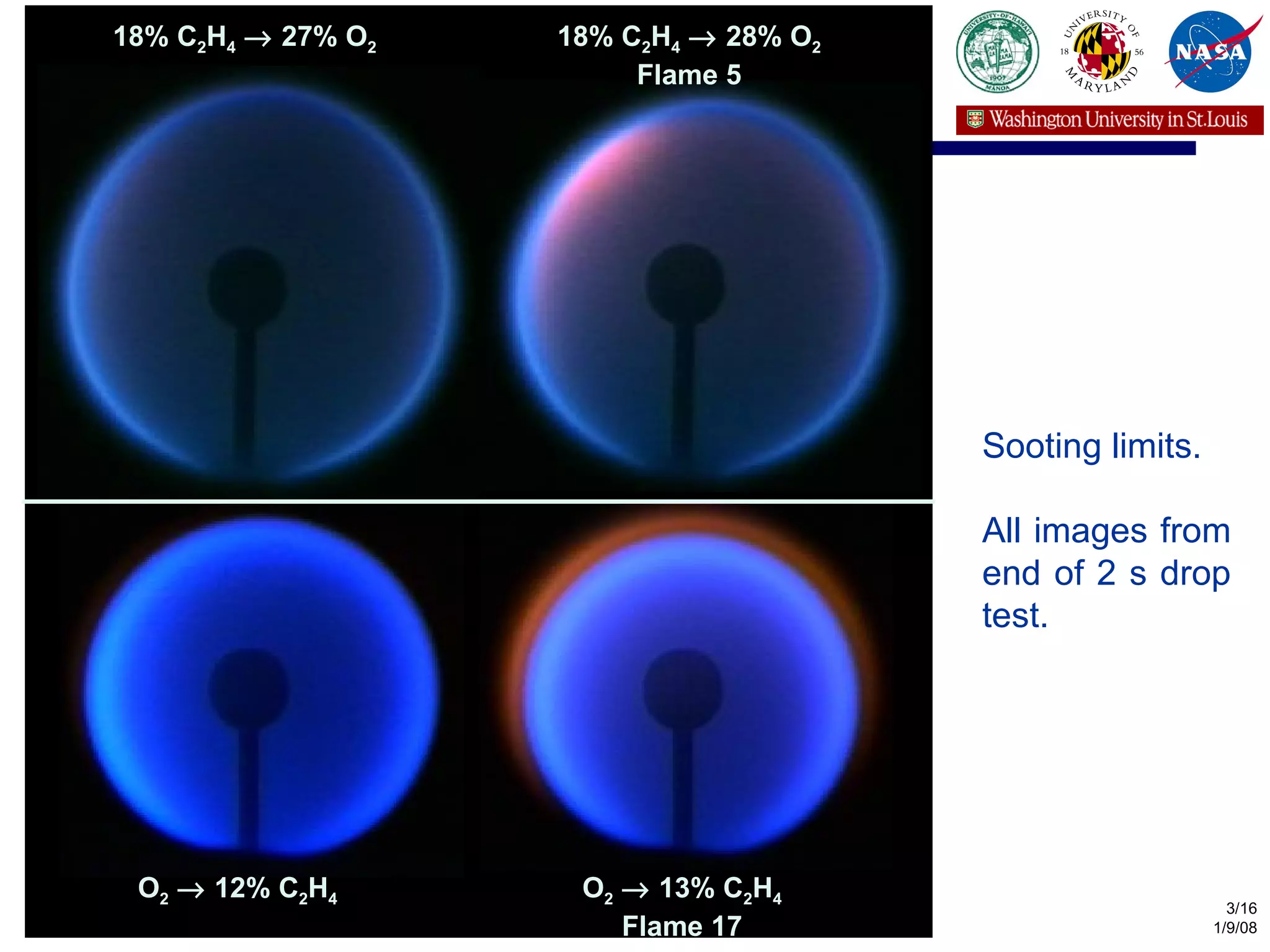
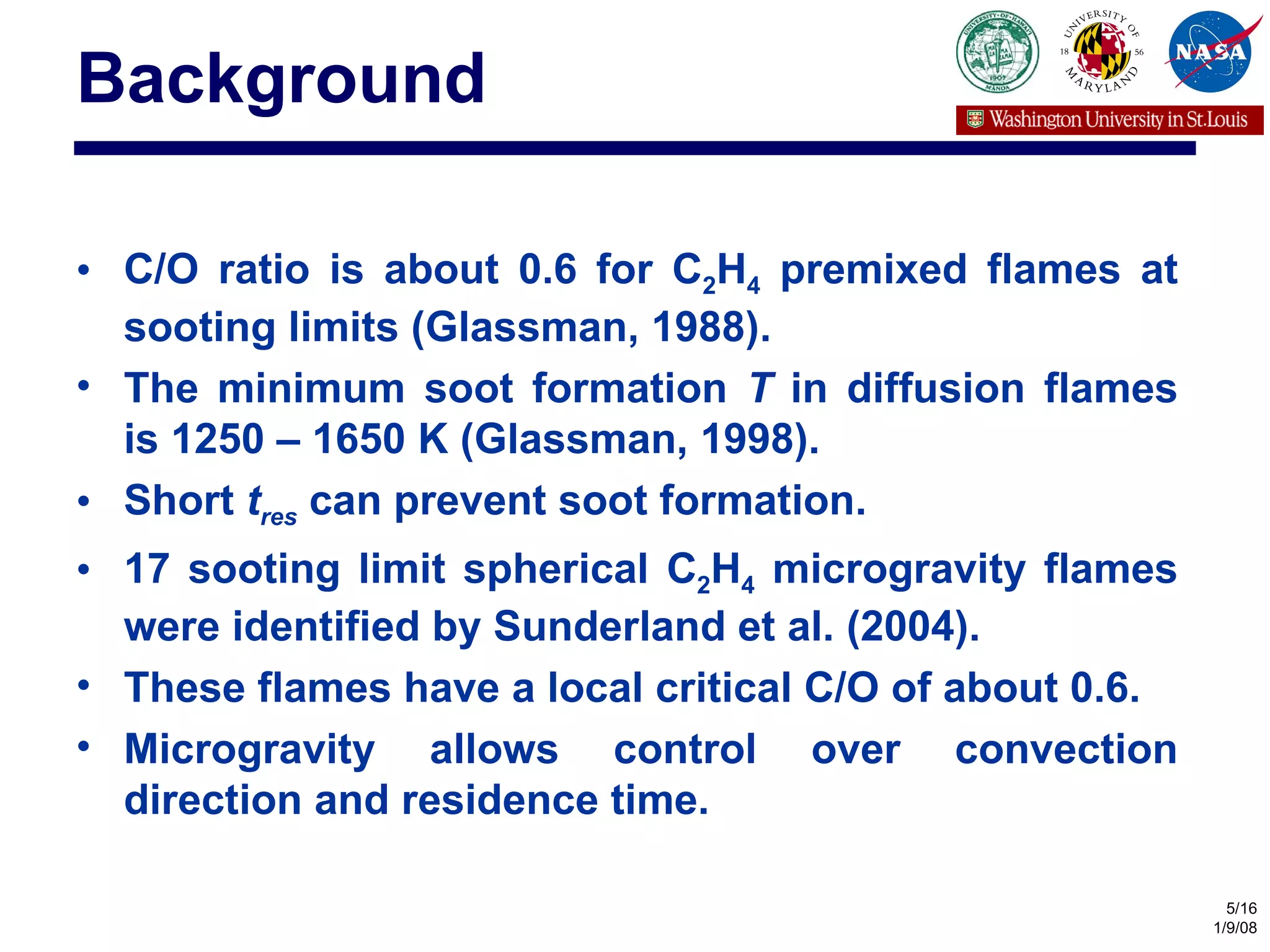
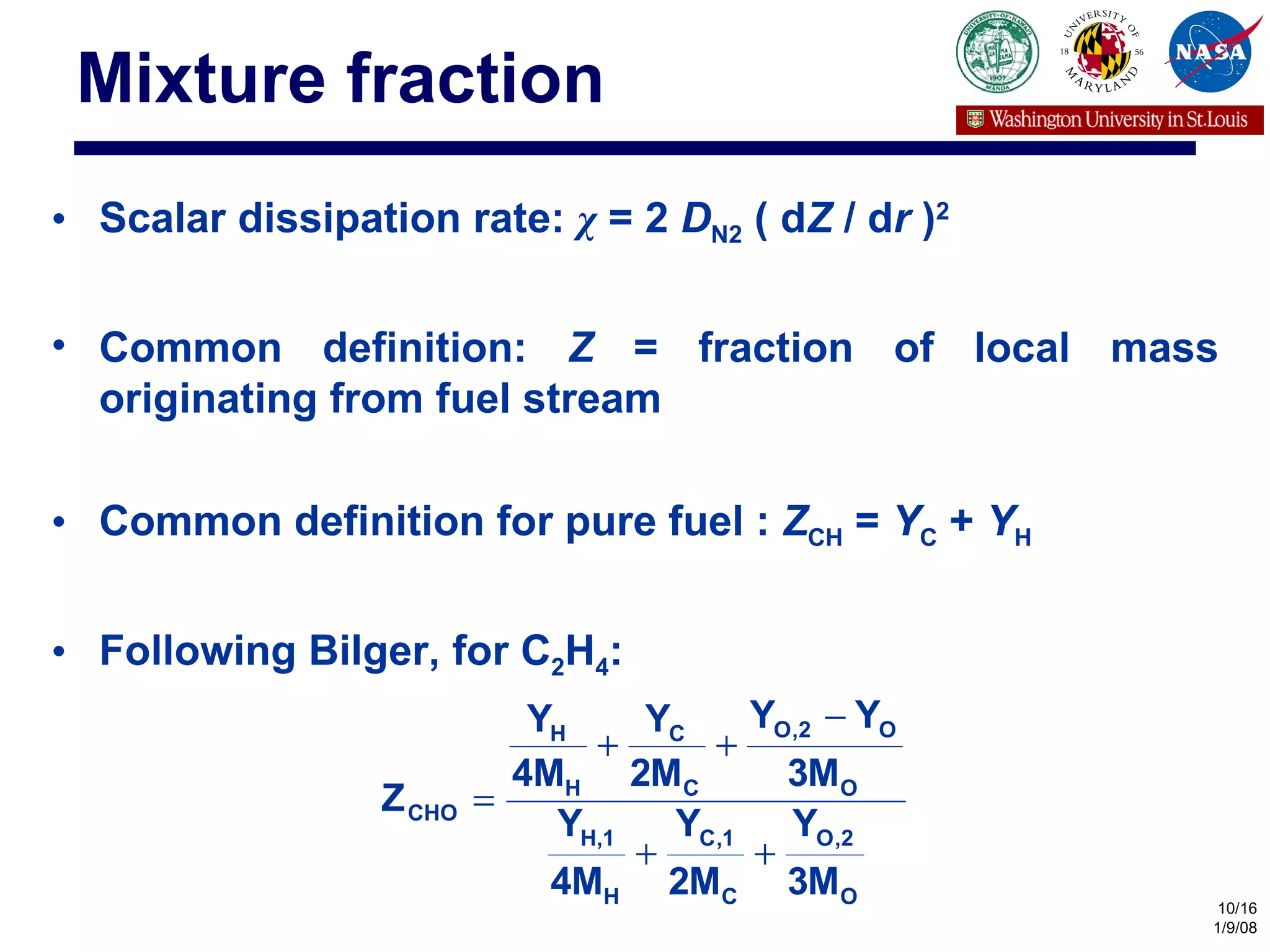
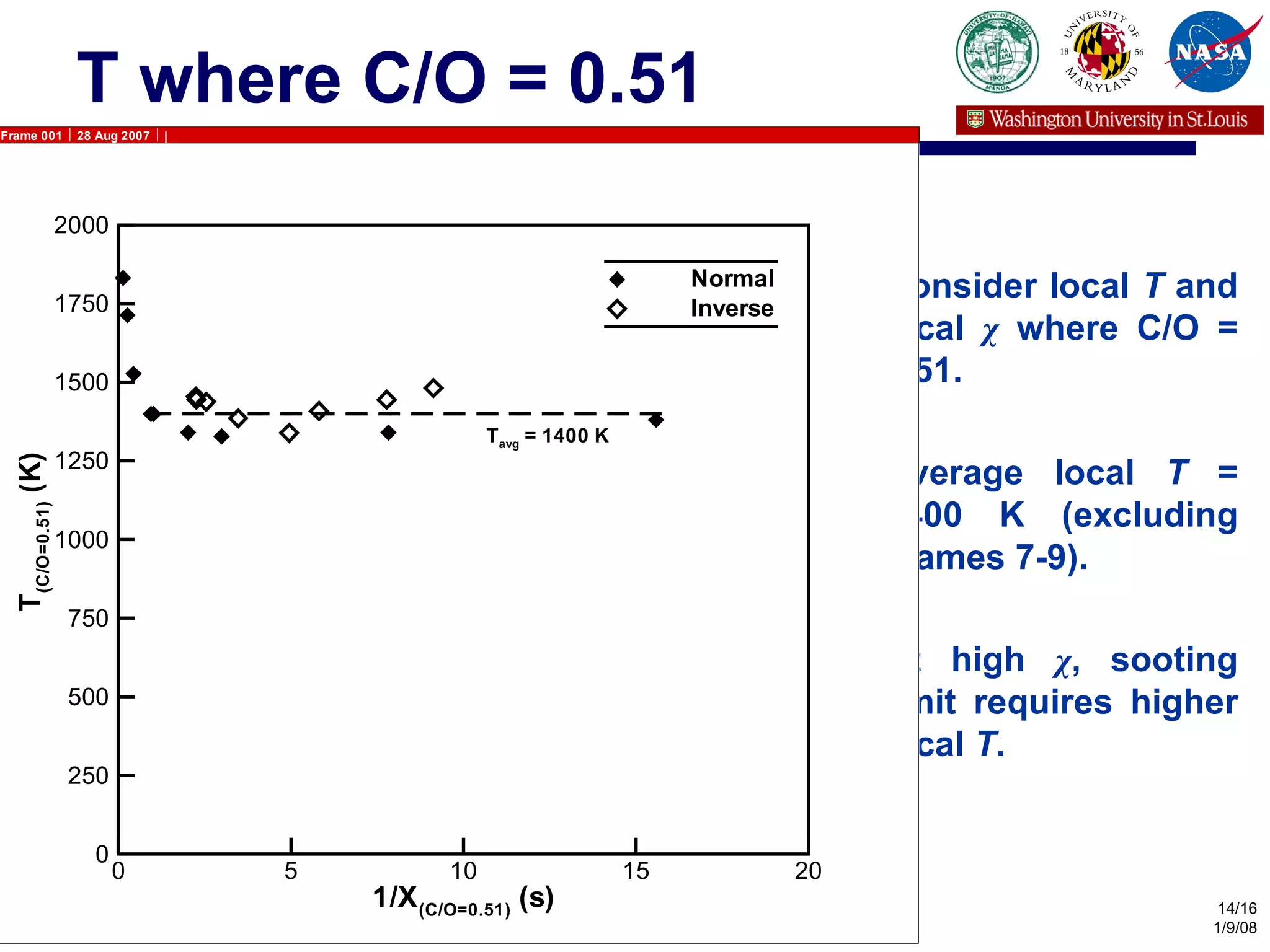
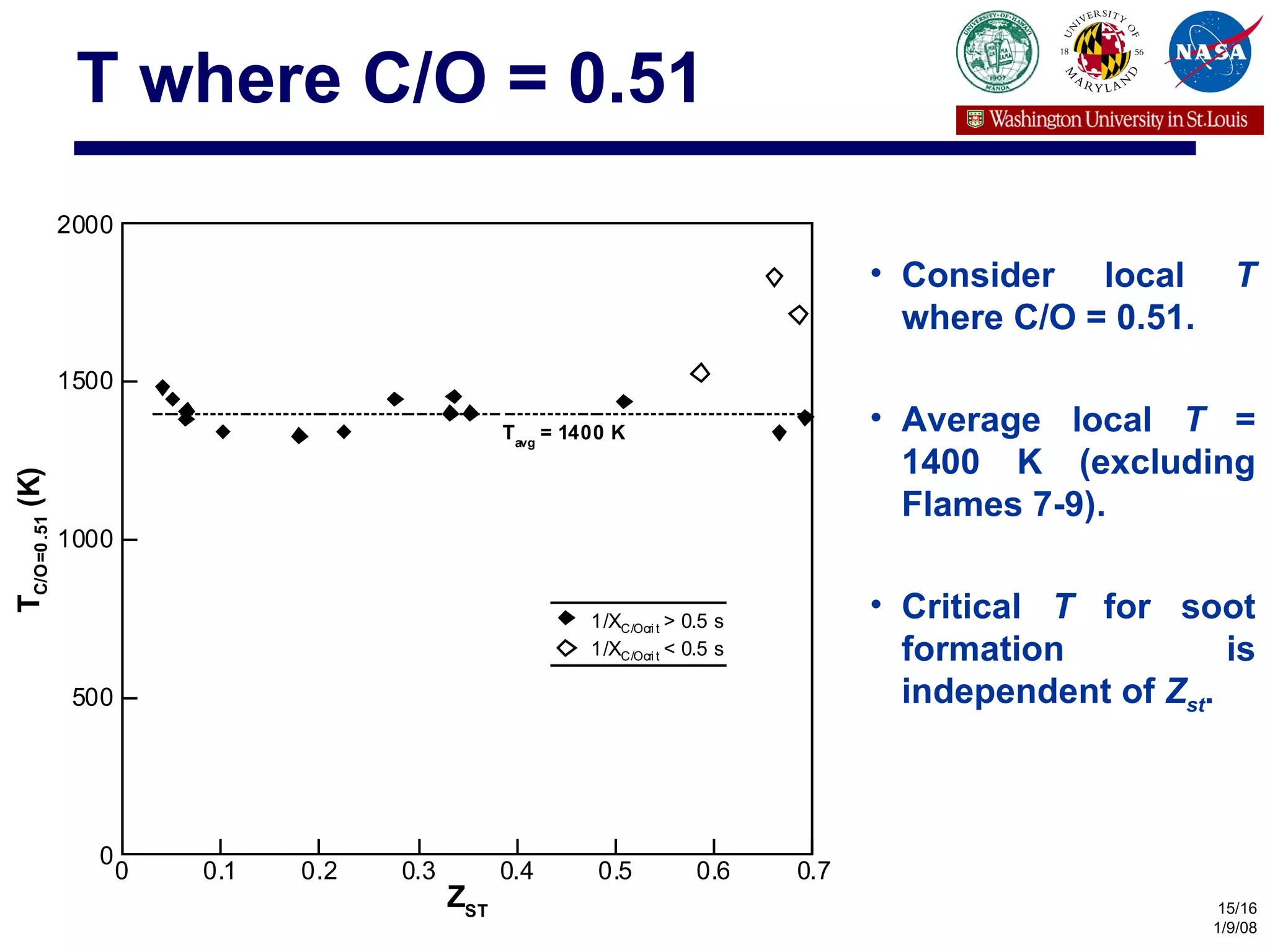
The document investigates the effects of carbon-to-oxygen (C/O) ratio and temperature on the sooting limits of spherical diffusion flames of ethylene. It finds that soot formation requires a local C/O ratio of at least 0.51 where the local temperature is 1400 K or higher. These critical values of C/O ratio and temperature for soot formation are independent of factors like convection direction, fuel/oxidizer concentrations, residence time, and scalar dissipation rate (except at very high dissipation rates).