provided where the ABG results indicate a mixed metabolic acidosis and respiratory acidosis based on application of the six step approach.
Abg analysis in emergency medicine department

This document provides an outline and overview of arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis. It begins with an introduction to the lung and kidney functions related to gas exchange and acid-base balance. It then defines an ABG test and lists common indications. The document outlines the components of an ABG, normal values, procedure steps, complications, and approaches to interpreting results including identifying acid-base disorders and assessing respiratory and renal compensation. It provides detail on sampling sites, transport considerations, and approaches to troubleshooting and solving acid-base disturbances based on ABG parameters.
respiratory monitoring backup.ppt

This document discusses various methods for respiratory monitoring including pulse oximetry, capnography, and continuous blood gas analysis. It provides details on how each method works and what patient conditions they can help evaluate. Pulse oximetry measures oxygen saturation using light absorption while capnography measures exhaled carbon dioxide. Continuous blood gas analysis uses a small fiber optic sensor to continuously monitor pH, carbon dioxide, and oxygen levels in the blood. Each method has benefits and limitations for assessing ventilation and oxygenation in critically ill patients.
Abg

The document discusses arterial blood gas analysis including normal values, procedures, indications, contraindications, and interpretation. It provides details on analyzing acid-base status, oxygenation, ventilation, and electrolyte balance based on ABG results. Physicians' accuracy in interpreting ABGs is low according to one survey. ICU patients often have acid-base disorders, demonstrating the importance of the test.
6.arterial blood gas analysis (2).ppt

This document provides information on acid-base balance and blood gas analysis (BGA). It discusses the components of a BGA profile and their normal reference ranges. Key points include that BGA can help establish diagnoses of acid-base disorders, guide treatment, and monitor ventilator management. A systematic approach is outlined to classify acid-base disorders based on pH, PCO2, and HCO3 levels. Causes and characteristics of respiratory acidosis, respiratory alkalosis, metabolic acidosis, and metabolic alkalosis are described. Compensation mechanisms for acute vs. chronic conditions are also summarized.
Acid base disorders

1. Acid-base disorders are common in ICU patients, affecting 90%. A structured approach is needed to identify and manage these disorders.
2. The blood gas machine measures pH, pCO2, and pO2 to determine HCO3 and base deficit using the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
3. Acid-base disorders are classified by the PCO2/HCO3 ratio and secondary responses evaluated to identify the primary disorder.
ABG Analysis in Pediatrics

This document provides an outline for a seminar on arterial blood gas analysis (ABG). The seminar will include an introduction to ABGs, indications for ordering ABGs, the procedure for arterial blood sampling, pulmonary gas exchange, acid-base disorders, and how to approach analyzing an ABG. Resident doctors from pediatrics and cardiology will present on these topics and discuss ABGs versus venous blood gases.
Arterial blood gas

An arterial blood gas (ABG) test measures important gas levels in arterial blood including oxygen, carbon dioxide, pH and bicarbonate. It involves puncturing an artery with a needle to draw blood directly from the circulatory system. The test is mainly used in critical care medicine to assess gas exchange and respiratory function, and can help diagnose conditions that affect oxygen and carbon dioxide levels like respiratory disease. Modern analyzers can also measure electrolytes, hemoglobin and other blood components from an ABG sample.
Arterial blood gas analysis

- Arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis measures pH and partial pressures of oxygen and carbon dioxide in arterial blood to assess acid-base balance and lung function.
- The pH measures acidity, PCO2 measures respiratory status, PO2 measures oxygenation, and HCO3 measures kidney function.
- Disturbances can be respiratory (high or low PCO2) or metabolic (high or low HCO3) in nature. The body compensates through respiratory rate or kidney bicarbonate levels to return pH to normal.
Arterial Blood Gas Analysis 

This document discusses arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis. It provides information on the procedure for ABG including ideal sample sites and precautions. It also lists the normal ranges for parameters measured in an ABG: pH, PaCO2, HCO3, and PaO2. Additionally, it discusses hydrogen ion regulation and the central equation and Henderson-Hasselbalch equation of acid-base physiology. The document interprets ABG ranges and factors that can affect ABG analysis results.
Arterial blood gas presentation in ICU/OT

This document discusses arterial blood gas (ABG) sampling and analysis. Some key points:
- ABG provides important information about respiratory, metabolic and mixed acid-base disorders through measurement of pH, pCO2 and HCO3 levels.
- It can help guide treatment, especially for critically ill patients, as results are rapidly available at the bedside.
- Samples must be taken and analyzed properly to avoid inaccuracies from factors like delayed analysis, air bubbles, excessive heparin or temperature changes.
- ABG interpretation involves classifying the primary acid-base disorder based on directional changes in pH and pCO2, and evaluating any secondary responses. This helps identify conditions like respiratory acid
Acid Base Balance and ABG by Dr.Tinku Joseph

This document discusses acid-base balance and disorders. It provides an overview of how the lungs and kidneys work to maintain acid-base homeostasis by regulating carbon dioxide and bicarbonate levels. It then outlines the steps for diagnosing and classifying acid-base disorders as either respiratory or metabolic in nature, and as compensated or uncompensated. Examples of respiratory alkalosis and its causes and manifestations are also provided.
ABG interpretation.

An arterial blood gas test measures pH, oxygen, and carbon dioxide levels in blood from an artery. It provides information about oxygenation, ventilation, and acid-base levels. ABGs are useful for evaluating respiratory failure, severe illnesses that can cause metabolic acidosis like cardiac or liver failure, and conditions in ventilated patients or those undergoing sleep studies. Interpretation of ABG results involves considering pH, carbon dioxide, bicarbonate, and oxygen levels to determine if any acid-base imbalances exist and their underlying cause.
Metabolic acidosis- Systematic analysis

This document discusses metabolic acidosis and provides a systematic approach to diagnosis and treatment. Key points include:
1. Metabolic acidosis is defined by a primary reduction in serum bicarbonate and low blood pH. Common causes seen in practice include lactic acidosis, diabetic ketoacidosis, and acute kidney injury.
2. Evaluation involves assessing the anion gap, bicarbonate levels, electrolytes, and clinical context to determine the underlying etiology. Mixed disorders can occur.
3. Treatment focuses on correcting the primary cause. Bicarbonate therapy may be used in severe cases to raise the pH, but adverse effects are possible and the underlying condition still needs treatment.
ARTERIAL BLOOD GAS ANALYSIS

This document provides information about arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis. It defines an ABG as a blood sample drawn from an artery to assess acid-base balance, oxygenation, and ventilation. ABGs are ordered to diagnose and monitor respiratory failure and changes in acid-base homeostasis. The components of an ABG include pH, PaCO2, PaO2, HCO3, O2 saturation, and base excess. Normal values for these components are provided. The document discusses how to properly collect an ABG sample and handle it to avoid inaccurate results. It also covers acid-base physiology and the four primary acid-base disorders: metabolic acidosis, metabolic alkalosis, respiratory acidosis, and respiratory alk
4Acid Base Disturbances.ppt

1. The document discusses acid-base disturbances and homeostasis. It defines acids and bases, and how the body maintains pH levels through buffers, respiration, and the kidneys.
2. Specific acid-base disorders are described in detail, including metabolic acidosis, alkalosis and respiratory acidosis, alkalosis. Causes, clinical presentations, diagnoses, and treatments are provided for each.
3. Case studies are presented and acid-base status can be determined by reviewing arterial blood gases to measure pH, PaCO2 and HCO3 levels.
ABG.pdf

This document provides an overview of arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis. It discusses the basic physiology of acid-base balance and the two main buffer systems - respiratory and renal. The respiratory system responds to changes in carbon dioxide (CO2) levels via respiration, while the renal system responds more slowly via bicarbonate ion regulation in the kidneys. Conditions that can cause acid-base imbalances like respiratory acidosis and metabolic alkalosis are described. Steps for interpreting an ABG report, including anticipating the disorder and checking for compensation, are outlined. Examples of interpreting ABG results in cases of metabolic acidosis, metabolic alkalosis, and a mixed disorder are provided.
Abg

This document provides information about arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis, including what it is, its purpose, interpretation, and conditions it can assess like diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). ABG measures oxygen, carbon dioxide, pH in blood and helps evaluate lung and kidney function in acid-base balance. It determines pH levels and the partial pressures of carbon dioxide and oxygen. The 6 steps to interpret ABGs are analyzing pH, pCO2, HCO3, matching acid-base disturbances, checking for compensation, and analyzing pO2 and oxygen saturation. DKA is a life-threatening complication of diabetes where lack of insulin causes ketone production from fat breakdown.
ABG ANALYSIS

This document provides information about arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis, including:
- ABG analysis measures blood pH, partial pressures of oxygen and carbon dioxide, and calculates bicarbonate levels. It is useful for evaluating respiratory, metabolic and renal function.
- The procedure involves puncturing an artery with a needle to draw blood into a syringe. Precautions must be taken to avoid complications and ensure proper sample handling for analysis.
- ABG values are interpreted using the Tic-Tac-Toe method to determine if any acid-base imbalances exist and their respiratory or metabolic origin. This allows clinicians to evaluate treatment for critically ill patients.
ABG Analysis 

The document discusses arterial blood gas analysis and interpretation. It provides an overview of gas exchange, acid-base homeostasis, and the basics of acid-base balance. It describes how to interpret an arterial blood gas report, including how to diagnose acid-base disorders and examples. Technical aspects like sampling technique and potential errors or complications are covered. Compensation mechanisms in response to primary acid-base disturbances are explained.
Biochemistry of cancer AND effect of factors on cancer growth.ppt

CANCER BIOCHEMISTRY, MEDICINE, TREATMENT AND DETAILS OF CANCER, MBBS AND PARAMEDICAL TEACHING,
CANCER AETIOLOGY, DETAILED GROWTH MECHANISMS,
role of physician AT MEDICAL COLLEGE AND SOCIETY.pptx

This document discusses the roles and responsibilities of physicians. It outlines that physicians should uphold professional qualities like compassion, ethics, and lifelong learning. Their key roles are to treat patients, participate in public health programs, educate communities, and ensure affordable healthcare. Physicians must continually learn and adapt to evolving standards and treatments to provide the best possible care.
More Related Content
Similar to ABG.pptx
Abg analysis in emergency medicine department

This document provides an outline and overview of arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis. It begins with an introduction to the lung and kidney functions related to gas exchange and acid-base balance. It then defines an ABG test and lists common indications. The document outlines the components of an ABG, normal values, procedure steps, complications, and approaches to interpreting results including identifying acid-base disorders and assessing respiratory and renal compensation. It provides detail on sampling sites, transport considerations, and approaches to troubleshooting and solving acid-base disturbances based on ABG parameters.
respiratory monitoring backup.ppt

This document discusses various methods for respiratory monitoring including pulse oximetry, capnography, and continuous blood gas analysis. It provides details on how each method works and what patient conditions they can help evaluate. Pulse oximetry measures oxygen saturation using light absorption while capnography measures exhaled carbon dioxide. Continuous blood gas analysis uses a small fiber optic sensor to continuously monitor pH, carbon dioxide, and oxygen levels in the blood. Each method has benefits and limitations for assessing ventilation and oxygenation in critically ill patients.
Abg

The document discusses arterial blood gas analysis including normal values, procedures, indications, contraindications, and interpretation. It provides details on analyzing acid-base status, oxygenation, ventilation, and electrolyte balance based on ABG results. Physicians' accuracy in interpreting ABGs is low according to one survey. ICU patients often have acid-base disorders, demonstrating the importance of the test.
6.arterial blood gas analysis (2).ppt

This document provides information on acid-base balance and blood gas analysis (BGA). It discusses the components of a BGA profile and their normal reference ranges. Key points include that BGA can help establish diagnoses of acid-base disorders, guide treatment, and monitor ventilator management. A systematic approach is outlined to classify acid-base disorders based on pH, PCO2, and HCO3 levels. Causes and characteristics of respiratory acidosis, respiratory alkalosis, metabolic acidosis, and metabolic alkalosis are described. Compensation mechanisms for acute vs. chronic conditions are also summarized.
Acid base disorders

1. Acid-base disorders are common in ICU patients, affecting 90%. A structured approach is needed to identify and manage these disorders.
2. The blood gas machine measures pH, pCO2, and pO2 to determine HCO3 and base deficit using the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
3. Acid-base disorders are classified by the PCO2/HCO3 ratio and secondary responses evaluated to identify the primary disorder.
ABG Analysis in Pediatrics

This document provides an outline for a seminar on arterial blood gas analysis (ABG). The seminar will include an introduction to ABGs, indications for ordering ABGs, the procedure for arterial blood sampling, pulmonary gas exchange, acid-base disorders, and how to approach analyzing an ABG. Resident doctors from pediatrics and cardiology will present on these topics and discuss ABGs versus venous blood gases.
Arterial blood gas

An arterial blood gas (ABG) test measures important gas levels in arterial blood including oxygen, carbon dioxide, pH and bicarbonate. It involves puncturing an artery with a needle to draw blood directly from the circulatory system. The test is mainly used in critical care medicine to assess gas exchange and respiratory function, and can help diagnose conditions that affect oxygen and carbon dioxide levels like respiratory disease. Modern analyzers can also measure electrolytes, hemoglobin and other blood components from an ABG sample.
Arterial blood gas analysis

- Arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis measures pH and partial pressures of oxygen and carbon dioxide in arterial blood to assess acid-base balance and lung function.
- The pH measures acidity, PCO2 measures respiratory status, PO2 measures oxygenation, and HCO3 measures kidney function.
- Disturbances can be respiratory (high or low PCO2) or metabolic (high or low HCO3) in nature. The body compensates through respiratory rate or kidney bicarbonate levels to return pH to normal.
Arterial Blood Gas Analysis 

This document discusses arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis. It provides information on the procedure for ABG including ideal sample sites and precautions. It also lists the normal ranges for parameters measured in an ABG: pH, PaCO2, HCO3, and PaO2. Additionally, it discusses hydrogen ion regulation and the central equation and Henderson-Hasselbalch equation of acid-base physiology. The document interprets ABG ranges and factors that can affect ABG analysis results.
Arterial blood gas presentation in ICU/OT

This document discusses arterial blood gas (ABG) sampling and analysis. Some key points:
- ABG provides important information about respiratory, metabolic and mixed acid-base disorders through measurement of pH, pCO2 and HCO3 levels.
- It can help guide treatment, especially for critically ill patients, as results are rapidly available at the bedside.
- Samples must be taken and analyzed properly to avoid inaccuracies from factors like delayed analysis, air bubbles, excessive heparin or temperature changes.
- ABG interpretation involves classifying the primary acid-base disorder based on directional changes in pH and pCO2, and evaluating any secondary responses. This helps identify conditions like respiratory acid
Acid Base Balance and ABG by Dr.Tinku Joseph

This document discusses acid-base balance and disorders. It provides an overview of how the lungs and kidneys work to maintain acid-base homeostasis by regulating carbon dioxide and bicarbonate levels. It then outlines the steps for diagnosing and classifying acid-base disorders as either respiratory or metabolic in nature, and as compensated or uncompensated. Examples of respiratory alkalosis and its causes and manifestations are also provided.
ABG interpretation.

An arterial blood gas test measures pH, oxygen, and carbon dioxide levels in blood from an artery. It provides information about oxygenation, ventilation, and acid-base levels. ABGs are useful for evaluating respiratory failure, severe illnesses that can cause metabolic acidosis like cardiac or liver failure, and conditions in ventilated patients or those undergoing sleep studies. Interpretation of ABG results involves considering pH, carbon dioxide, bicarbonate, and oxygen levels to determine if any acid-base imbalances exist and their underlying cause.
Metabolic acidosis- Systematic analysis

This document discusses metabolic acidosis and provides a systematic approach to diagnosis and treatment. Key points include:
1. Metabolic acidosis is defined by a primary reduction in serum bicarbonate and low blood pH. Common causes seen in practice include lactic acidosis, diabetic ketoacidosis, and acute kidney injury.
2. Evaluation involves assessing the anion gap, bicarbonate levels, electrolytes, and clinical context to determine the underlying etiology. Mixed disorders can occur.
3. Treatment focuses on correcting the primary cause. Bicarbonate therapy may be used in severe cases to raise the pH, but adverse effects are possible and the underlying condition still needs treatment.
ARTERIAL BLOOD GAS ANALYSIS

This document provides information about arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis. It defines an ABG as a blood sample drawn from an artery to assess acid-base balance, oxygenation, and ventilation. ABGs are ordered to diagnose and monitor respiratory failure and changes in acid-base homeostasis. The components of an ABG include pH, PaCO2, PaO2, HCO3, O2 saturation, and base excess. Normal values for these components are provided. The document discusses how to properly collect an ABG sample and handle it to avoid inaccurate results. It also covers acid-base physiology and the four primary acid-base disorders: metabolic acidosis, metabolic alkalosis, respiratory acidosis, and respiratory alk
4Acid Base Disturbances.ppt

1. The document discusses acid-base disturbances and homeostasis. It defines acids and bases, and how the body maintains pH levels through buffers, respiration, and the kidneys.
2. Specific acid-base disorders are described in detail, including metabolic acidosis, alkalosis and respiratory acidosis, alkalosis. Causes, clinical presentations, diagnoses, and treatments are provided for each.
3. Case studies are presented and acid-base status can be determined by reviewing arterial blood gases to measure pH, PaCO2 and HCO3 levels.
ABG.pdf

This document provides an overview of arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis. It discusses the basic physiology of acid-base balance and the two main buffer systems - respiratory and renal. The respiratory system responds to changes in carbon dioxide (CO2) levels via respiration, while the renal system responds more slowly via bicarbonate ion regulation in the kidneys. Conditions that can cause acid-base imbalances like respiratory acidosis and metabolic alkalosis are described. Steps for interpreting an ABG report, including anticipating the disorder and checking for compensation, are outlined. Examples of interpreting ABG results in cases of metabolic acidosis, metabolic alkalosis, and a mixed disorder are provided.
Abg

This document provides information about arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis, including what it is, its purpose, interpretation, and conditions it can assess like diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). ABG measures oxygen, carbon dioxide, pH in blood and helps evaluate lung and kidney function in acid-base balance. It determines pH levels and the partial pressures of carbon dioxide and oxygen. The 6 steps to interpret ABGs are analyzing pH, pCO2, HCO3, matching acid-base disturbances, checking for compensation, and analyzing pO2 and oxygen saturation. DKA is a life-threatening complication of diabetes where lack of insulin causes ketone production from fat breakdown.
ABG ANALYSIS

This document provides information about arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis, including:
- ABG analysis measures blood pH, partial pressures of oxygen and carbon dioxide, and calculates bicarbonate levels. It is useful for evaluating respiratory, metabolic and renal function.
- The procedure involves puncturing an artery with a needle to draw blood into a syringe. Precautions must be taken to avoid complications and ensure proper sample handling for analysis.
- ABG values are interpreted using the Tic-Tac-Toe method to determine if any acid-base imbalances exist and their respiratory or metabolic origin. This allows clinicians to evaluate treatment for critically ill patients.
ABG Analysis 

The document discusses arterial blood gas analysis and interpretation. It provides an overview of gas exchange, acid-base homeostasis, and the basics of acid-base balance. It describes how to interpret an arterial blood gas report, including how to diagnose acid-base disorders and examples. Technical aspects like sampling technique and potential errors or complications are covered. Compensation mechanisms in response to primary acid-base disturbances are explained.
Similar to ABG.pptx (20)
Abg analysis presentation for undergraduates and postgraduates

Abg analysis presentation for undergraduates and postgraduates
More from RAJNKIT
Biochemistry of cancer AND effect of factors on cancer growth.ppt

CANCER BIOCHEMISTRY, MEDICINE, TREATMENT AND DETAILS OF CANCER, MBBS AND PARAMEDICAL TEACHING,
CANCER AETIOLOGY, DETAILED GROWTH MECHANISMS,
role of physician AT MEDICAL COLLEGE AND SOCIETY.pptx

This document discusses the roles and responsibilities of physicians. It outlines that physicians should uphold professional qualities like compassion, ethics, and lifelong learning. Their key roles are to treat patients, participate in public health programs, educate communities, and ensure affordable healthcare. Physicians must continually learn and adapt to evolving standards and treatments to provide the best possible care.
RENAL FUNCTION TESTS FOR PARAMEDICAL AND MEDICAL STUDENTS

This document discusses renal function tests (RFTs). It begins by describing the functions of the kidney including formation of urine, excretion of waste products, and regulation of water and electrolytes. It then outlines the purposes of RFTs which are to assess renal damage, monitor disease progression, and adjust medication doses. RFTs measure glomerular function through tests of renal clearance and blood analytes like creatinine and urea. They also study tubular function using urine concentration, dilution, and other specialized tests. Common RFTs and their clinical significance are described in detail.
LFT.pptx

The document discusses liver function tests and their use in evaluating liver health and disease. It covers the metabolic, excretory, synthetic, detoxification and storage functions of the liver. Liver function tests are classified based on the liver's excretory, detoxification, and synthetic functions. Enzymes like ALT, AST, GGT, ALP, and bilirubin are discussed in the context of diagnosing different types of liver disease and jaundice. The document also discusses pancreatic function tests and enzymes like amylase and lipase that are indicators of pancreatic health and diseases like pancreatitis.
Chemistry of protein and Amino Acids.pptx

The document discusses the chemistry, digestion, and absorption of proteins and amino acids. It covers the structure and properties of proteins and the 20 standard amino acids. Key points include:
- Proteins are polymers of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. They serve structural, enzymatic, transport, storage, and other functions in the body.
- Amino acids vary in their side chains, determining properties like charge, solubility, and metabolism. They are classified by properties like polarity, acid/base characteristics, and essential/non-essential status.
- Protein structure is determined by amino acid sequence and interactions between R groups. Secondary structures like alpha helices influence 3D shape.
IRON.pptx

Iron is an essential trace element required for oxygen transport and many enzymatic processes. Women and children have higher iron requirements. Dietary sources like jaggery are rich in iron while milk is poor. Factors like calcium, phytates and oxalates inhibit iron absorption in the duodenum and jejunum, while vitamin C and cysteine enhance absorption. Iron is important for carrying oxygen via hemoglobin, acting as an enzyme cofactor, and supporting brain and cell functions. Iron deficiency anemia results from low intake or increased losses and is characterized by low hemoglobin and red blood cell changes. It is commonly seen in pregnant women and treated with oral or parenteral iron supplements.
SERUM AMYLASE.pptx

This document discusses the estimation of serum amylase levels. It describes amylase as the main enzyme for carbohydrate digestion produced by the salivary glands and pancreas. It then outlines two main methods for estimating serum amylase - the iodometric method and saccharogenic method. The iodometric method measures the decrease in color intensity of a starch-iodine solution after hydrolysis by serum amylase. Normal serum amylase levels are 25-125 U/L, and increased levels can indicate conditions like acute pancreatitis while decreased levels may be seen in necrotic pancreatitis or hepatitis.
Automatio.pptx

Automation in clinical chemistry involves using laboratory instruments and equipment to perform clinical assays with minimal technologist involvement. Automation replaces human effort with mechanical devices regulated by feedback to be self-monitoring. The IUPAC defines automation as the replacement of human manipulation with instrumental devices regulated by feedback for self-adjustment. Colorimetry uses Beer's Law and Lambert's Law, where the amount of light transmitted through colored solutions decreases exponentially with increasing concentration or thickness according to the laws.
photometry.pptx

Optical techniques like photometry, spectrophotometry, and colorimetry are used in clinical laboratories. They are based on Beer's law and Lambert's law. Spectrophotometry measures light intensity at selected wavelengths using a light source, monochromator, sample cuvettes, detector, and display. It provides more sensitivity than colorimetry which determines color intensity based on light absorption. Both techniques rely on the principle that absorbed light is inversely proportional to concentration according to Beer-Lambert's law.
ELECTROCHEMISTRY.pptx

Electrochemistry deals with oxidation-reduction reactions where chemical energy is converted to electrical energy and vice versa. It involves the transfer of electrons between oxidizing and reducing agents. An electrochemical cell allows a redox reaction to occur by transferring electrons through an external connector. The potential difference between the anode and cathode is called the electromotive force (emf). Various electroanalytical techniques like potentiometry, voltammetry, conductometry, and coulometry are used for clinical applications such as measuring blood gases, electrolytes, and analytes. Optical chemical sensors called optodes are also used as they offer advantages over traditional electrodes.
bioenergetics.pptx

This document discusses bioenergetics and the role of ATP in living systems. It explains that ATP stores and transports chemical energy within cells, which is released through its hydrolysis into ADP and phosphate. The hydrolysis of ATP is highly exergonic, with a large negative standard free energy change of -30.5 kJ/mol. This energy from ATP hydrolysis drives endergonic biochemical reactions and processes, such as the synthesis of glucose-6-phosphate from glucose and phosphate. The energy from ATP hydrolysis is efficiently coupled to these endergonic reactions through a cyclic process of ATP synthesis and breakdown.
COLORIMETER & LAMBERTS – BEER’S LAW.pptx

colorimeter is used in lab diagnostic medicine and is based on lamberts and beer s law. these ppts gives a clear view regarding the mentioned subject.
RADIOACTIVITY

This document discusses radioactivity and atomic structure. It begins by explaining the need to study radioactivity for diagnosis, therapy, and medical research. It then defines atoms and their structure, including atomic number and mass number. The document discusses isotopes and radioactive decay, including different types of decay and half-life. It also covers radiation properties, detection and measurement of radioactivity, and radiation safety quantities and units.
Spots for Biochemistry 

Based on the information provided:
Q1. Identify the disease?
Refsum disease
Q2. What is accumulated?
Phytanic acid
More from RAJNKIT (14)
Biochemistry of cancer AND effect of factors on cancer growth.ppt

Biochemistry of cancer AND effect of factors on cancer growth.ppt
role of physician AT MEDICAL COLLEGE AND SOCIETY.pptx

role of physician AT MEDICAL COLLEGE AND SOCIETY.pptx
RENAL FUNCTION TESTS FOR PARAMEDICAL AND MEDICAL STUDENTS

RENAL FUNCTION TESTS FOR PARAMEDICAL AND MEDICAL STUDENTS
Recently uploaded
Cell Therapy Expansion and Challenges in Autoimmune Disease

There is increasing confidence that cell therapies will soon play a role in the treatment of autoimmune disorders, but the extent of this impact remains to be seen. Early readouts on autologous CAR-Ts in lupus are encouraging, but manufacturing and cost limitations are likely to restrict access to highly refractory patients. Allogeneic CAR-Ts have the potential to broaden access to earlier lines of treatment due to their inherent cost benefits, however they will need to demonstrate comparable or improved efficacy to established modalities.
In addition to infrastructure and capacity constraints, CAR-Ts face a very different risk-benefit dynamic in autoimmune compared to oncology, highlighting the need for tolerable therapies with low adverse event risk. CAR-NK and Treg-based therapies are also being developed in certain autoimmune disorders and may demonstrate favorable safety profiles. Several novel non-cell therapies such as bispecific antibodies, nanobodies, and RNAi drugs, may also offer future alternative competitive solutions with variable value propositions.
Widespread adoption of cell therapies will not only require strong efficacy and safety data, but also adapted pricing and access strategies. At oncology-based price points, CAR-Ts are unlikely to achieve broad market access in autoimmune disorders, with eligible patient populations that are potentially orders of magnitude greater than the number of currently addressable cancer patients. Developers have made strides towards reducing cell therapy COGS while improving manufacturing efficiency, but payors will inevitably restrict access until more sustainable pricing is achieved.
Despite these headwinds, industry leaders and investors remain confident that cell therapies are poised to address significant unmet need in patients suffering from autoimmune disorders. However, the extent of this impact on the treatment landscape remains to be seen, as the industry rapidly approaches an inflection point.
Acute Gout Care & Urate Lowering Therapy .pdf

In this document , the management of acute gout attacks and a description of urate lowering therapy is mentioned.
The Nervous and Chemical Regulation of Respiration

These lecture slides, by Dr Sidra Arshad, offer a simplified look into the mechanisms involved in the regulation of respiration:
Learning objectives:
1. Describe the organisation of respiratory center
2. Describe the nervous control of inspiration and respiratory rhythm
3. Describe the functions of the dorsal and respiratory groups of neurons
4. Describe the influences of the Pneumotaxic and Apneustic centers
5. Explain the role of Hering-Breur inflation reflex in regulation of inspiration
6. Explain the role of central chemoreceptors in regulation of respiration
7. Explain the role of peripheral chemoreceptors in regulation of respiration
8. Explain the regulation of respiration during exercise
9. Integrate the respiratory regulatory mechanisms
10. Describe the Cheyne-Stokes breathing
Study Resources:
1. Chapter 42, Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology, 14th edition
2. Chapter 36, Ganong’s Review of Medical Physiology, 26th edition
3. Chapter 13, Human Physiology by Lauralee Sherwood, 9th edition
Histololgy of Female Reproductive System.pptx

Dive into an in-depth exploration of the histological structure of female reproductive system with this comprehensive lecture. Presented by Dr. Ayesha Irfan, Assistant Professor of Anatomy, this presentation covers the Gross anatomy and functional histology of the female reproductive organs. Ideal for students, educators, and anyone interested in medical science, this lecture provides clear explanations, detailed diagrams, and valuable insights into female reproductive system. Enhance your knowledge and understanding of this essential aspect of human biology.
CLEAR ALIGNER THERAPY IN ORTHODONTICS .pptx

Dr. ZANAB FARHEEN FAYAZ ,MDS(ORTHODONTICS & DENTOFACIAL ORTHOPEDICS ).
Travel Clinic Cardiff: Health Advice for International Travelers

Travel Clinic Cardiff offers comprehensive travel health services, including vaccinations, travel advice, and preventive care for international travelers. Our expert team ensures you are well-prepared and protected for your journey, providing personalized consultations tailored to your destination. Conveniently located in Cardiff, we help you travel with confidence and peace of mind. Visit us: www.nxhealthcare.co.uk
Promoting Wellbeing - Applied Social Psychology - Psychology SuperNotes

A proprietary approach developed by bringing together the best of learning theories from Psychology, design principles from the world of visualization, and pedagogical methods from over a decade of training experience, that enables you to: Learn better, faster!
Artificial Intelligence Symposium (THAIS)

Artificial Intelligence Symposium (THAIS). Parc Taulí. Sabadell
Medical Quiz ( Online Quiz for API Meet 2024 ).pdf

This quiz was conducted as a promotional event for the 2024 Annual Meet of Kerala Chapter of API.
More than 20 participants took part everyday !
REGULATION FOR COMBINATION PRODUCTS AND MEDICAL DEVICES.pptx

It includes regulation of combination products and medical devices. FDA and industry liaisons.
Adhd Medication Shortage Uk - trinexpharmacy.com

The UK is currently facing a Adhd Medication Shortage Uk, which has left many patients and their families grappling with uncertainty and frustration. ADHD, or Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, is a chronic condition that requires consistent medication to manage effectively. This shortage has highlighted the critical role these medications play in the daily lives of those affected by ADHD. Contact : +1 (747) 209 – 3649 E-mail : sales@trinexpharmacy.com
DECLARATION OF HELSINKI - History and principles

This SlideShare presentation provides a comprehensive overview of the Declaration of Helsinki, a foundational document outlining ethical guidelines for conducting medical research involving human subjects.
Osteoporosis - Definition , Evaluation and Management .pdf

Osteoporosis is an increasing cause of morbidity among the elderly.
In this document , a brief outline of osteoporosis is given , including the risk factors of osteoporosis fractures , the indications for testing bone mineral density and the management of osteoporosis
How to choose the best dermatologists in Indore.

The skin is the largest organ and its health plays a vital role among the other sense organs. The skin concerns like acne breakout, psoriasis, or anything similar along the lines, finding a qualified and experienced dermatologist becomes paramount.
Does Over-Masturbation Contribute to Chronic Prostatitis.pptx

In some case, your chronic prostatitis may be related to over-masturbation. Generally, natural medicine Diuretic and Anti-inflammatory Pill can help mee get a cure.
Recently uploaded (20)
Cell Therapy Expansion and Challenges in Autoimmune Disease

Cell Therapy Expansion and Challenges in Autoimmune Disease
The Nervous and Chemical Regulation of Respiration

The Nervous and Chemical Regulation of Respiration
Travel Clinic Cardiff: Health Advice for International Travelers

Travel Clinic Cardiff: Health Advice for International Travelers
Promoting Wellbeing - Applied Social Psychology - Psychology SuperNotes

Promoting Wellbeing - Applied Social Psychology - Psychology SuperNotes
CHEMOTHERAPY_RDP_CHAPTER 6_Anti Malarial Drugs.pdf

CHEMOTHERAPY_RDP_CHAPTER 6_Anti Malarial Drugs.pdf
Medical Quiz ( Online Quiz for API Meet 2024 ).pdf

Medical Quiz ( Online Quiz for API Meet 2024 ).pdf
REGULATION FOR COMBINATION PRODUCTS AND MEDICAL DEVICES.pptx

REGULATION FOR COMBINATION PRODUCTS AND MEDICAL DEVICES.pptx
Osteoporosis - Definition , Evaluation and Management .pdf

Osteoporosis - Definition , Evaluation and Management .pdf
Does Over-Masturbation Contribute to Chronic Prostatitis.pptx

Does Over-Masturbation Contribute to Chronic Prostatitis.pptx
ABG.pptx
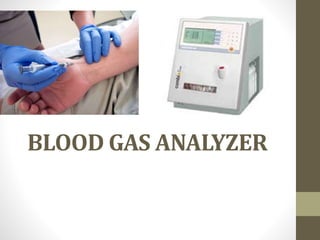
- 2. • Clinical management of respiratory and metabolic disorders often depends on rapid accurate measurements of oxygen and carbon-dioxide in blood. • Determination of blood gases also plays an important role in detection of acid-base balance and monitoring the effect of therapy. • Modern instruments for blood gas determinations are simple to operate and are quite reliable and rapid.
- 3. The blood gas analyzer is designed to quantitatively determine 125 µL of blood sample for- • pH, • PCO2, • PO2 by means of electrode and a potentiometer.
- 4. On the basis of these, it can calculate other parameters like • bicarbonate (HCO3 -), • actual base excess, • total CO2, • oxygen saturation and • total oxygen content (ctO2) in the blood.
- 5. Specimens: • Arterial or venous whole blood specimens are obtained following all universal precautions for infection control and collected anaerobically with heparin anticoagulant (1mg/ml) in sterile syringes. • Arterial puncture carries a slight medical risk and should be performed by a trained medical personnel only. • No tourniquet is used and no pull applied to the plunger of syringe as arterial blood pressure pushes blood into the syringe.
- 6. Analysis of pH: • pH measuring system comprises of a glass electrode, a reference electrode and a liquid junction between the two electrodes. • Reference electrodes are usually Ag/AgCl electrode and calomel electrode. • Potential of glass electrode varies with changes in the pH. H+ in the blood sample will exchange with metallic ions in the glass membrane of the glass electrode.
- 7. Analysis of PCO2: • PCO2 is measured by isolating a glass electrode in a weak bicarbonate buffer and separating this buffer from the blood sample by a membrane permeable to CO2 in the specimen. • The CO2 diffuses into a bicarbonate buffer solution inside the electrode and the following reaction occurs: CO2 + H2O ↔ H2CO3 ↔ H+ + HCO3 -
- 8. • The change in H+ concentration in the buffer is then measured inside the PCO2 electrode by same type of components found in pH electrode.
- 9. Analysis of PO2: • Measurement of PO2 relies on the electrochemical measurement of O2 that diffuses across a gas permeable membrane into an electrolyte that is within a Clark electrode, which comprises of a silver anode and a platinum cathode immersed in an electrolyte buffer. • The buffer solution consists of KCl and phosphate buffer, or buffered KOH in water.
- 10. • Oxygen is reduced at platinum cathode as follows: O2 + 2H+ + 4e- ---- H2O2 + 2e- ------- 2OH- • The reduction of oxygen at cathode results in the flow of current between cathode and anode. The amount of current flow is measured and related to amount of O2 in the sample.
- 11. Directly measured parameters: • AIR PRESSURE: The current air pressure is measured continuously by an integrated air pressure sensor. The value of PCO2 and PO2 are dependent on the current air pressure. • PARTIAL PRESSURE OF OXYGEN (PO2) AND CARBONDIOXIDE (PCO2): These are measured with help of sensors and expressed as mmHg/ kPa.
- 12. • pH: It is expressed within a range above and below which >>>> or <<<< appears. • ELECTROLYTES: K+, Na+, Ca++, Li+ and Cl- can be measured. • HEMOGLOBIN: The instrument may also measures patient’s hemoglobin.
- 13. Calculated parameters: • ACTUAL BICARBONATE (HCO3 -): This is important in diagnosis of metabolic acid-base imbalance and is influenced by lung function also. • It is calculated using Henderson- Hasselbach equation. cHCO3 - pH = pk’ + Log ------------ α X PCO2 where α is solubility coefficient for CO2 and its value for plasma at 37oC is 0.0306 mmol/L /mmHg.
- 14. • STANDARD BICARBONATE (HCO3 -): It is a measure of bicarbonate concentration in plasma at a pCO2 of 40 mm Hg, a temperature of 37oC and complete oxygen saturation of Hb. • BASE EXCESS (BE): It is defined as the concentration of titratable base when titrating the plasma with strong acid or base to pH 7.4 at pCO2 40 mmHg at 37o C.
- 15. • TOTAL CARBONDIOXIDE (tCO2): Total CO2 is that liberated from dissolved CO2 and bicarbonate present in plasma when blood is drawn anaerobically. • OXYGEN SATURATION OF HEMOGLOBIN (O2 Sat): It shows the percentage of possible bonding points of the hemoglobin which are occupied by oxygen. O2 Sat is independent of Hb concentration.
- 16. • TOTAL OXYGEN CONCENTRATION (ctO2): It is the sum of physically dissolved and chemically bonded oxygen and is mainly determined by PO2 and Hb. • BUFFER BASES (BB):It shows the sum of all buffer’s anion concentration in blood (Hb, HCO3 -, proteins, phosphates).
- 17. • P50 (SEMISATURATION PRESSURE): The semisaturation pressure P50 shows the PO2 at which Hb is 50% loaded with O2. • ALVEOLAR- ARTERIAL OXYGEN PRESSURE DIFFERENCE (AaDO2): It is defined as the difference of oxygen content between alveolar air and the arterial blood (measured PO2). • HEMATOCRIT: It is defined as the percentage of red blood cells to the total blood volume.
- 18. Procedure: After ensuring that the sample is not coagulated, expel a drop of blood on tissue paper and inject the sample into the instrument and wait for the results.
- 20. Precautions: • Sample should not be coagulated as clots can harm the instrument. • Take readings as early as possible after taking the sample. • Blood sample preferably should be arterial.
- 21. • Blood should not be exposed to air. The needle should be bent after sample collection or a rubber cock can be used for this purpose. • In hypothermia, a correction can be made for low body temperature. The measurements are made at 37o C. ToC = pH at 37oC + 0.014 ( 37- T) where T is the actual body temperature
- 22. Reference values: PH = 7.35 – 7.45 PCO2 = 35 – 48 mm Hg / 4.66 – 6.38 kPa in males 32 – 45 mm Hg / 4.26 – 5.99 kPa in females HCO3 - = 22 – 26 mmol/L PO2 = 83 – 108 mmHg / 11.1 – 14.4 kPa tCO2 = 22 – 28 mmol/L O2 sat = 95 – 98% BE = (-2) to (+3) mmol/L
- 23. •Types of possible acid base disturbances:
- 24. 1. Metabolic acidosis: It is primarily due to decrease in HCO3 - which is either due to increased production or decreased removal of acids. Common causes are: • Diabetic ketoacidosis • Mild ketoacidosis • Lacticacidosis • Chronic renal failure and renal tubular acidosis type I
- 25. • Ingestion of NH4Cl produces acidosis since NH3 gets converted to urea liberating H+ which neutralize HCO3 - • Severe diarrhoea, intestinal/ biliary/pancreatic fistula and renal tubular acidosis Type II due to direct loss of bicarbonates.
- 26. 2. Respiratory acidosis: • It is due to increased PCO2 when there is impaired excretion of CO2 from lungs and rebreathing air containing CO2. Common causes are: • Chronic lung diseases that may be primary or secondary to some heart disease. Common causes are chronic bronchitis, pulmonary fibrosis or acute bronchial asthma.
- 27. Metabolic Alkalosis: • It is due to primary increase in plasma bicarbonate due to accumulation of base or loss of acid other than carbonic acid. Causes are: • excessive dose of NaHCO3 in treatment of metabolic acidosis • massive blood transfusion with blood containing sodium citrate
- 28. 4. Respiratory alkalosis: • The primary decrease in pCO2 is due to excessive ventilation. Common causes are: • encephalitis • hysterical attacks • physiologically at high altitude
- 29. Some imp. Terms: Terms Definition pH Negative logarithm of hydrogen ion. Normal value-7.38-7.42 Acids Proton donors. pH <7 Bases Proton acceptors. pH>7 Strong acid Acid which ionize completely. Eg HCl Weak acid Acid which ionize incompletely. Eg H2CO3 pK value pH at which acid is half ionized. Salt : acid=1:1 Alkali reserve HCO3 - available to neutralize acids. Normal range- 22-26 mmol/L Buffers Solutions which minimize changes in pH
- 31. •Thank You