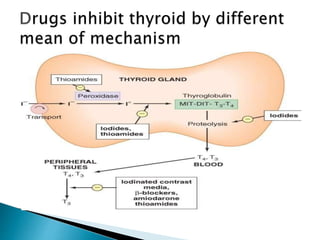
Methimazole and propylthiouracil are the major drugs used to treat thyrotoxicosis. Methimazole is more potent and can be given once daily, while propylthiouracil is dosed more frequently. Both drugs inhibit thyroid hormone production and propylthiouracil also blocks peripheral conversion of T4 to T3. Iodide salts like Lugol's solution rapidly reduce hormone synthesis and release within a week. Radioactive iodine is used to ablate the thyroid gland and provide long-term control of Graves' disease, with effects seen over months. Propranolol provides symptomatic relief by blocking sympathetic overactivity in thyrotoxicosis.