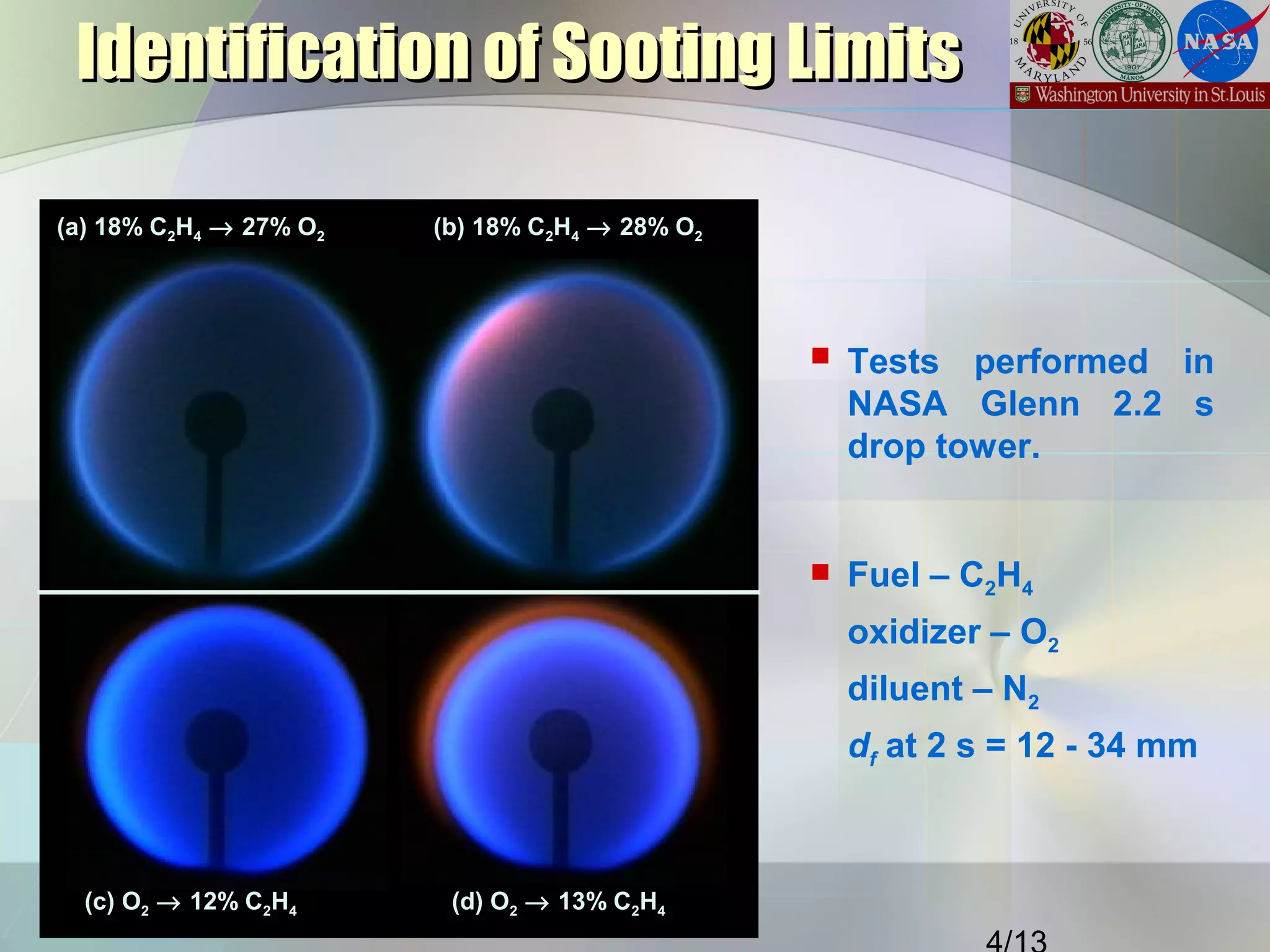
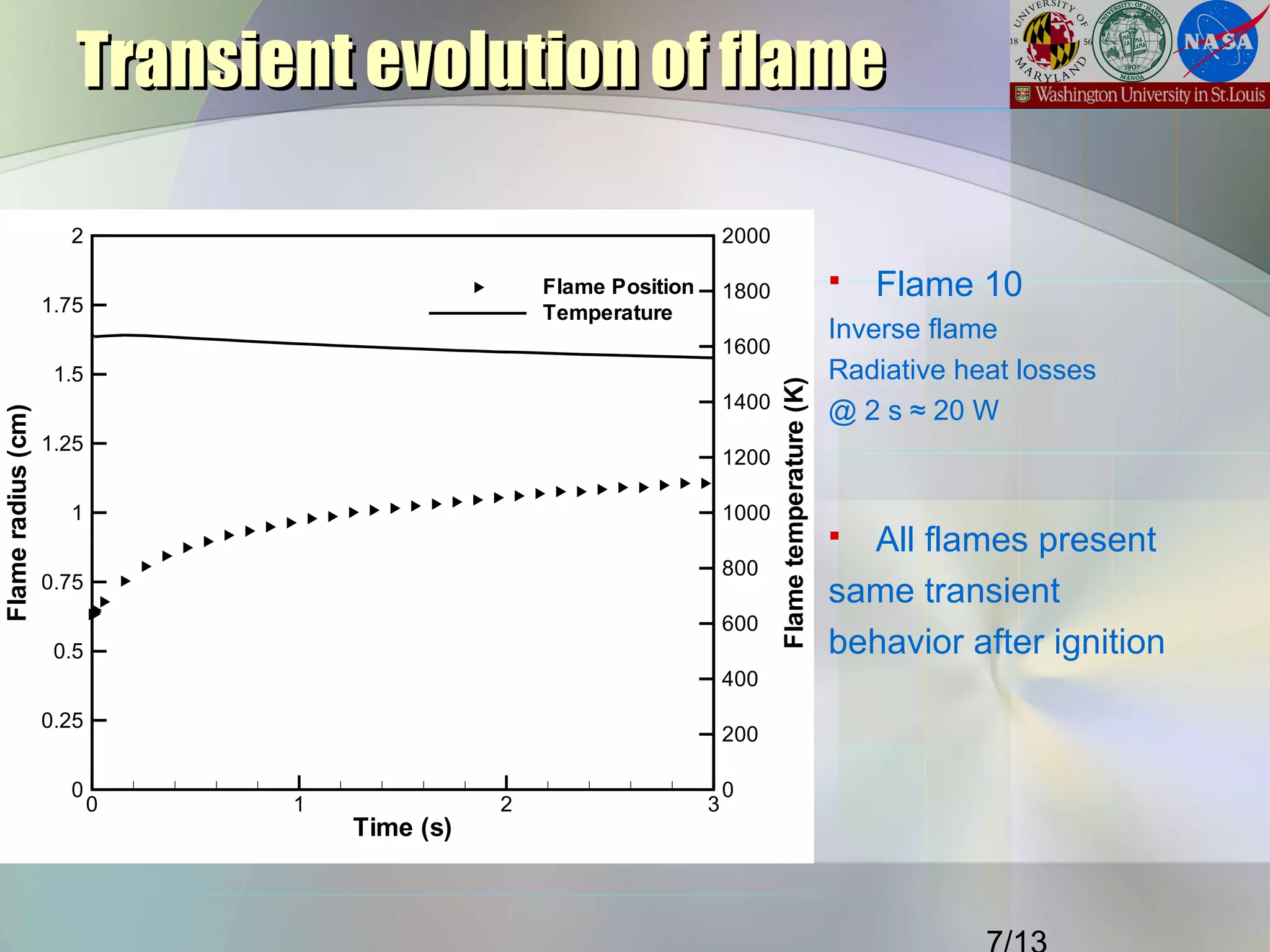
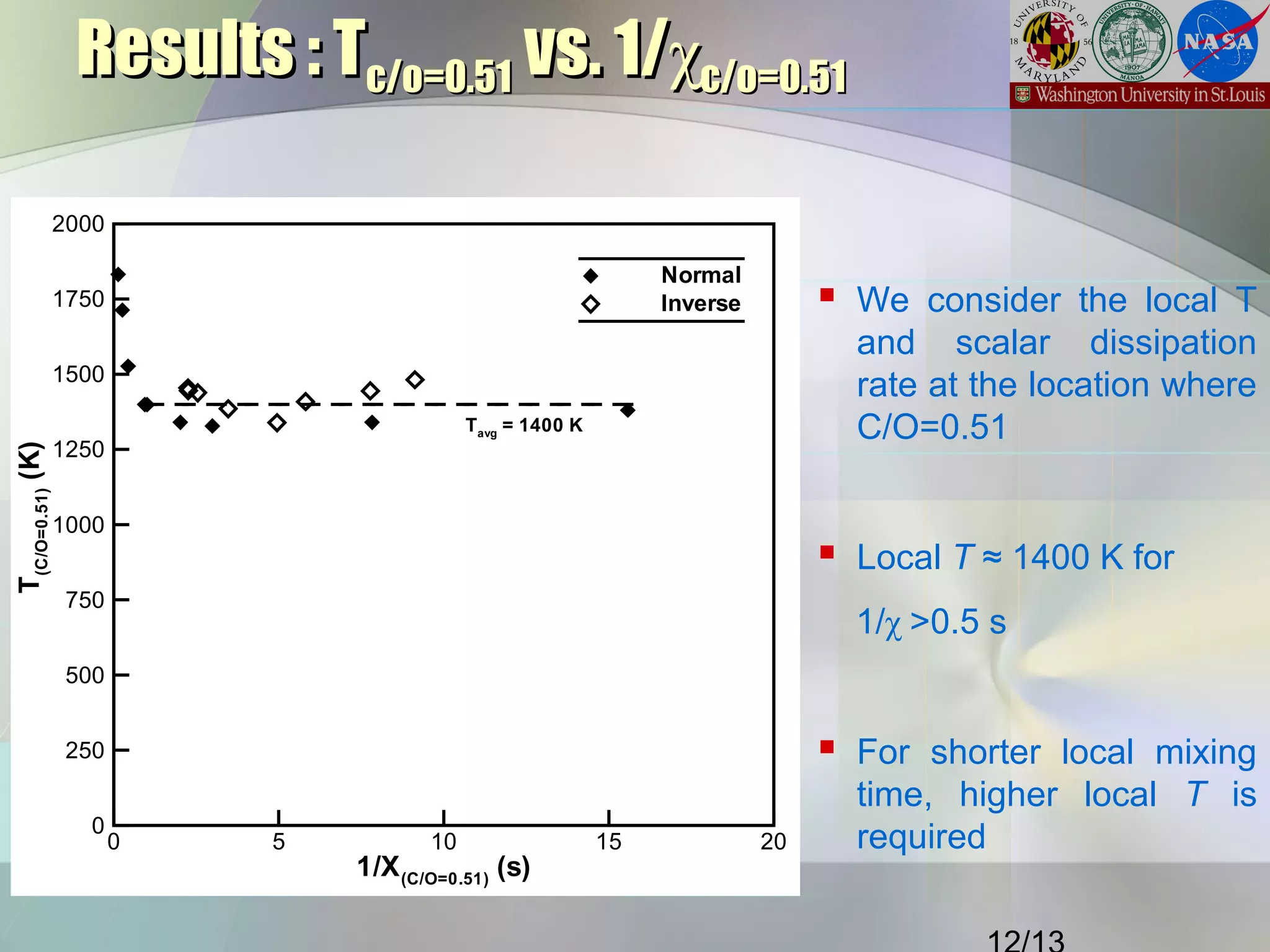
This document summarizes a study on the effects of local carbon-to-oxygen (C/O) ratio and scalar dissipation rate on the sooting limits of spherical non-premixed ethylene flames. The study used detailed chemistry modeling to analyze 17 microgravity flame experiments. It identified a critical local C/O ratio of 0.51 for soot formation and found that flames with scalar dissipation rates below 2 s-1 at this location had average temperatures of 1400K, regardless of stoichiometry, while higher rates required higher temperatures to form soot.