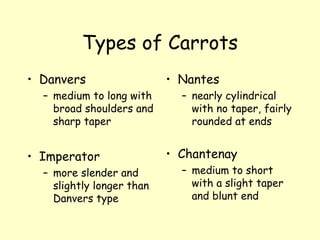
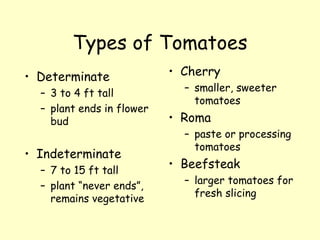
The document is an alphabetized guide to common vegetables from A to Z. Each entry provides 1-2 sentences on the plant facts, 1-2 sentences on nutritional value or culture, and may include additional details. The guide covers 26 vegetables from Asparagus to Zucchini, describing their botanical name, family, origin, folk uses, growing tips, and varieties. It aims to educate readers on the diversity of vegetables and their nutritional and cultural aspects.







































































![The A to Z of Veggies Dr. Patti Nagai Horticulture Educator UW Extension - Racine County 14200 Washington Avenue Sturtevant, WI 53177 Phone: 262-886-8460 e-mail: [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/atozveggies-1233256992657364-1/85/A-to-Z-veggies-75-320.jpg)