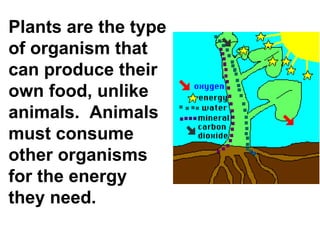
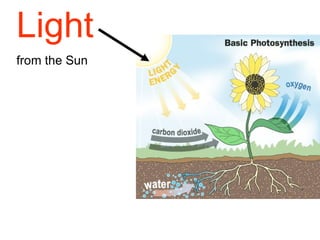
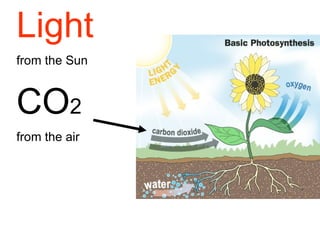
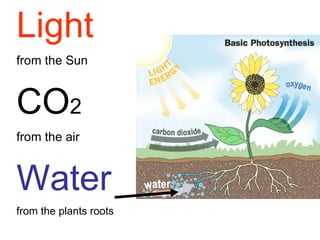
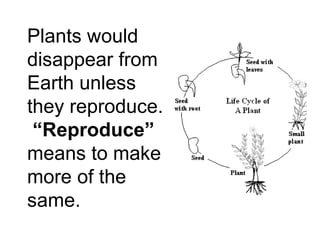
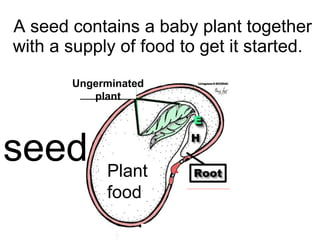
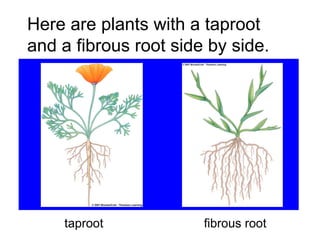
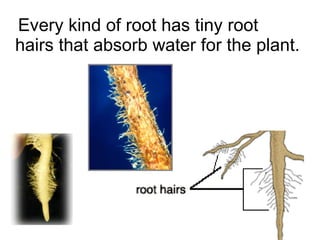
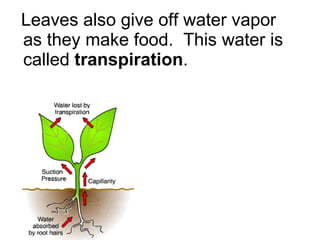
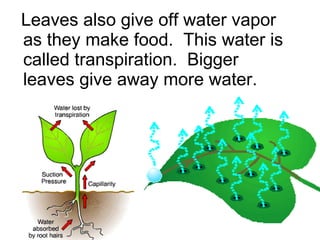
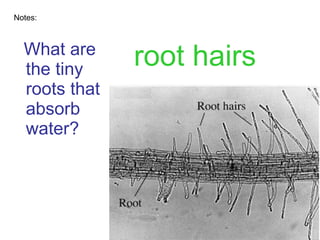
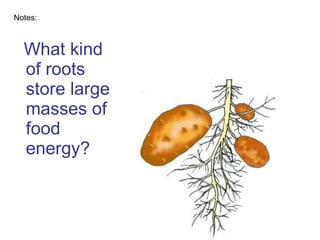
Plants are able to produce their own food through the process of photosynthesis. Photosynthesis requires light from the sun, carbon dioxide from the air, and water from the plant's roots. Most plants reproduce by making seeds, which first requires the plant to get pollen from a similar plant. Pollen can be transferred by wind or by animals like bees. Seeds contain a baby plant and food to help it grow. Plants must adapt to their environment through adaptations like leaves, roots, and other structures in order to survive.