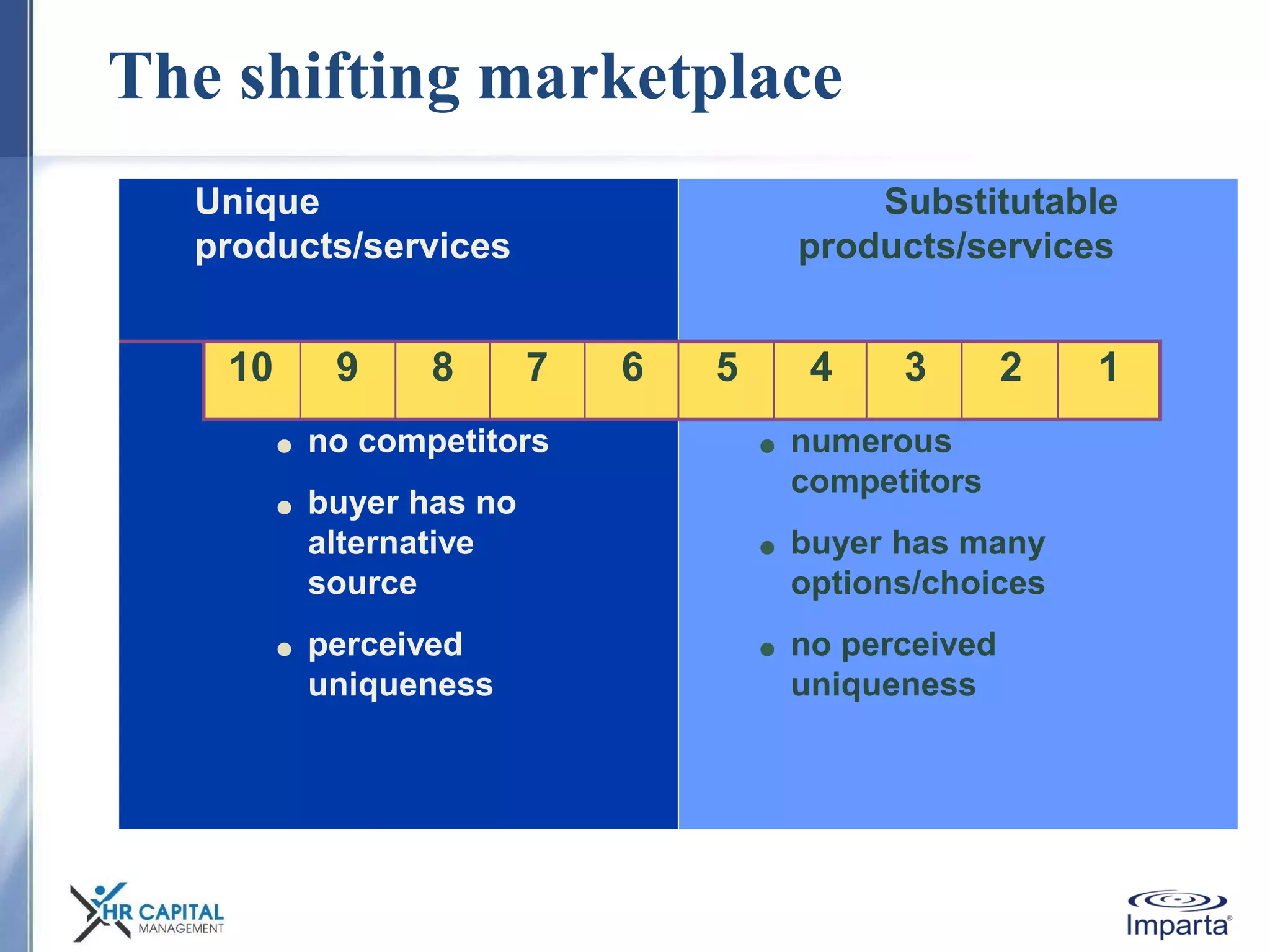
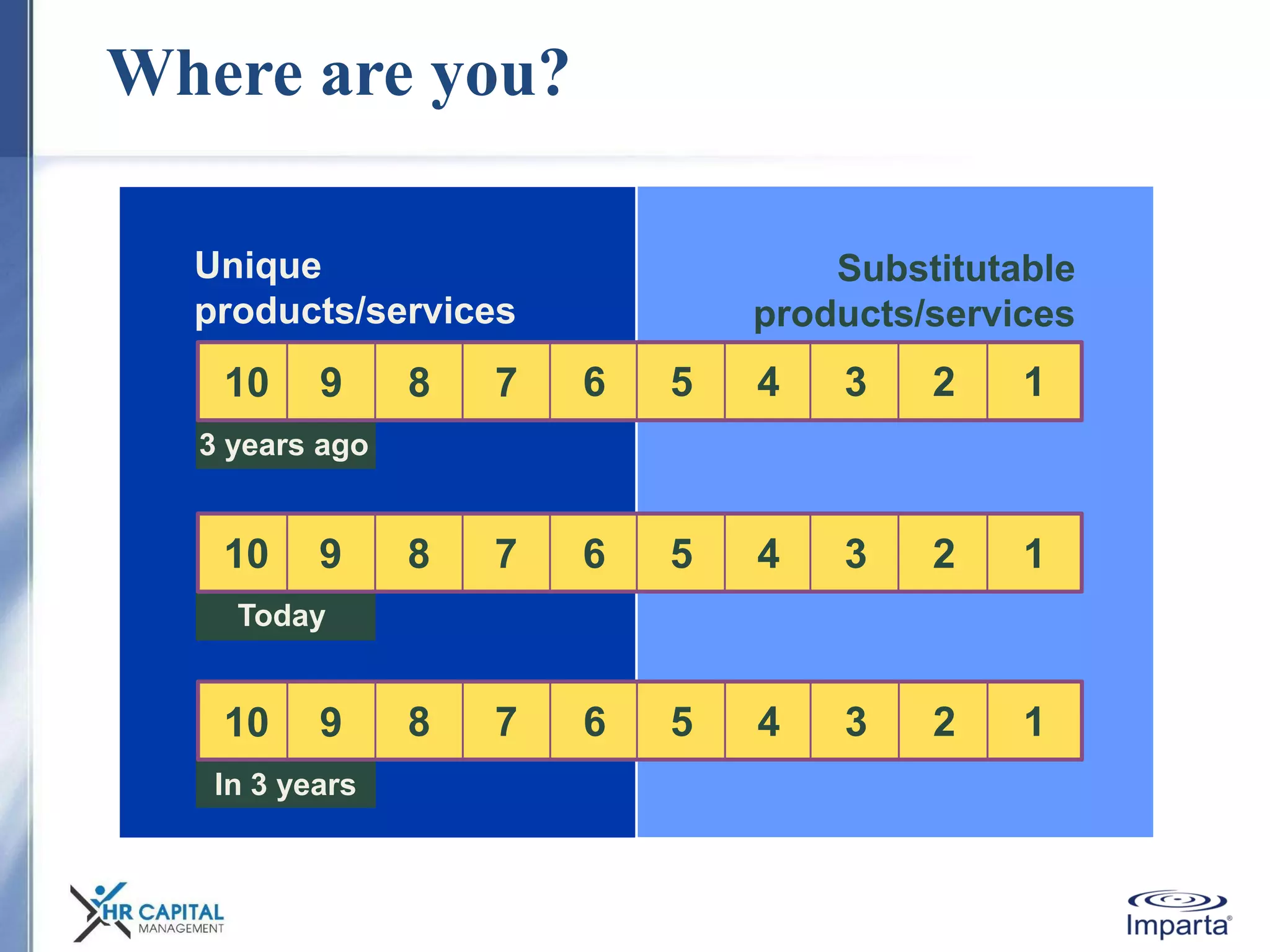
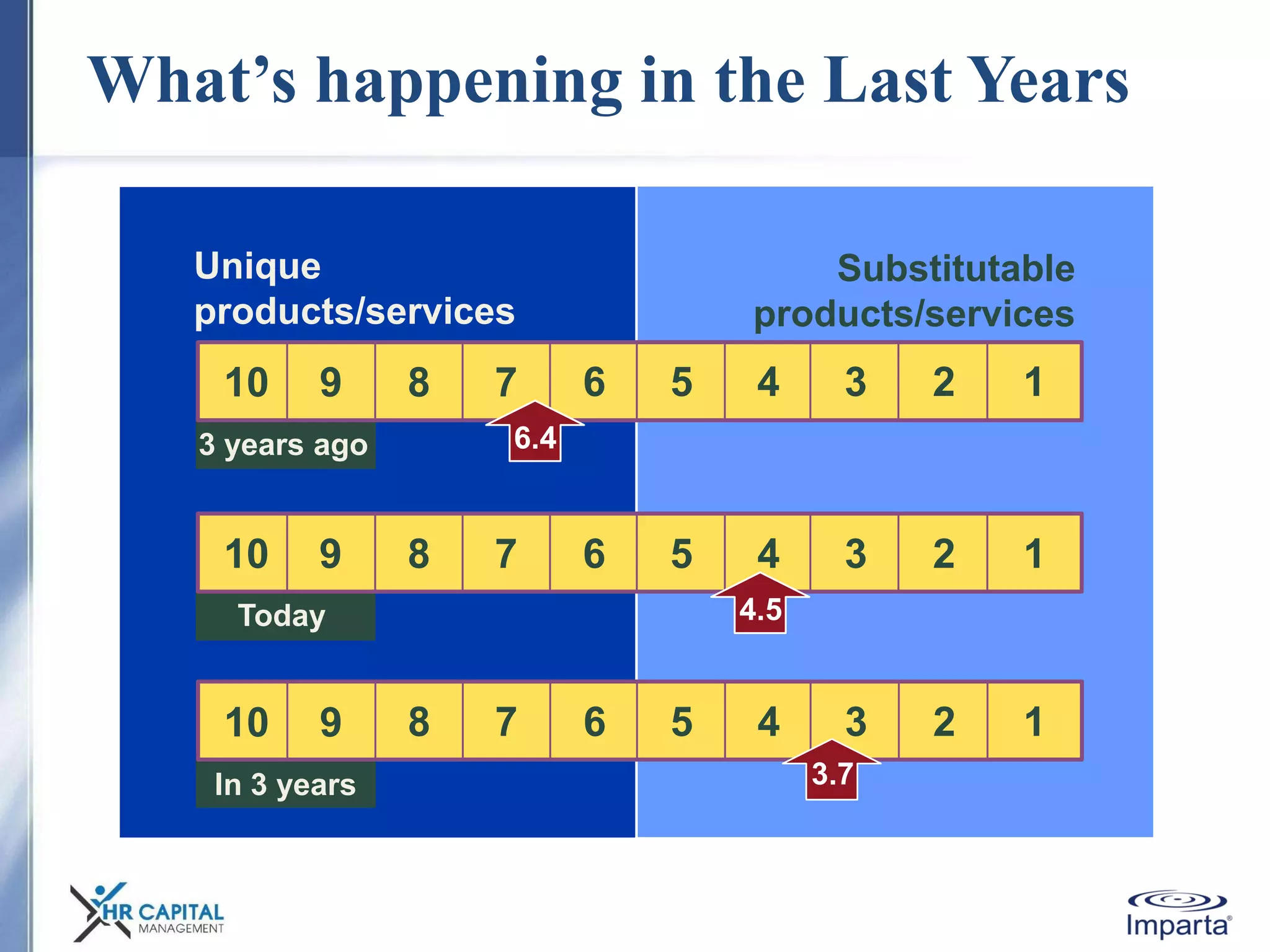
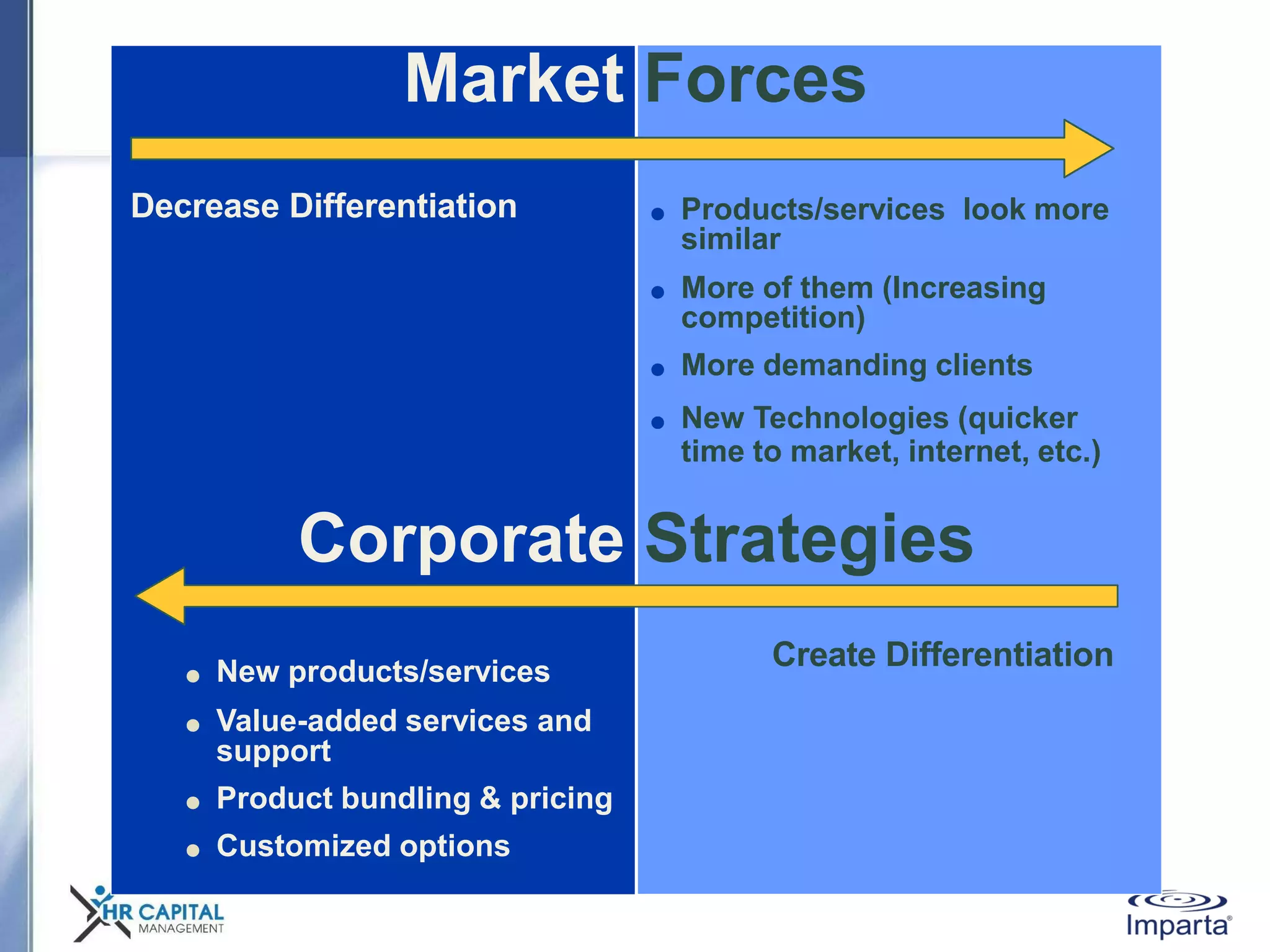
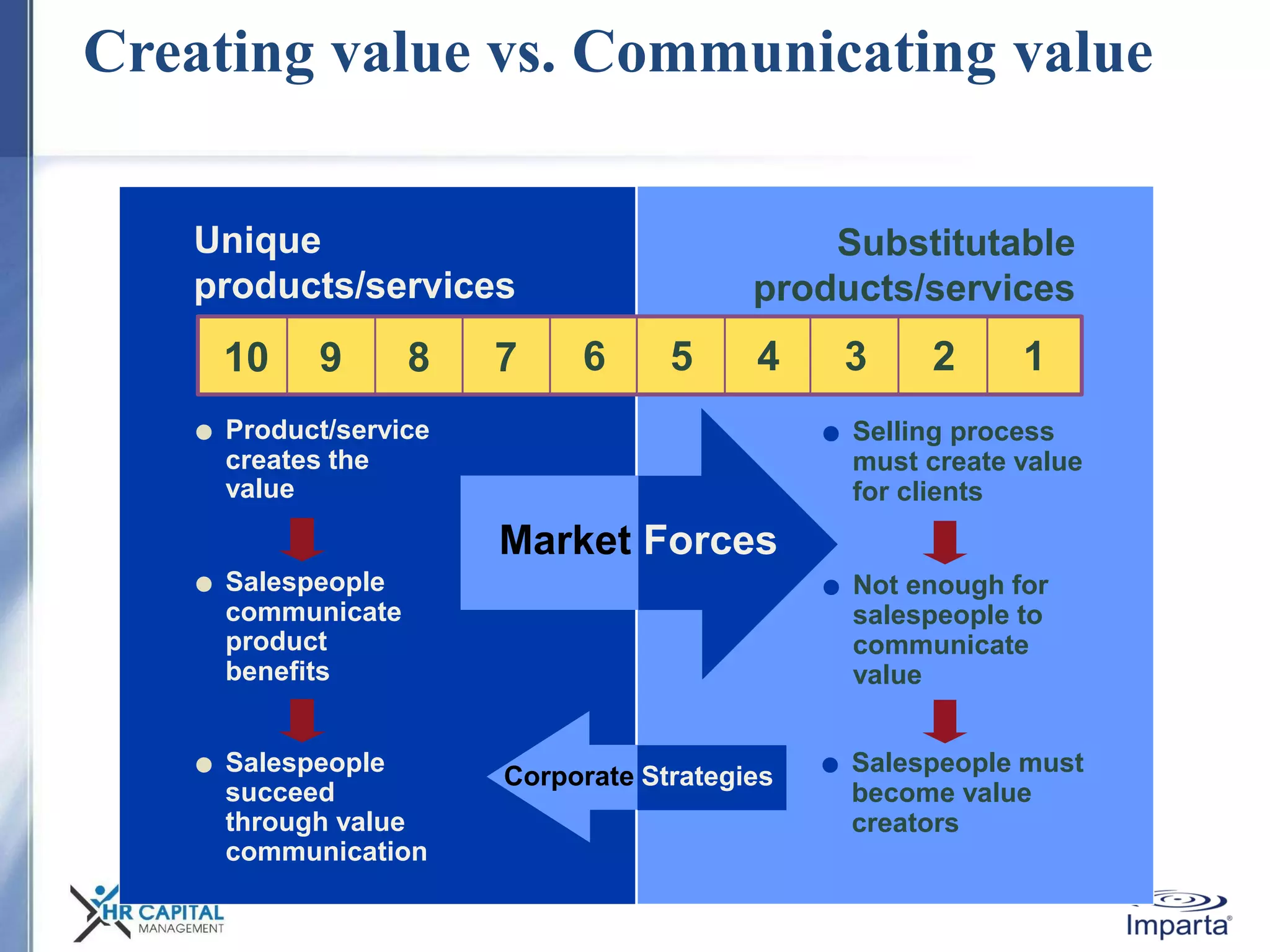
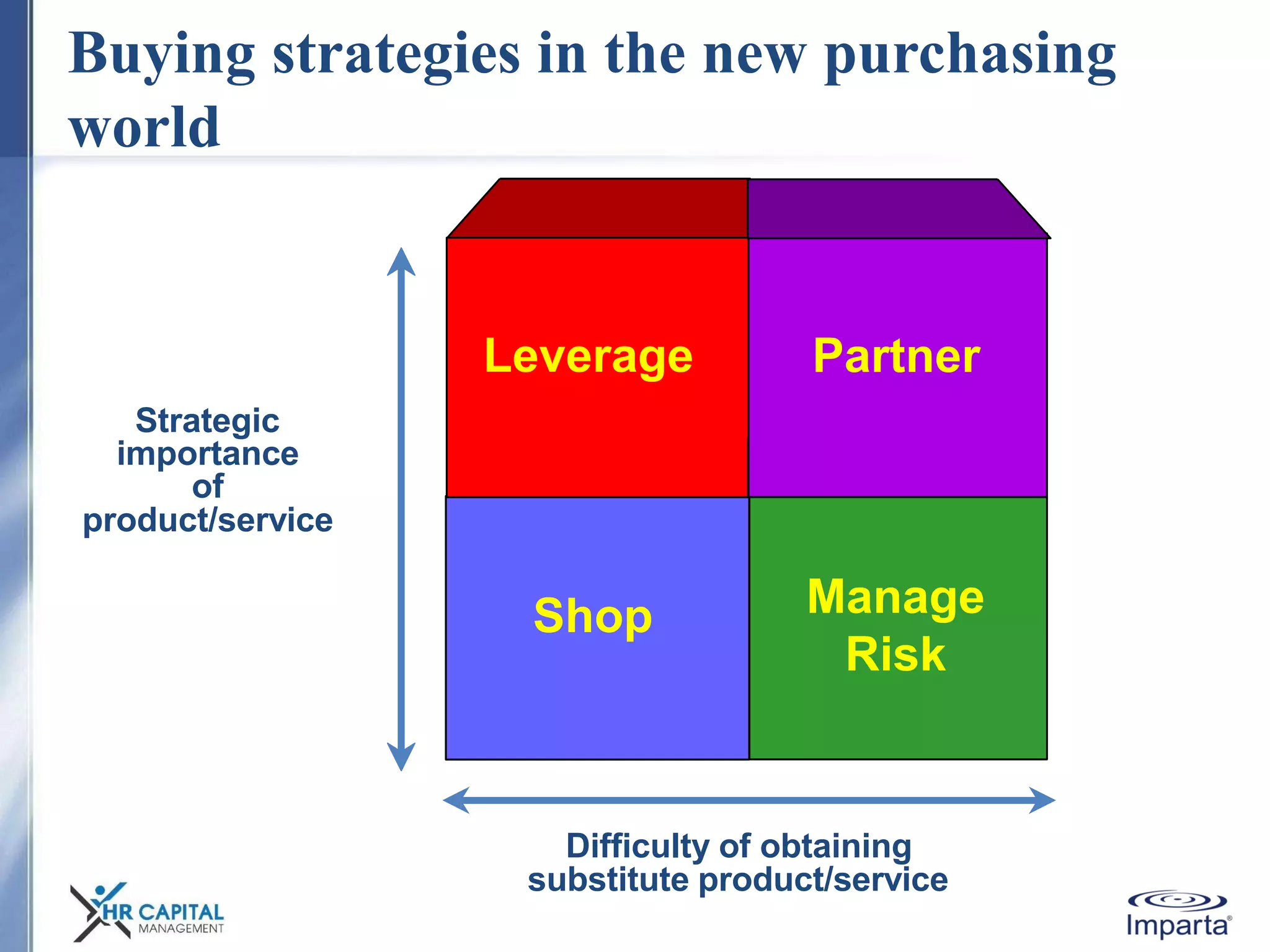
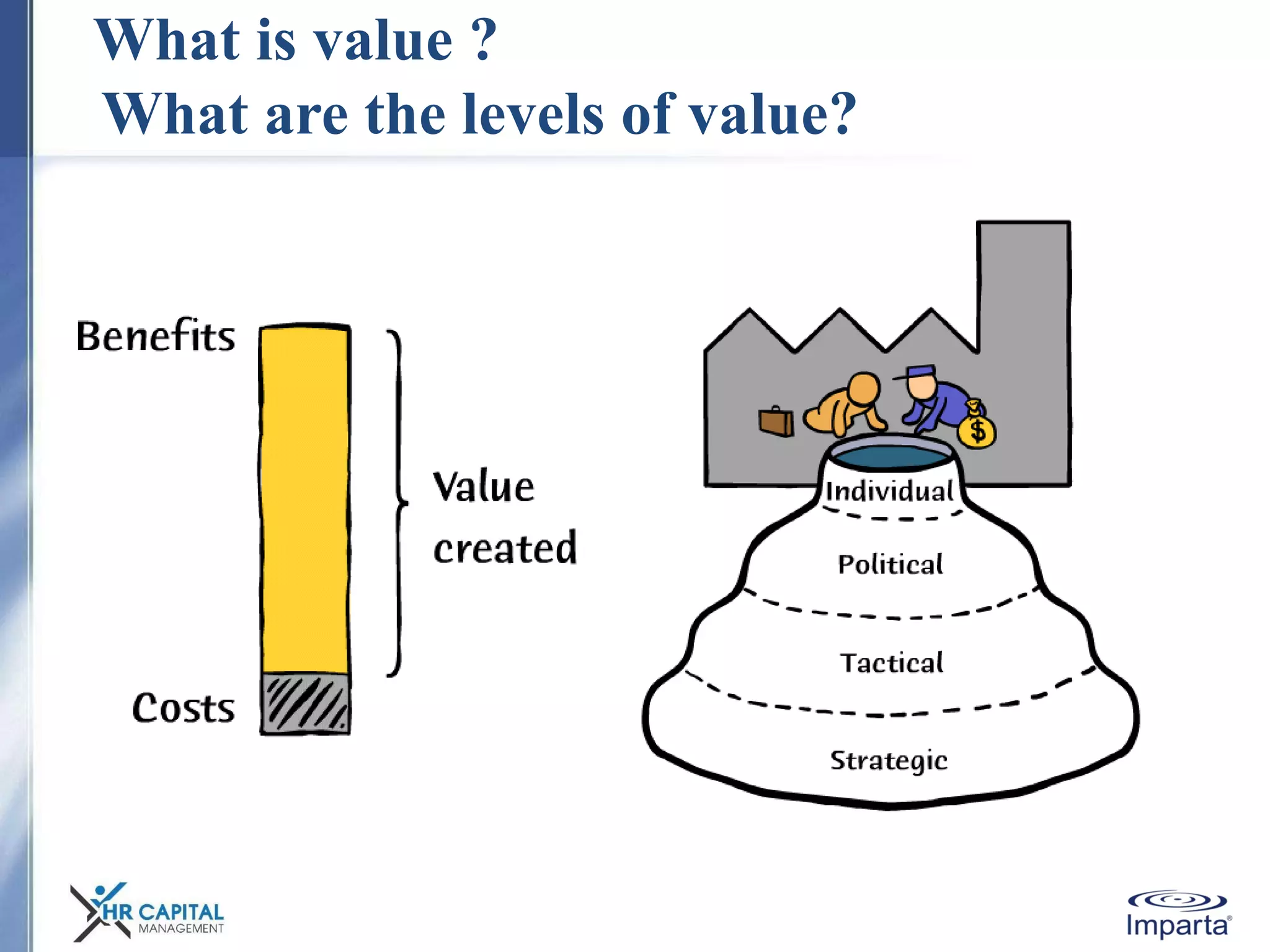
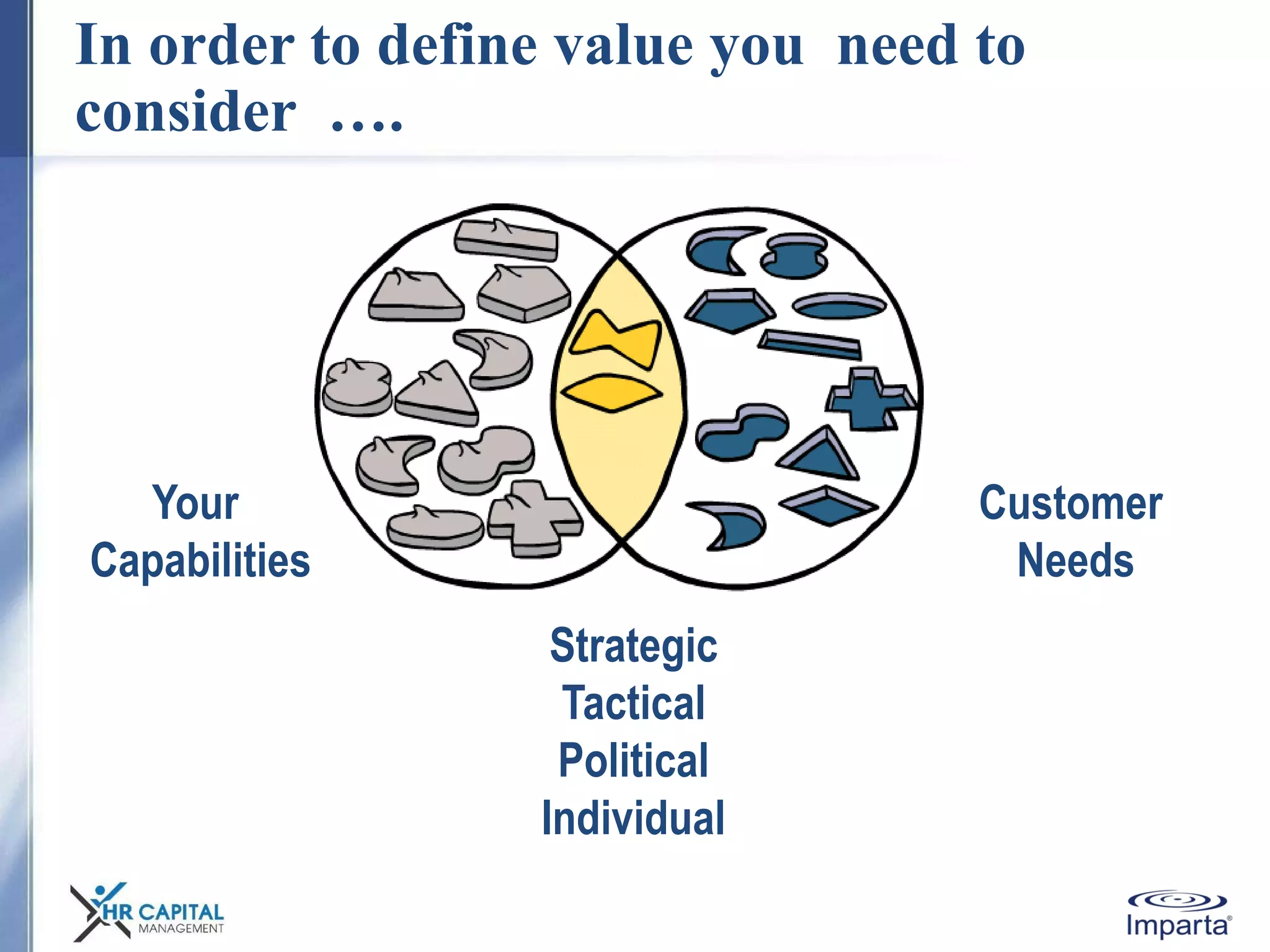
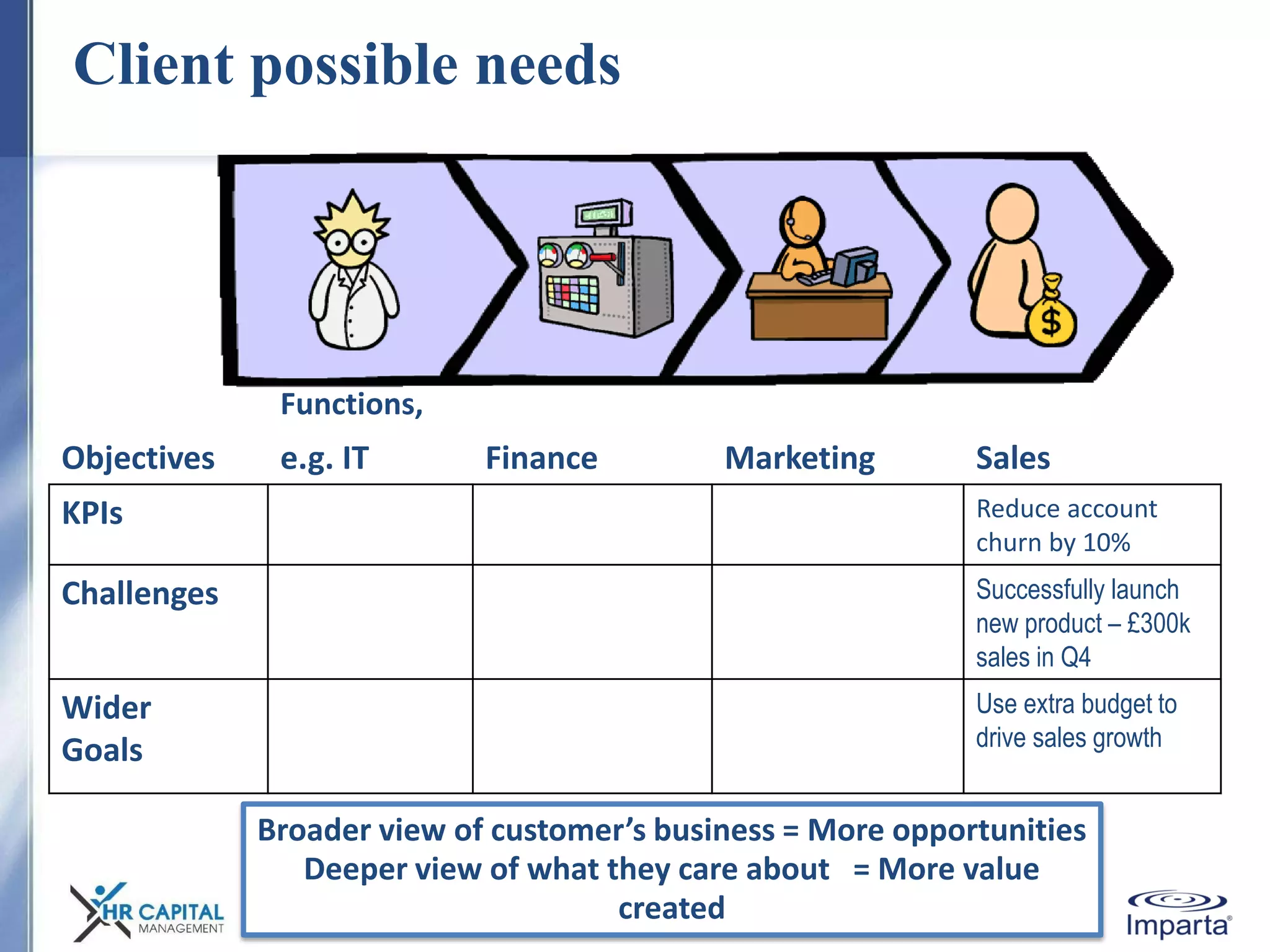
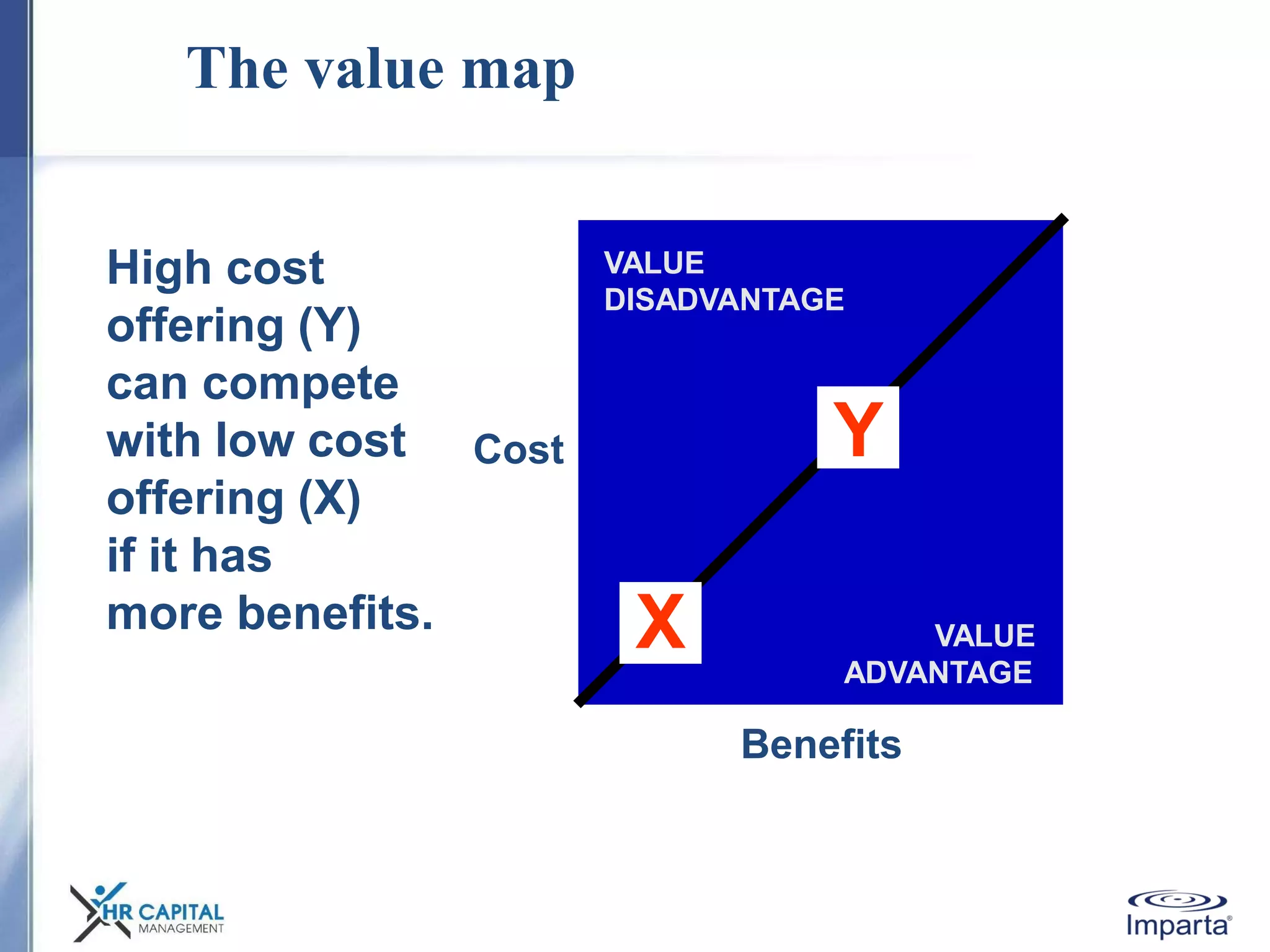
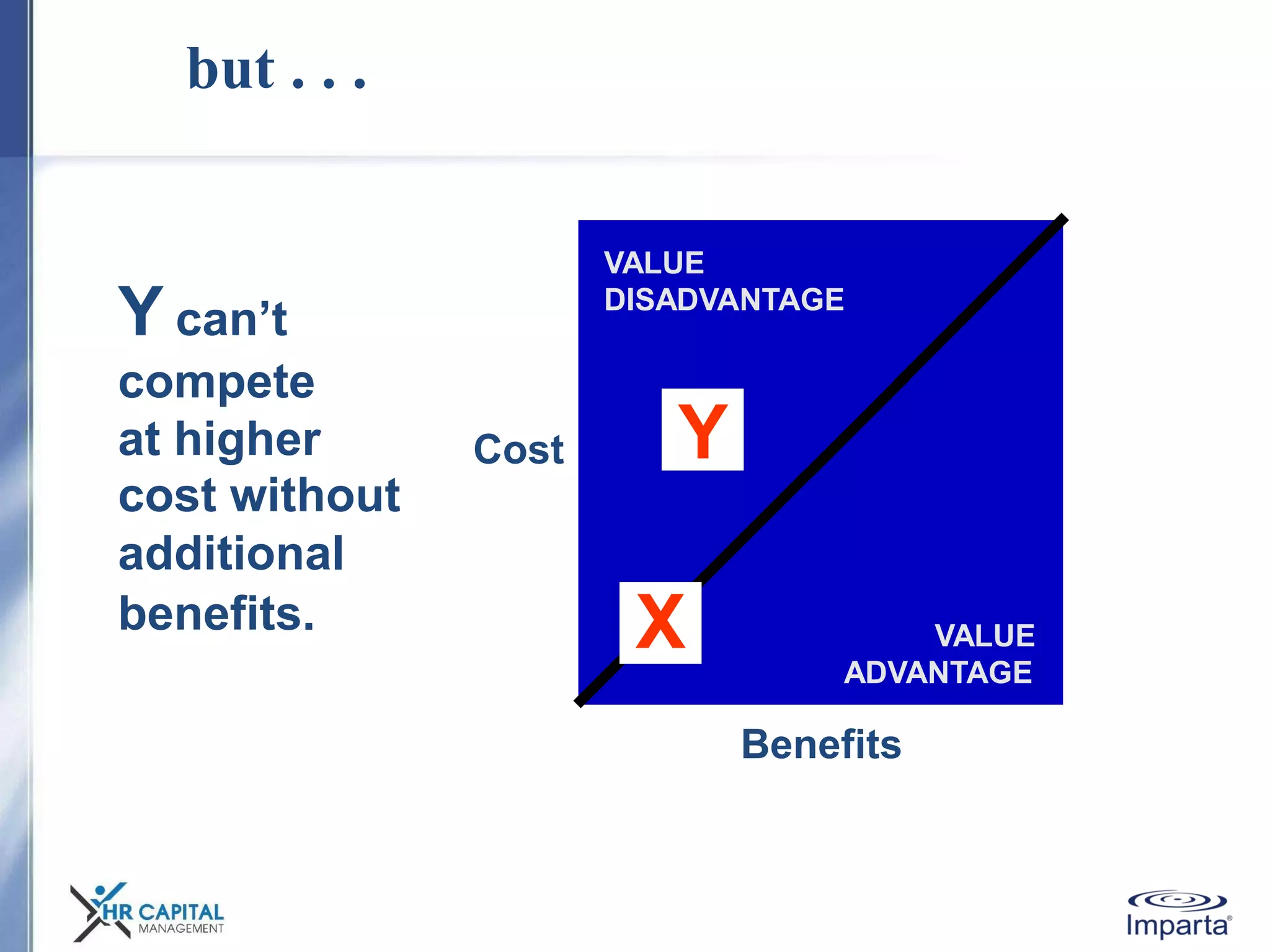
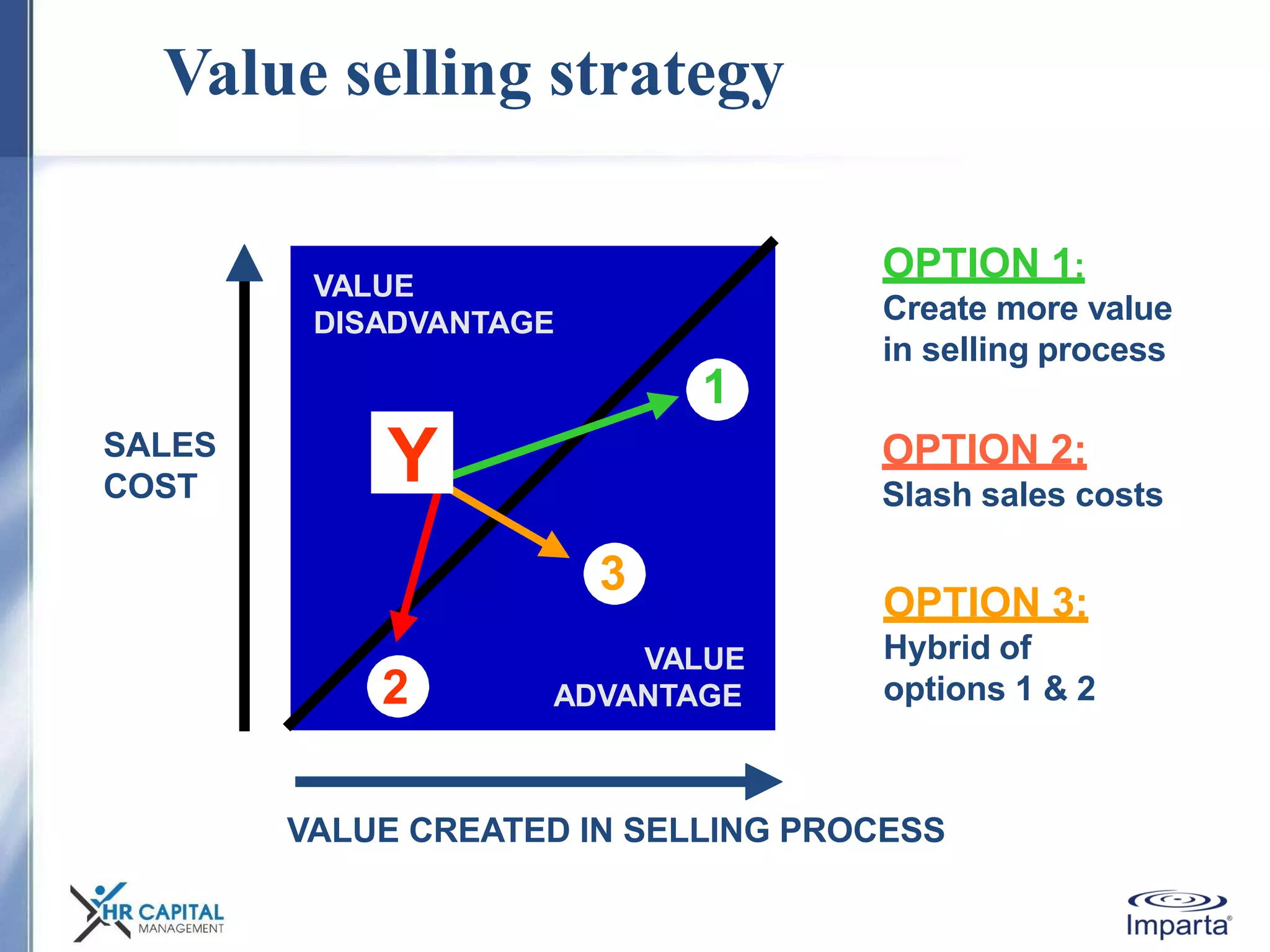
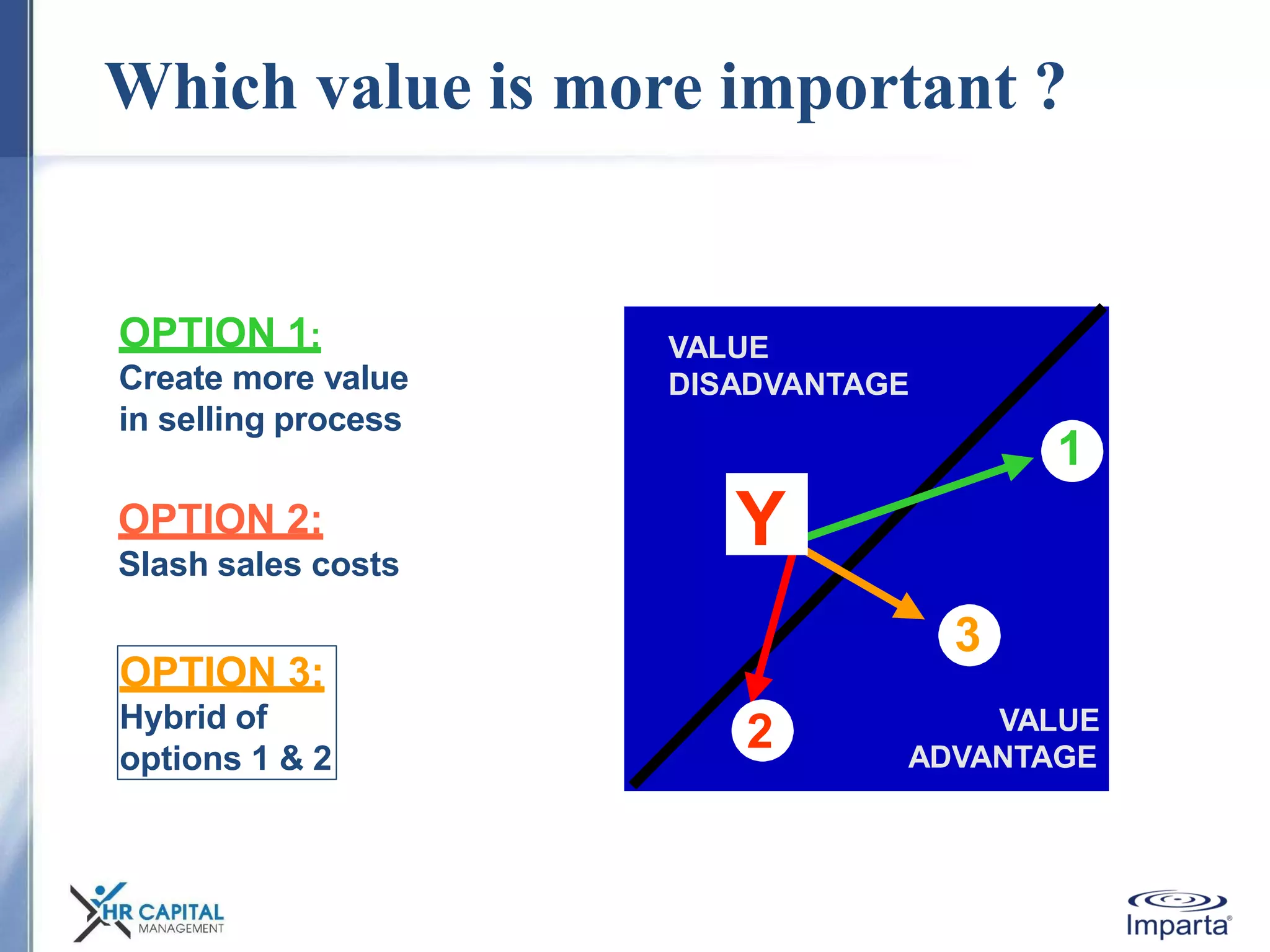
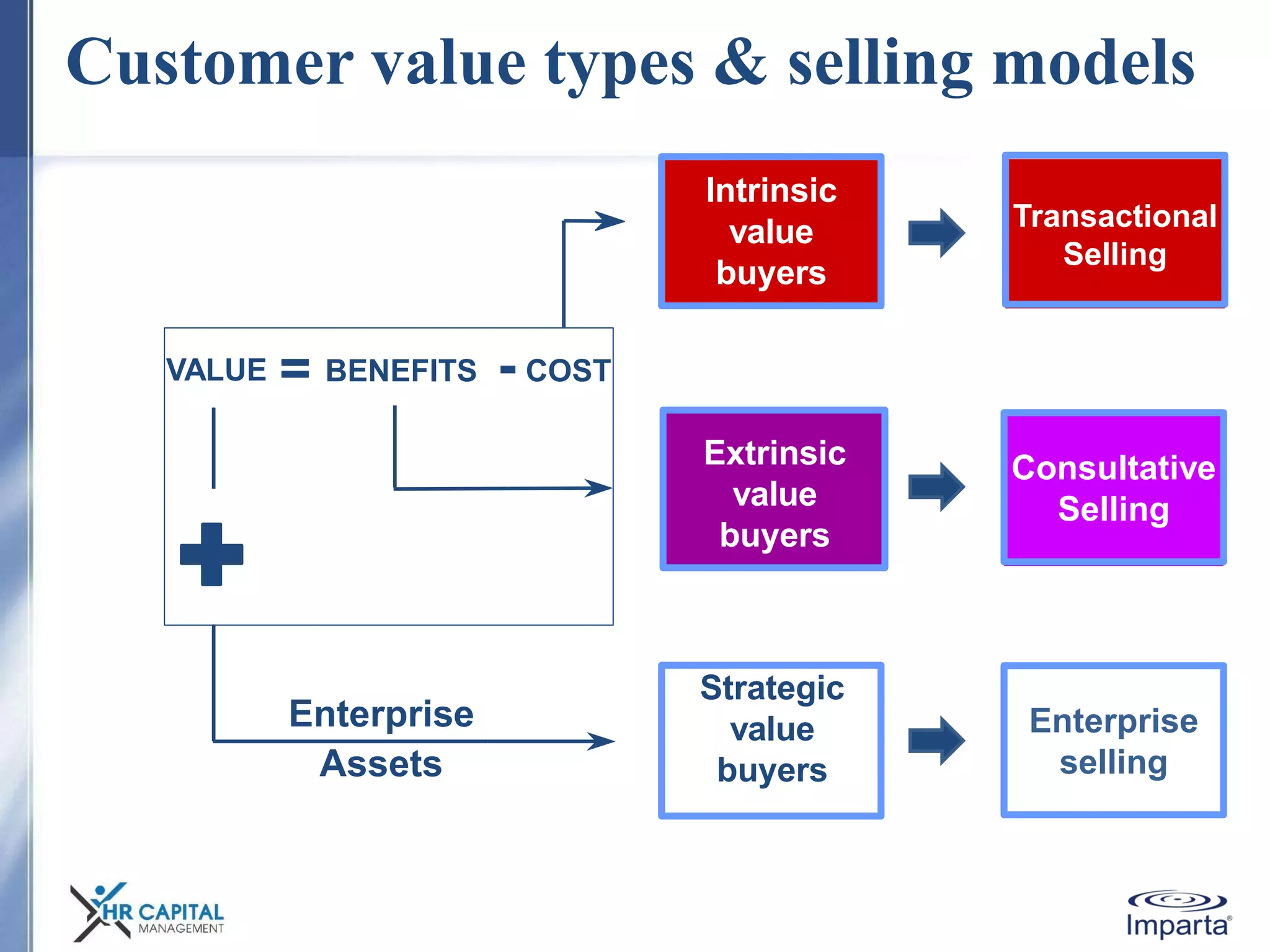
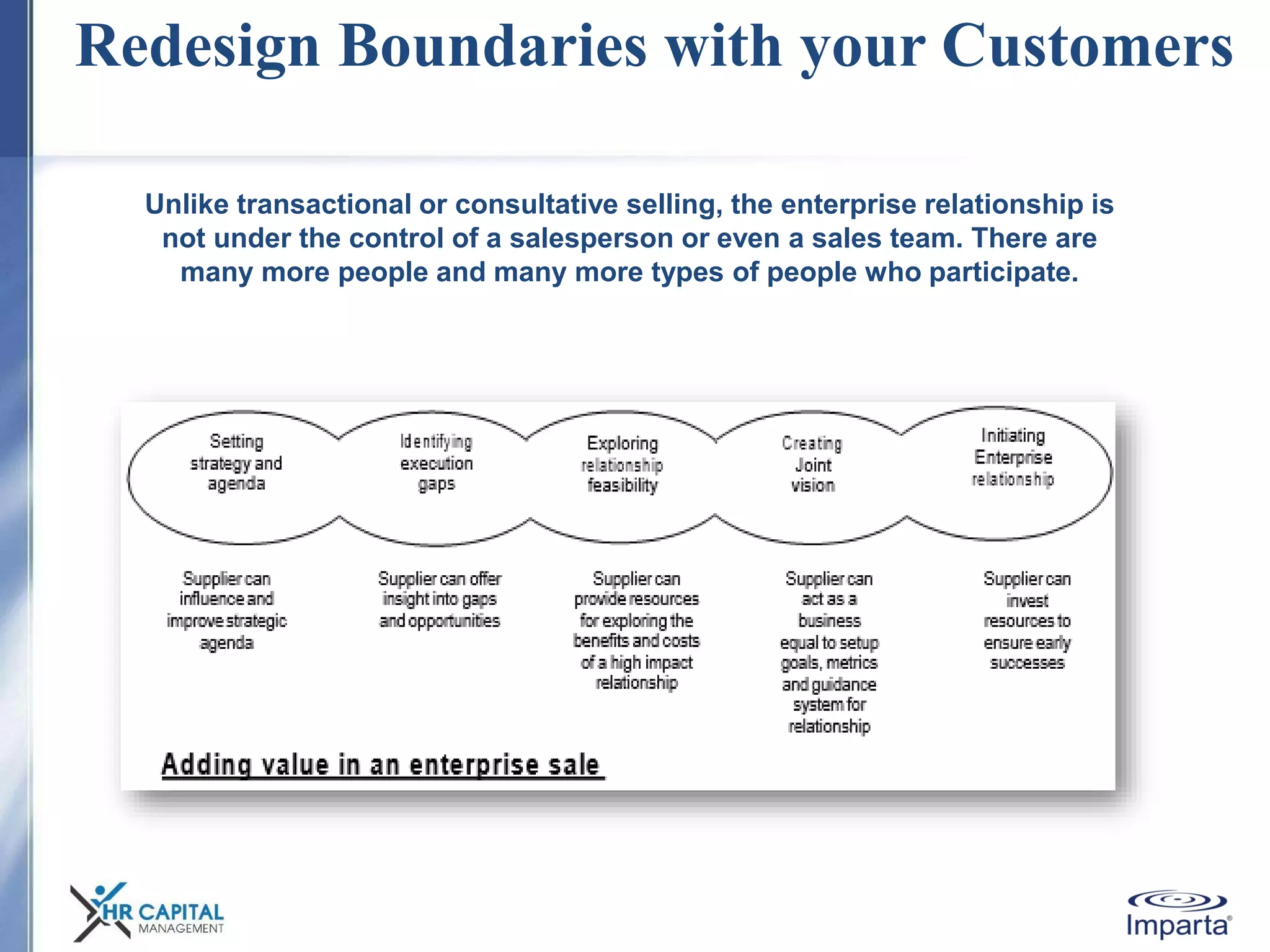
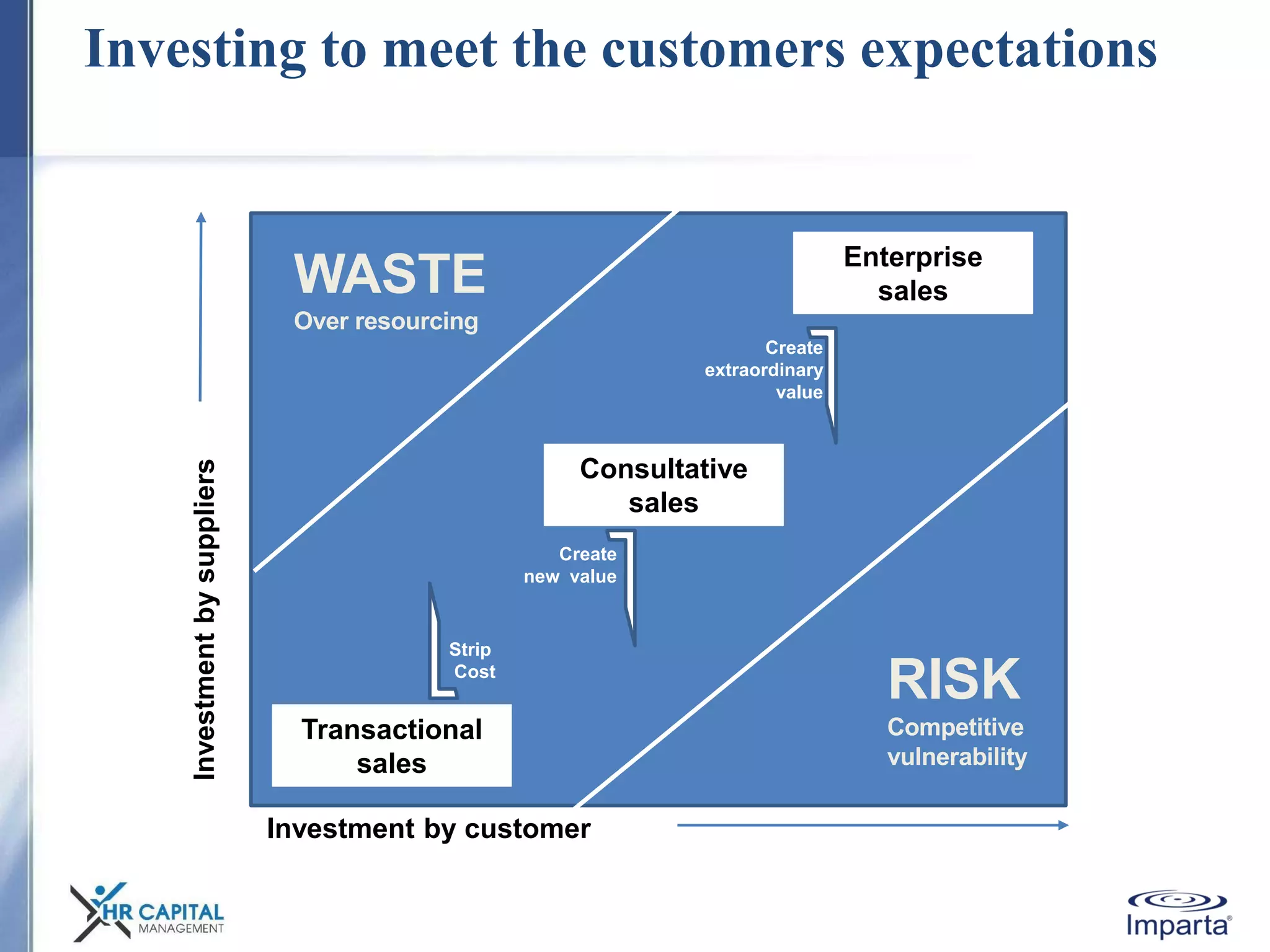
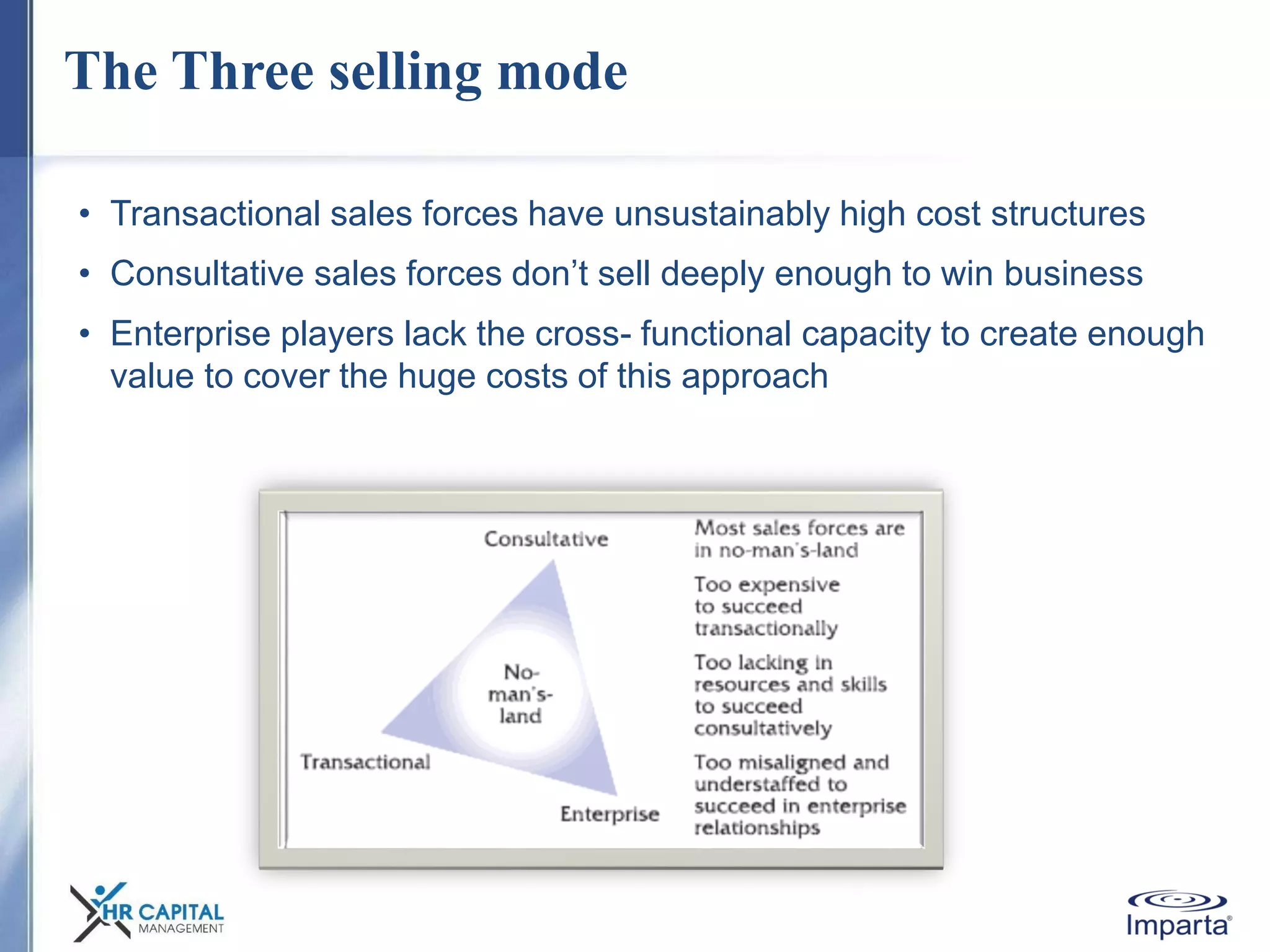
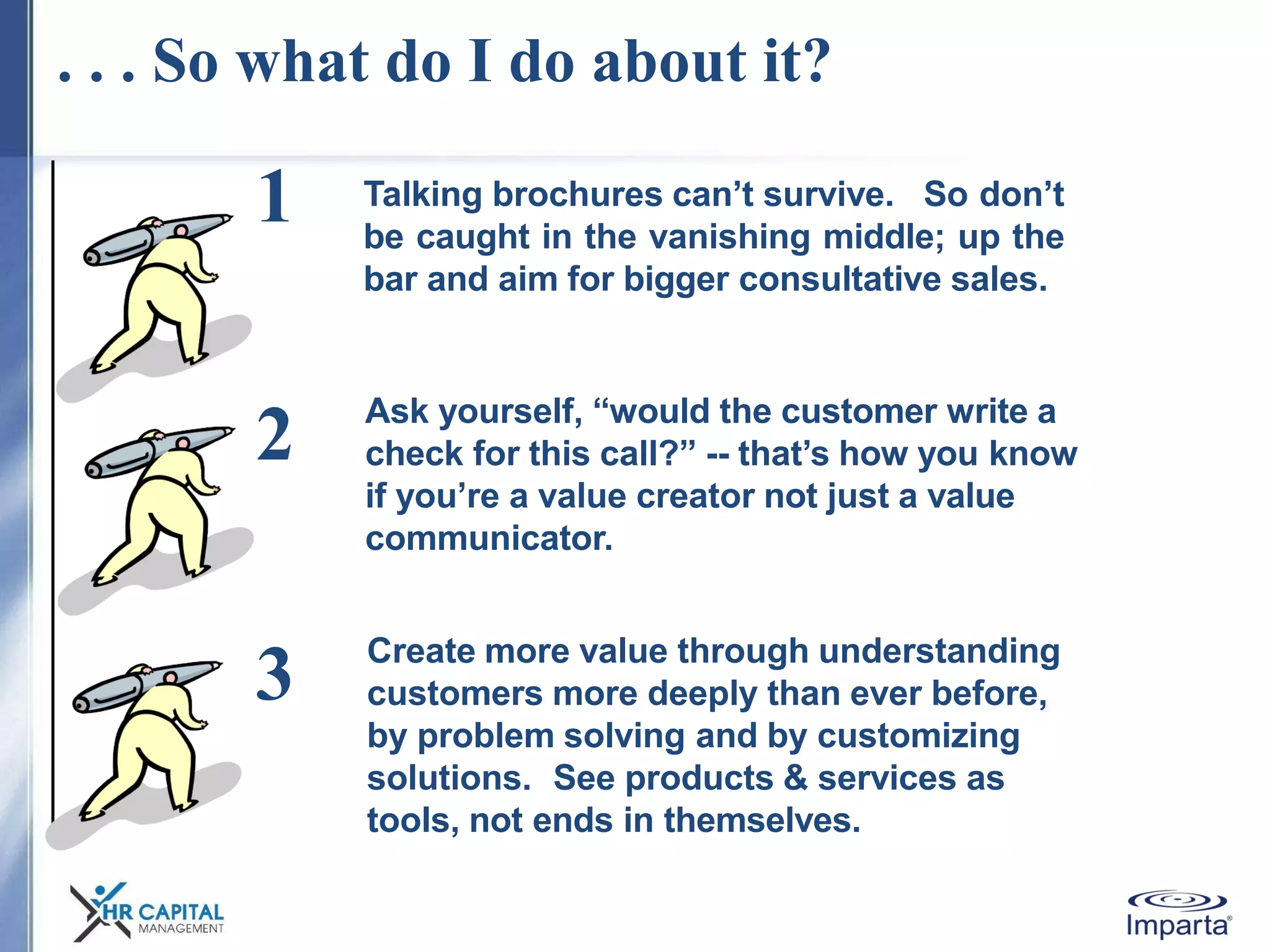
The document discusses the purpose and shifting role of sales forces. It notes that as products and services become more substitutable, the purpose of sales forces is moving from communicating value to creating value. It suggests sales forces need to take a consultative or enterprise approach focused on deeply understanding customer needs and customizing solutions in order to create enough value to justify their costs. The document advocates eliminating barriers between functions to organize work around core processes and create extraordinary value for key customers.