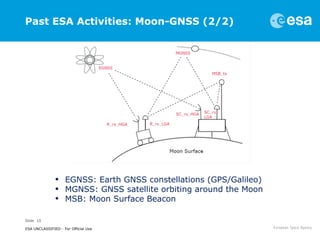
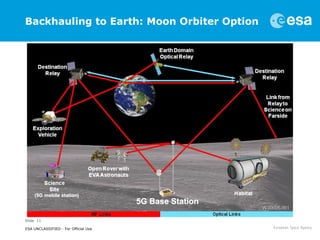
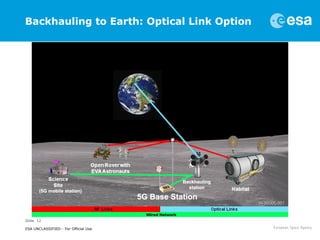
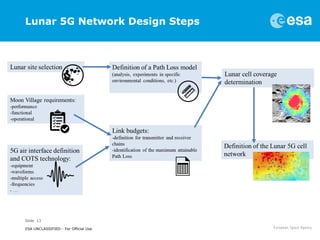
This document discusses proposals for establishing a communications and navigation network to support human and robotic exploration of the Moon. It summarizes past ESA studies on using GPS and developing lunar navigation and communication satellites. It then proposes a modular, expandable approach using commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) technologies like LTE and the forthcoming 5G standard. This COTS-based lunar network would provide reliable communication and navigation services to support colonization of the Moon and Mars through permanent base stations. It would satisfy requirements for performance, reliability, affordability and sustainability by leveraging commercial technologies and allowing incremental expansion over time.