The document provides guidance on interpreting arterial blood gas (ABG) results. It discusses the following key steps:
1. Evaluating oxygenation levels and determining if hypoxia is present.
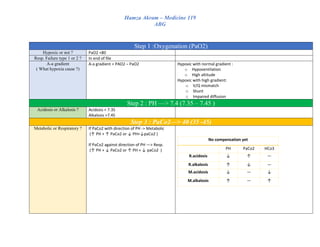
2. Analyzing pH levels to identify acidosis or alkalosis.
3. Examining PaCO2 levels to determine if an acid-base imbalance is respiratory or metabolic in nature.
4. Calculating anion gap and osmolar gap to classify metabolic acidosis as high anion gap or normal anion gap, and identify the potential causes.
5. Assessing for the presence of compensation mechanisms, the degree of compensation, and whether an acid-base disturbance is simple or
![Hamza Akram – Medicine 119
ABG
Step 4 : compensated or not? Partially or fully ? Simple or mixed ?
Resp. Acidosis
[PH ↓+ PaCo2. ↑]
Compensation (Renal)
✓ Increase HCo3 reap.
✓ Increase H excretion
✓ Hyperventilation (increase Co2 out )
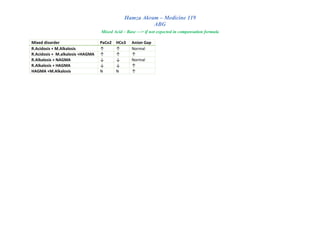
Disorder PH PaCo2 HCo3
Partial compensation
R.acidosis ↓ ↑ ↑
R.alkalosis ↑ ↓ ↓
M.acidosis ↓ ↓ ↓
M.alkalosis ↑ ↑ ↑
Full compensation
R.acidosis Inside limit but <7.4 ↑ ↑
R.alkalosis Inside limit but >7.4 ↓ ↓
M.acidosis Inside limit but <7.4 ↓ ↓
M.alkalosis Inside limit but >7.4 ↑ ↑
Resp. Alkalosis
[PH↑ + PaCo2 ↓
Compensation (renal)
✓ Decrease HCo3 reap.
✓ Decrease H excretion
✓ Hypoventilation (decrease Co2 out )
Metabolic. Acidosis
[PH ↓ + HCo3↓]
Compensation (pulmonary)
✓ Hyperventilation (increase Co2 out )
Metabolic. Alkalosis
[PH ↑+ HCo3↑]
Compensation (pulmonary)
✓ Hypoventilation (decrease Co2 out )
Simple or mixed ? According to Expected compensation?
If not expected —> Mixed Acid Base balance
If expected —> compensated
Partial or full compensation? According to PH
Partial —> PH out of limit (7.35-7.45)
Full—> PH inside limit but still in border
Step 5 : HAGMA OR NAGMA (just if M.acidosis)
Calculate anionic Gab AG = Na – (Cl + HCo3)
Normal = 12 ± 2
Normal AG M.acidosis (NAGMA)
• Renal loss of HCo3
o RTA 1 (MM , cystinosis , Wilson disease.)
o RTA 2 (SLE, Sjögren syndrome , amphotericin B.)
o Carbonic anhydrase inhibition (acetazolamide)
• GI loss of HCo3
o Diarrhea
o Pancreatic or small bowel fistula
o Ureterosigmoidostomy
To differentiate B/W renal & GI loss —> Urine AG = Na + K – Cl
➔ +ve U.AG —> Renal loss
➔ -ve U.AG —> GI loss
Don’t forget that
Albumin Affect Anion
Gab even if no Acid
base imbalance
Decrease serum Albumin —> Reduce AG
Corrected AG = Observed AG + 2.5 (4.5 – measured Albumin )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/abg-221229163602-b4b7a165/85/ABG-pdf-3-320.jpg)
![Hamza Akram – Medicine 119
ABG
High AG M.acidosis (HAGMA) – MUDPILES
o M: Methanol, Metformin
o U: Uremia (chronic kidney failure)
o D: Diabetic ketoacidosis
o P: Paracetamol, Propylene glycol
o I: Infection, Iron, Isoniazid Inborn errors of metabolism
o L:Lactic acidosis
o E: Ethylene glycol
o S: Salicylates (ASA)
Calculate Osmolar Gab ✓ OG =measured osmolality − calculated
osmolality
✓ Normal OG <10
✓ calculated osmolality = 2 x [Na mmol/L] +
[glucose mg/dL] / 18 + [BUN mg/dL] / 2.8
If HAGMA with high OG ( >10) —> presence of osmotically active particles
o mannitol,methanol, ethylene glycol, sorbitol, polyethylene glycol
o propylene glycol (IV lorazepam, diazepam and phenytoin)
o glycine (TURP syndrome), maltose
Step 6 : Mixed MA or pure
Calculate Delta Gab Delta ration = (AG measured - AG normal) /
(HCO3 normal - HCO3 measured)
Normal HCo3 = 24
Normal AG = 12
Normal delta = 0.8-2
✓ High delta (>2)—> HAGMA + M.alkalosis
✓ NORMAL Delta (0.8-2) —> pure HAGMA
✓ Low delta —> HAGMA + NAGMA
o <0.4: Hyperchloremic NAGMA
o 0.4-.08: HAGMA with NAGMA
Step7 : U.Cl & volume responsive & HTN ( just if M.Alkalosis)
1. U.Cl.?
2. Volume responsive or
not ?
3. HTN?
Volume unresponsive( High U.Cl)
• HTN present
o Hyperaldosterone
• HTN absence
o Bartter & Gitelman syndromes
Volume responsive (Low U.Cl)
• Vomiting , NG suction
• Prior diuretic use](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/abg-221229163602-b4b7a165/85/ABG-pdf-4-320.jpg)
![Hamza Akram – Medicine 119
ABG
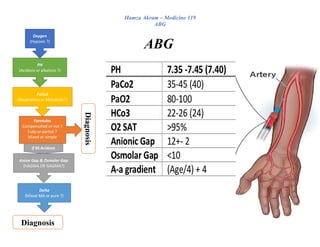
A-a gradient = PAO2 -PaO2
Normal A-a gradient = (age/4) + 4
PaO2 From ABG
PAO2 FiO2 × [Pi–PH2O] – [PaCO2/RQ]
✓ FiO2: fraction of inspired O2 (=0.21 in room air)
✓ Pi: total pressure of inspired air ( = 760 mmHg at sea level )
✓ PH2O: partial pressure of H2O (vapor pressure) in alveoli ( = 47mmHg)
✓ PaCo2 : from ABG
✓ RQ: respiratory quotient ( = 0.8 )
If tell u in question that in room air & sea level —> A-a gradient = 150 – (PaCo2/0.8)
Compensation
Compensation or not ?
Respiratory (look at HCo3 for comp) Metabolic (look at PaCo2 for comp)
Acidosis Alkalosis Acidosis Alkalosis
Acute Chronic Acute Chronic PaCO2 = 1.5× (HCO3) +8 ± 2 PaCO2 ↑ by 0.7 for each ↑ of
HCO3 by 1 mEq.
HCO3 ↑ by 1
for each 10
PCO2 above
40 mmHg
HCO3 ↑ by 3
for each 10
PCO2 above
40 mmHg
HCO3 ↓ by 2
mEq/l for
each 10
mmHg PCO2
is below 40
mmHg
HCO3 ↓ by 4
mEq/l for
each 10
mmHg PCO2
is below 40
mmHg
Must calculate Anionic Gab
Fully or partial ?
According to PH ✓ Partial —> PH out of limit (7.35-7.45)
✓ Full—> PH inside limit but still in border
According to case scenario](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/abg-221229163602-b4b7a165/85/ABG-pdf-5-320.jpg)