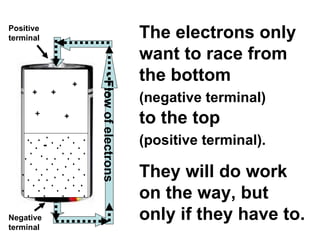
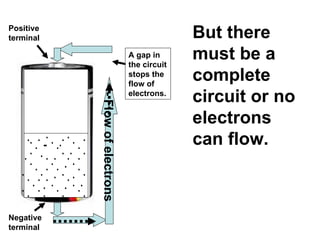
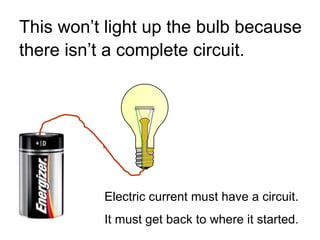
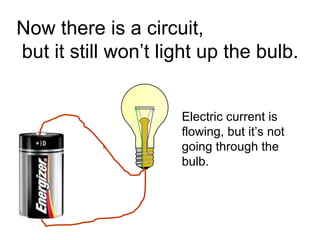
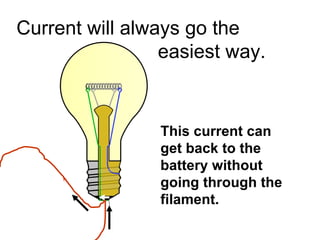
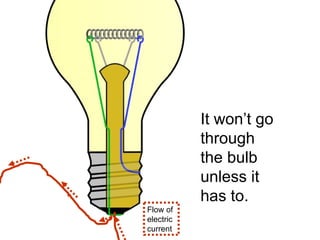
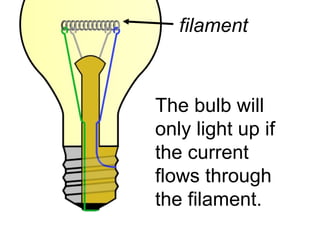
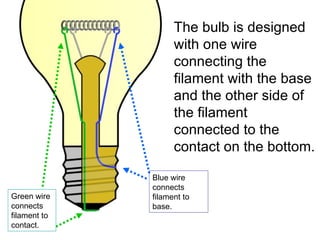
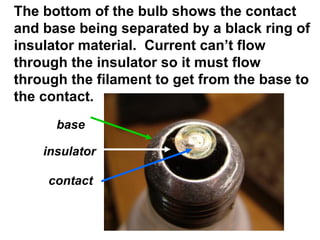
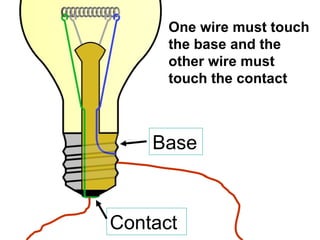
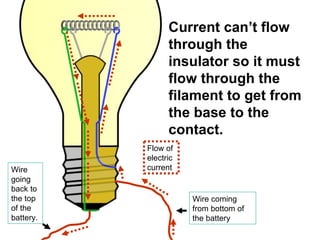
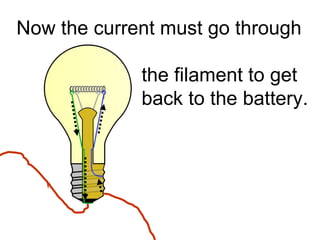
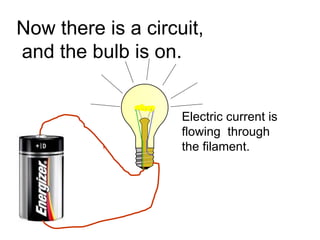
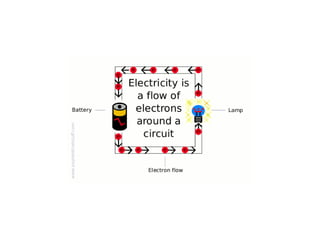
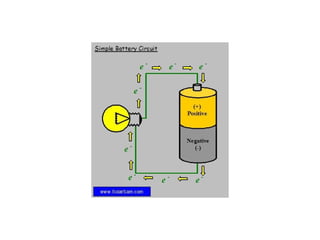
A charged battery contains electrons that want to flow from the negative to positive terminal. For a light bulb to turn on, there must be a complete circuit for the electrons to flow through. Simply connecting wires to the battery and bulb is not enough, as the electrons will take the easiest path without going through the bulb's filament. The bulb is designed so that the only way for electrons to travel from the base to the contact is by flowing through the filament, causing it to light up. When wires create a complete circuit with the battery, base, and contact, current will pass through the filament, turning on the bulb.