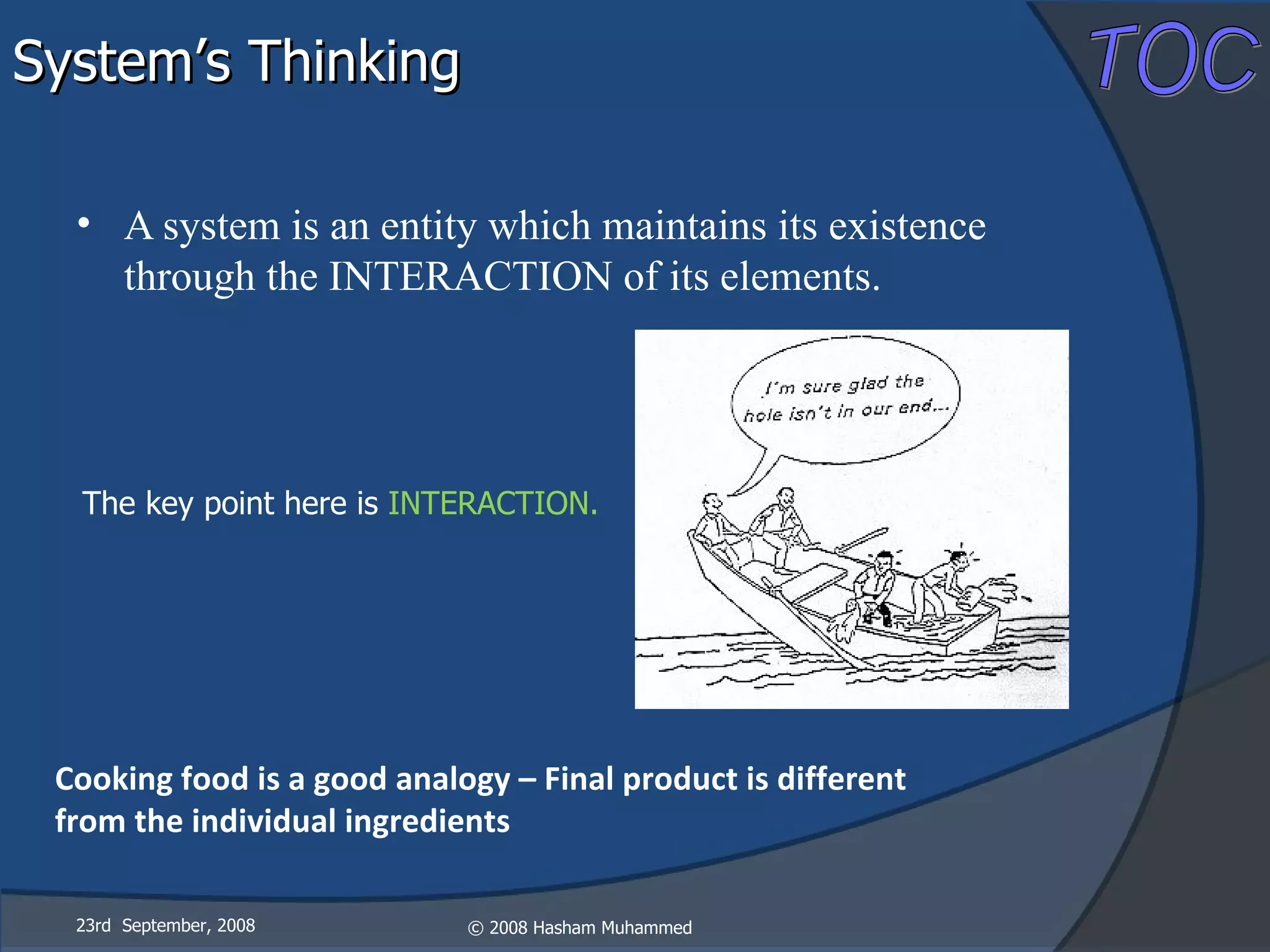
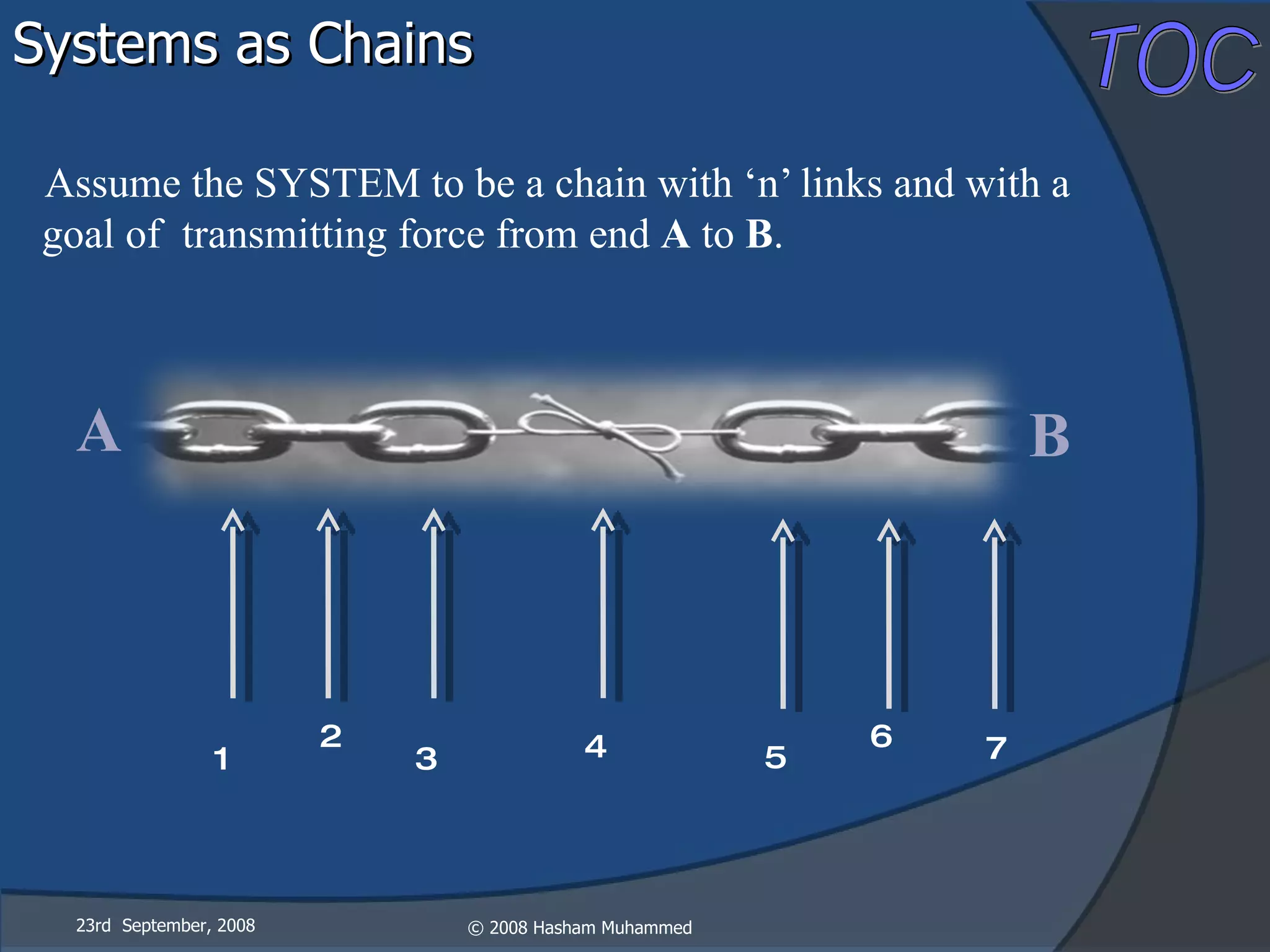
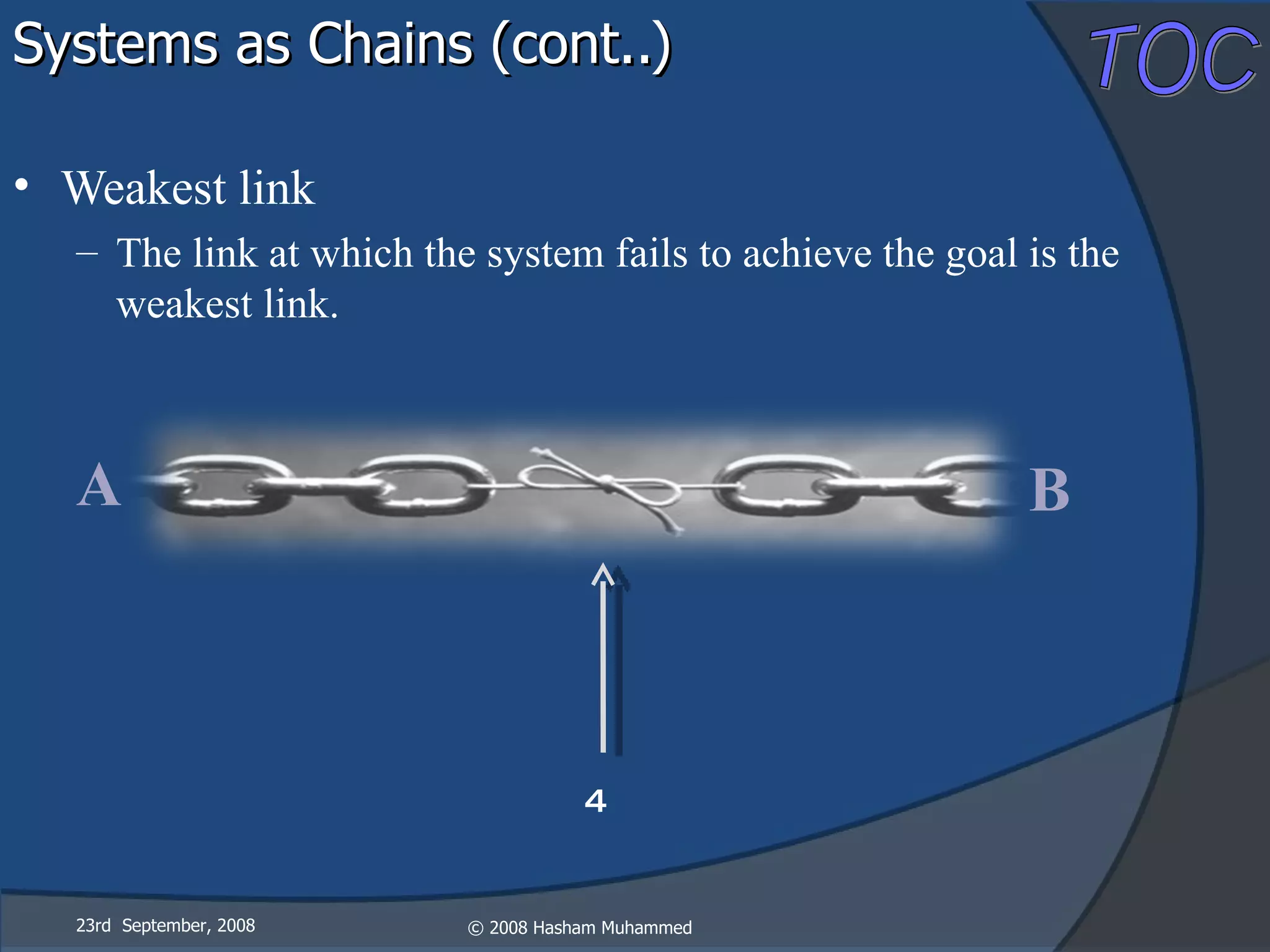
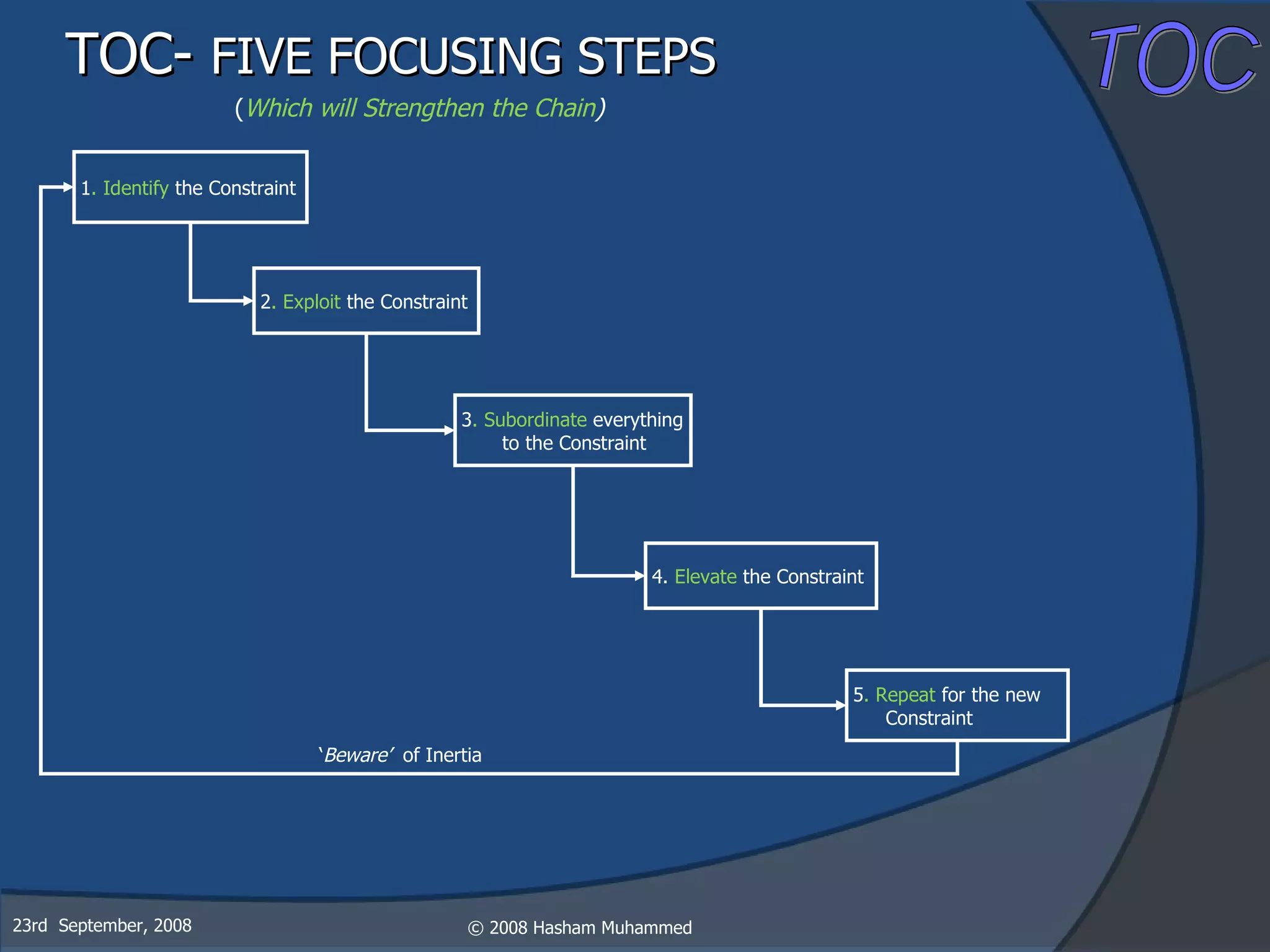
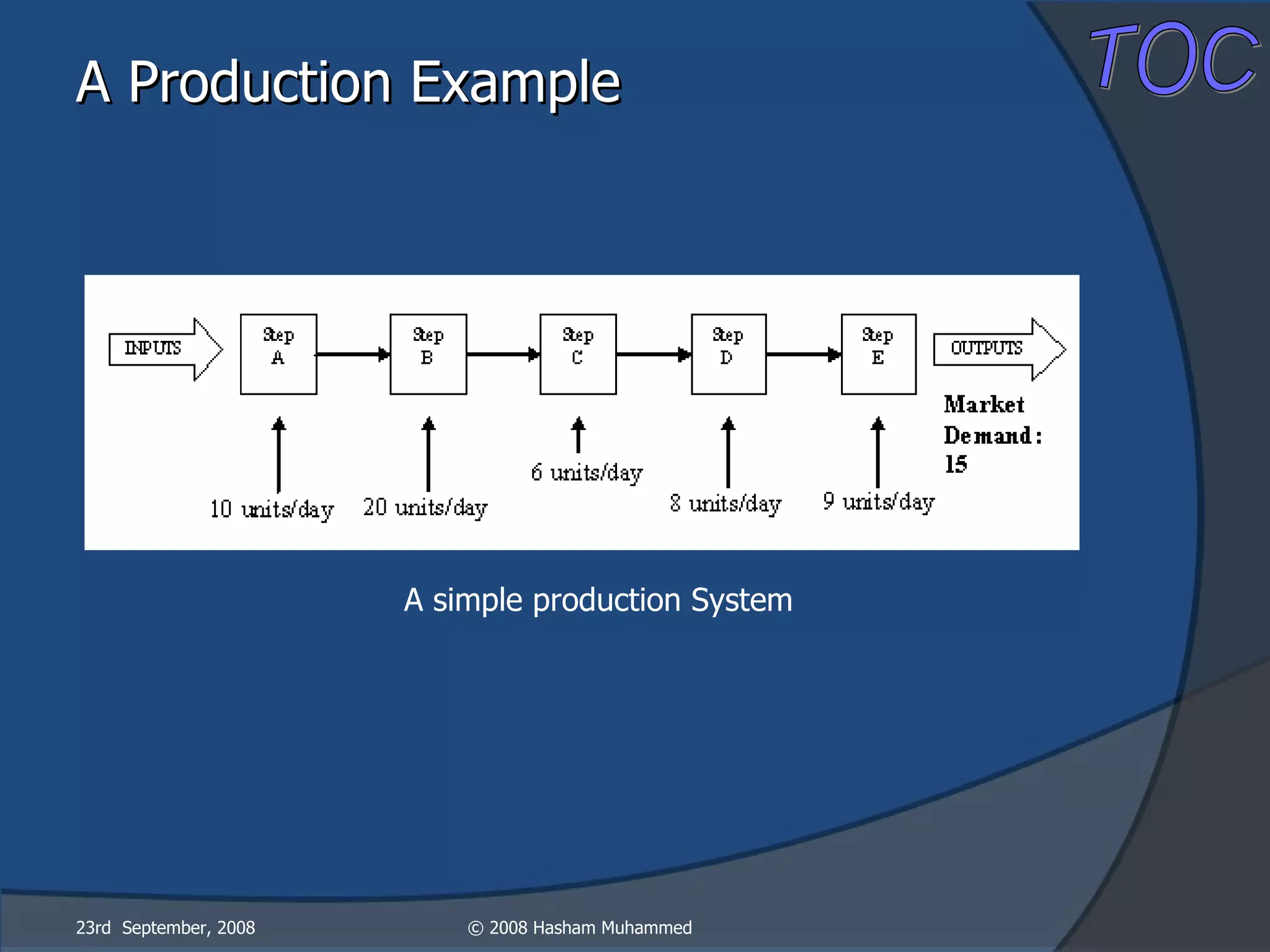
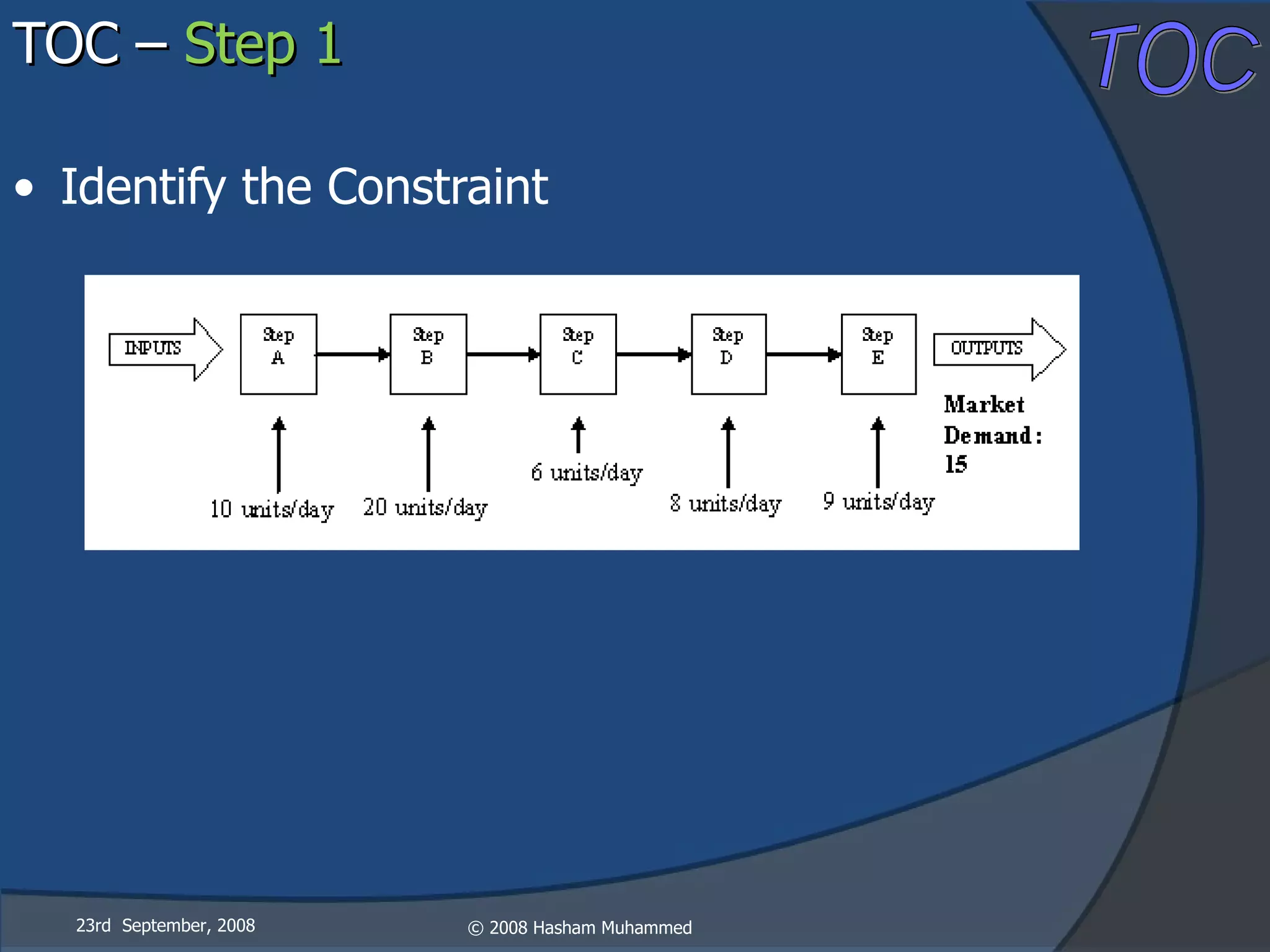
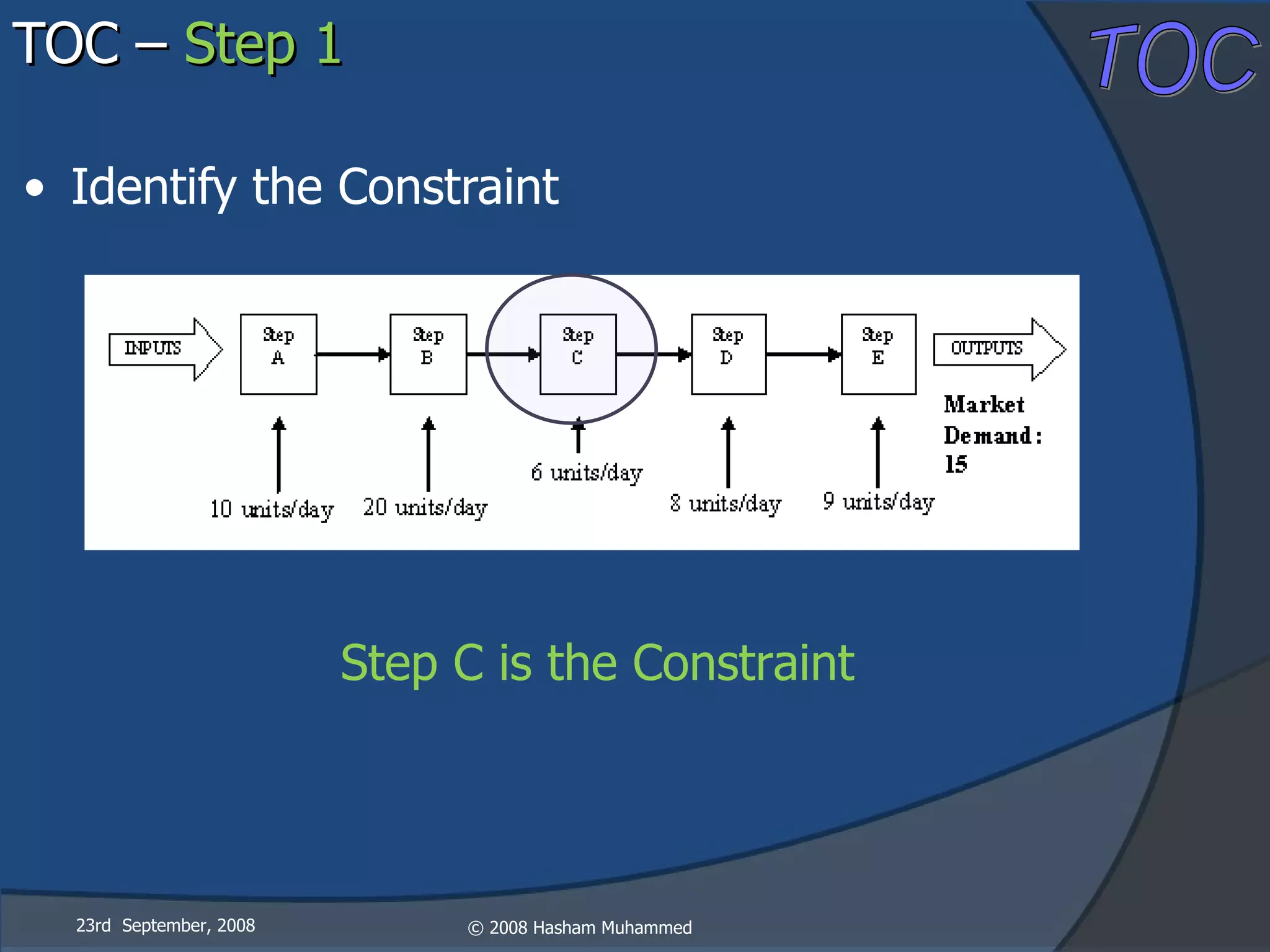
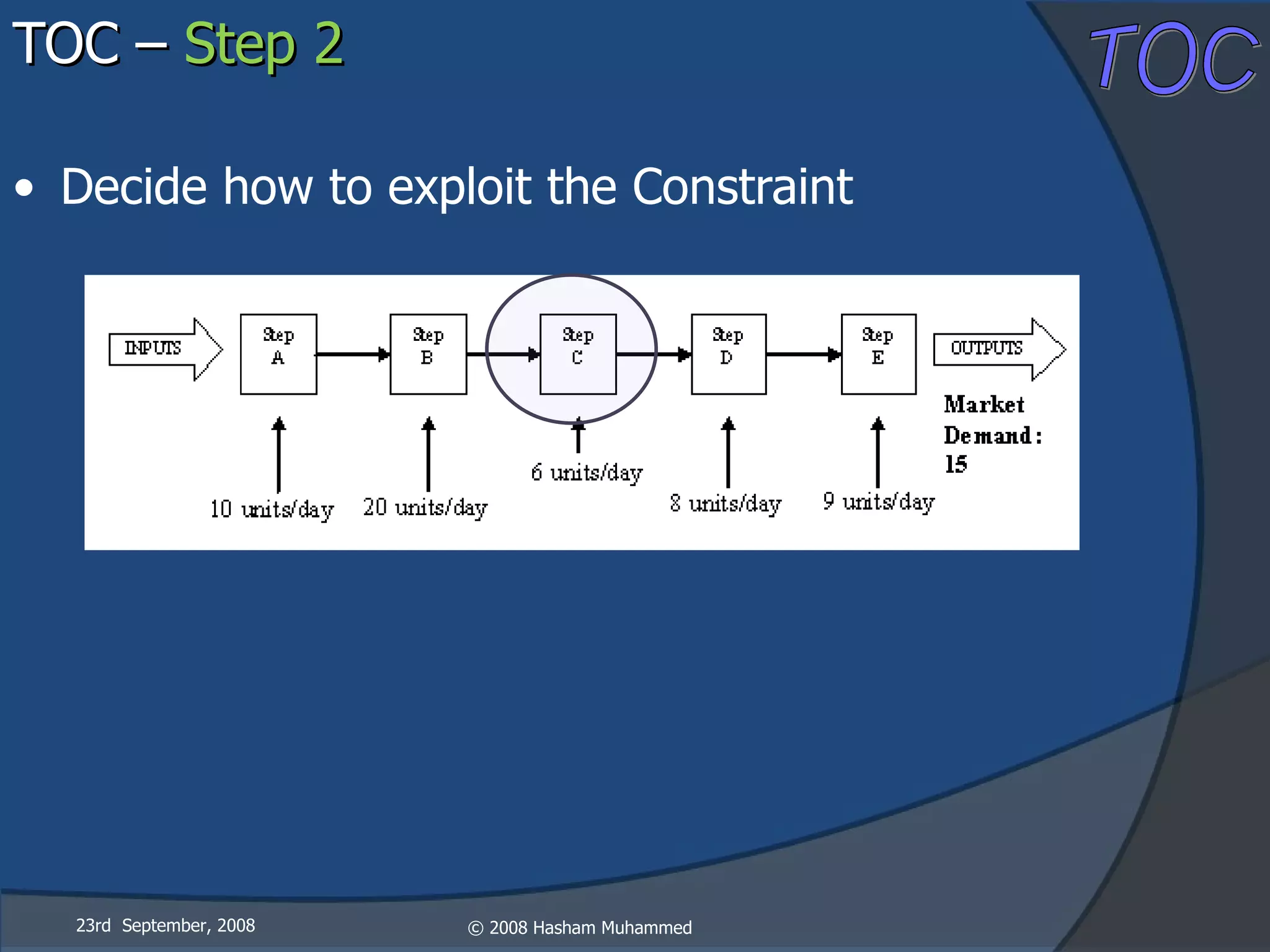
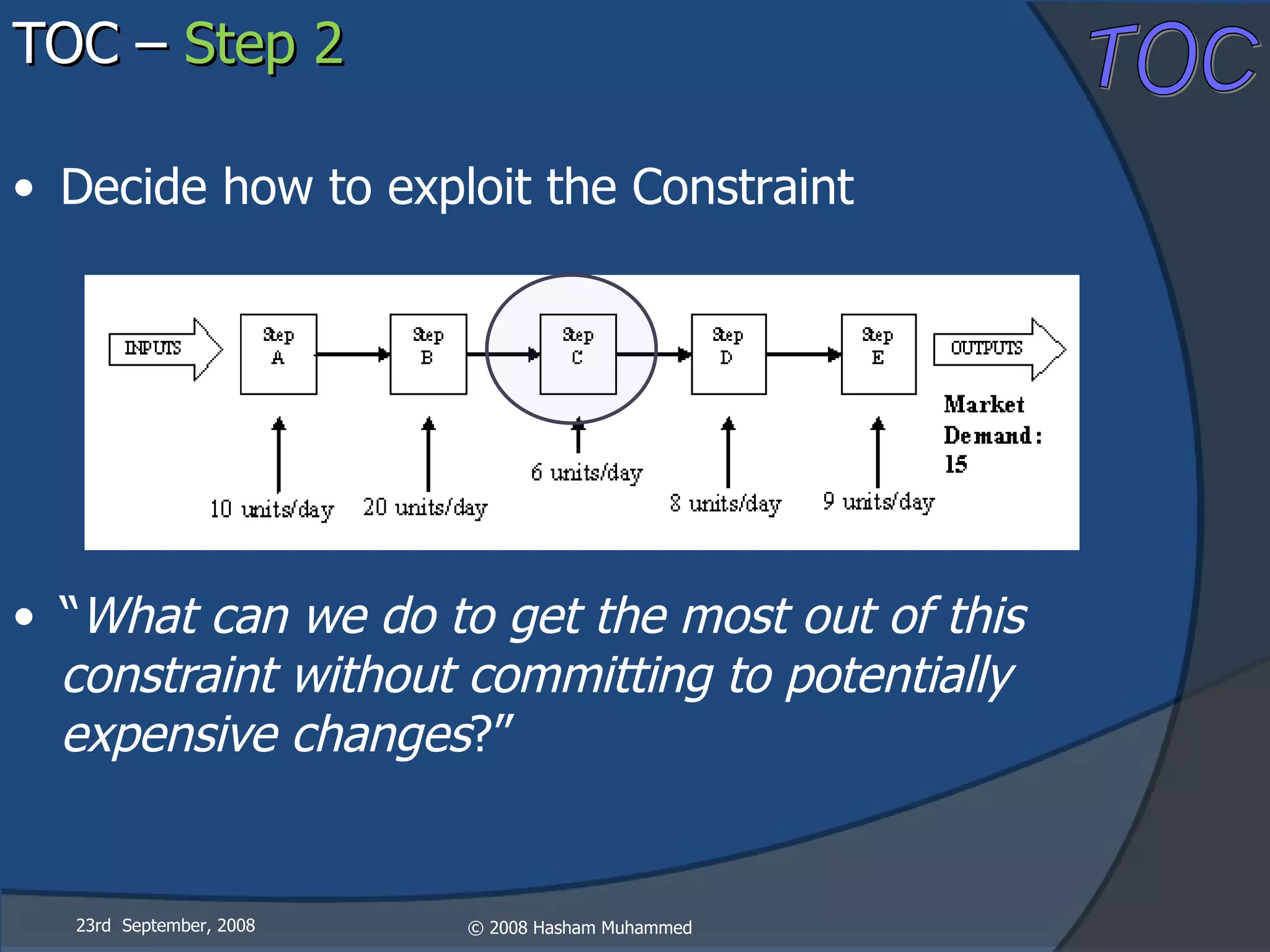
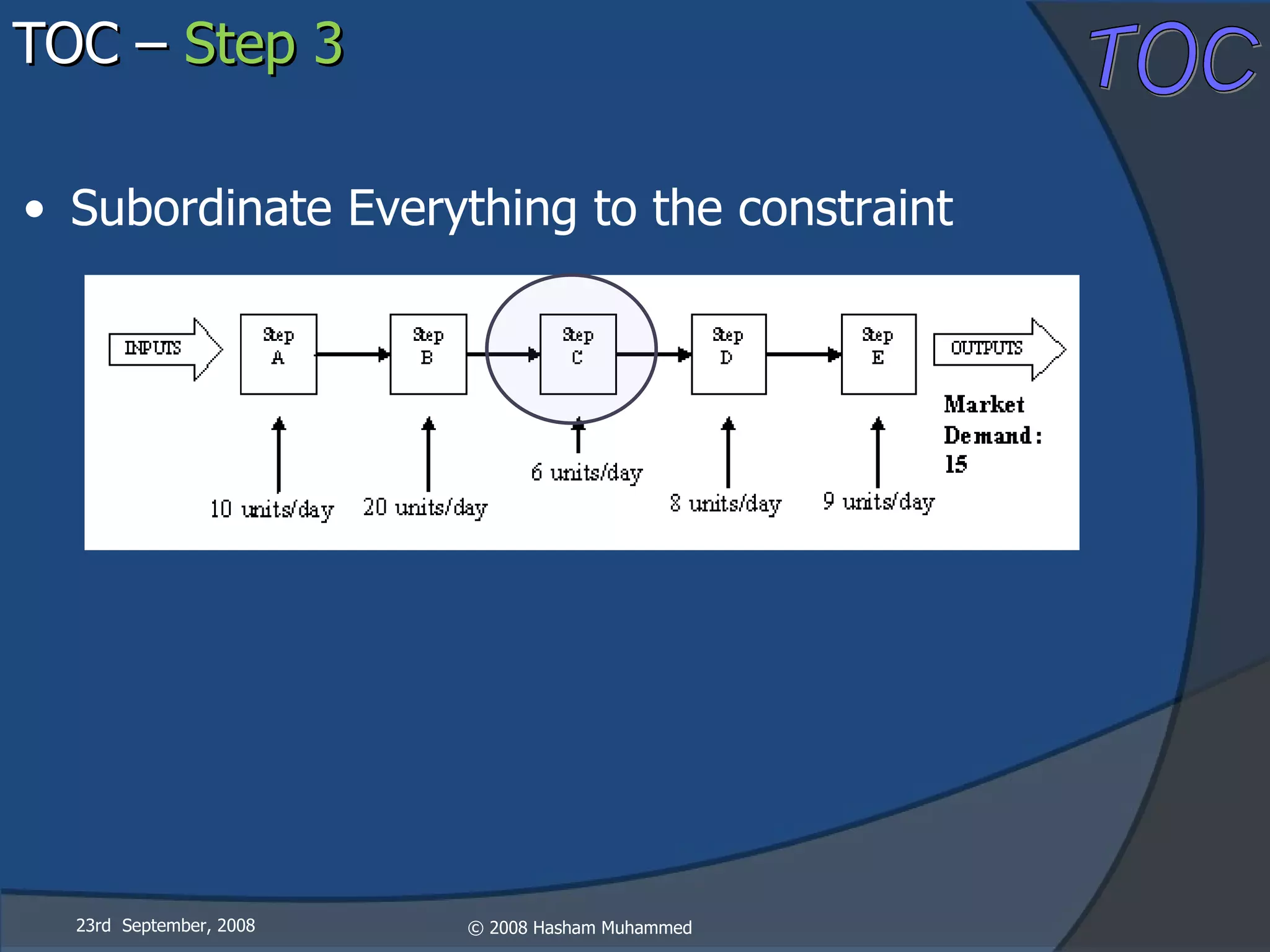
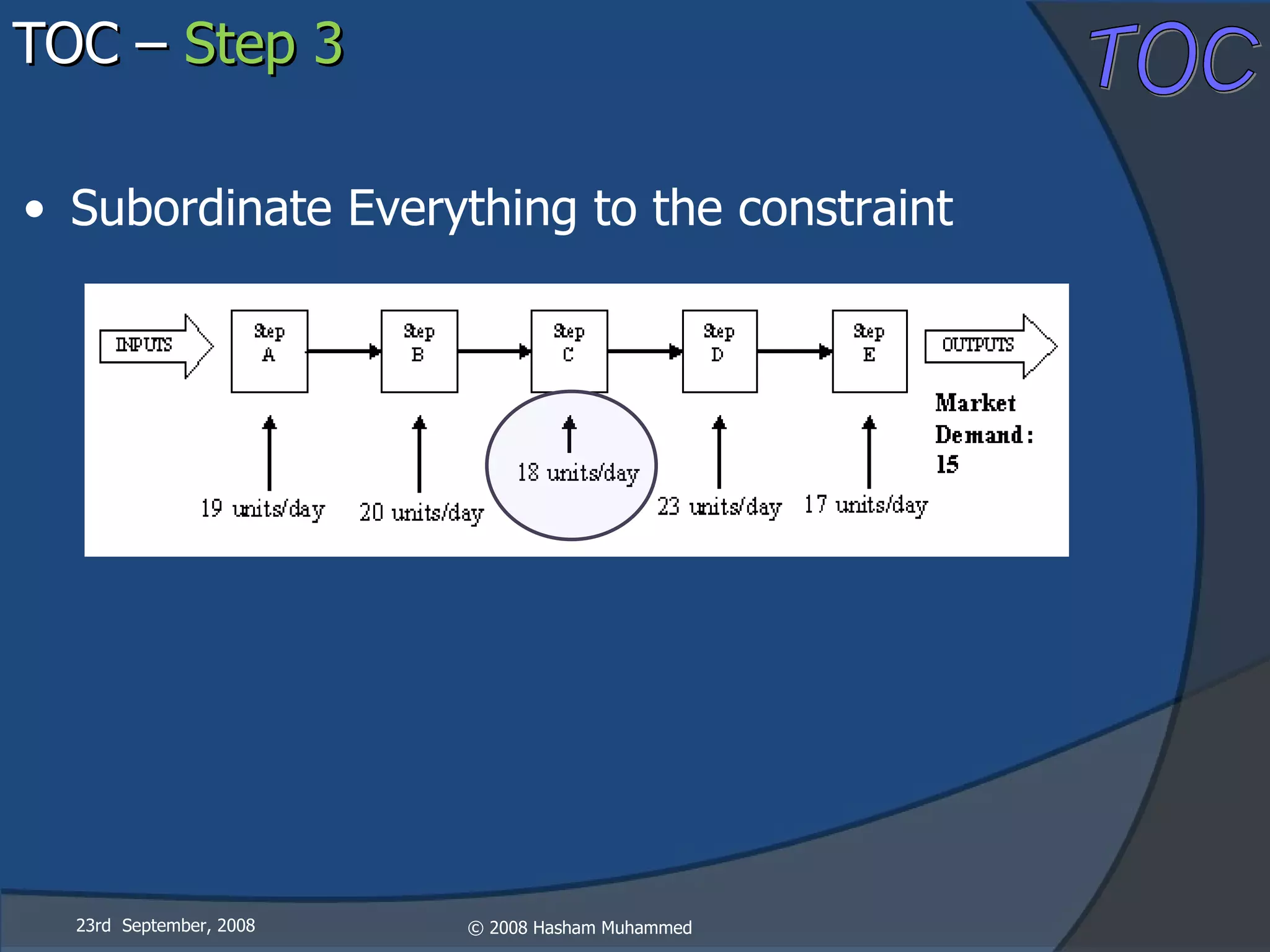
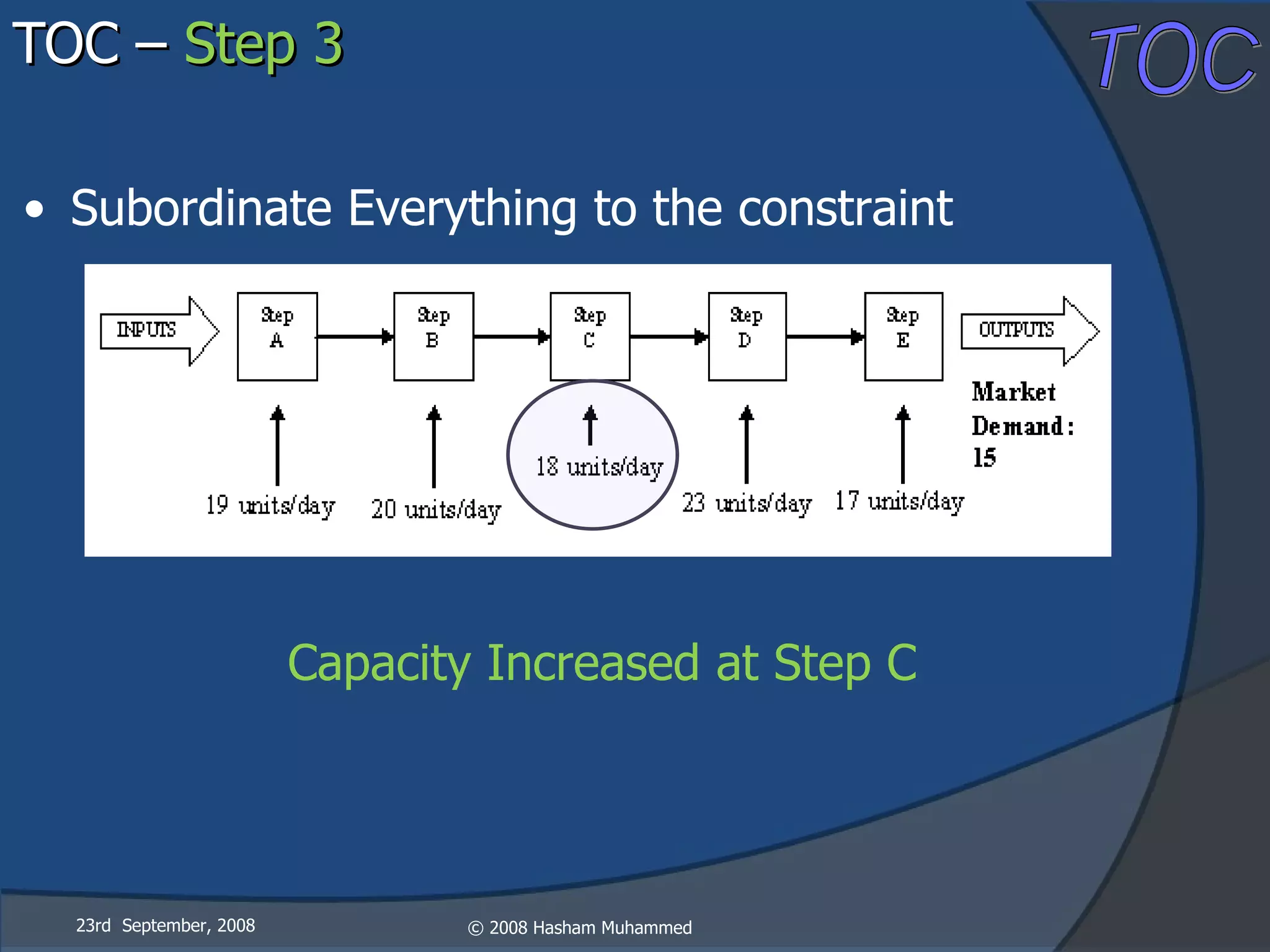
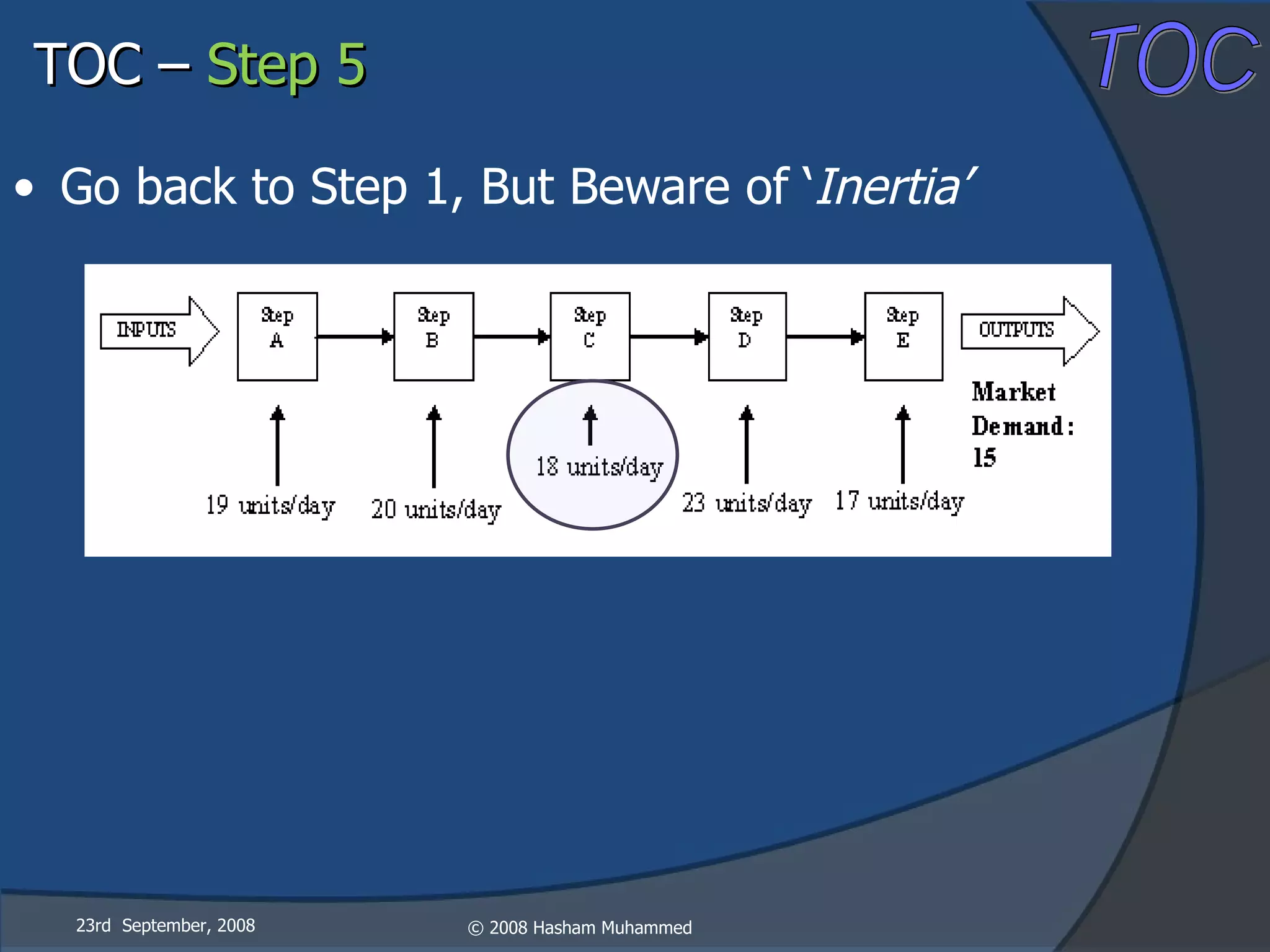
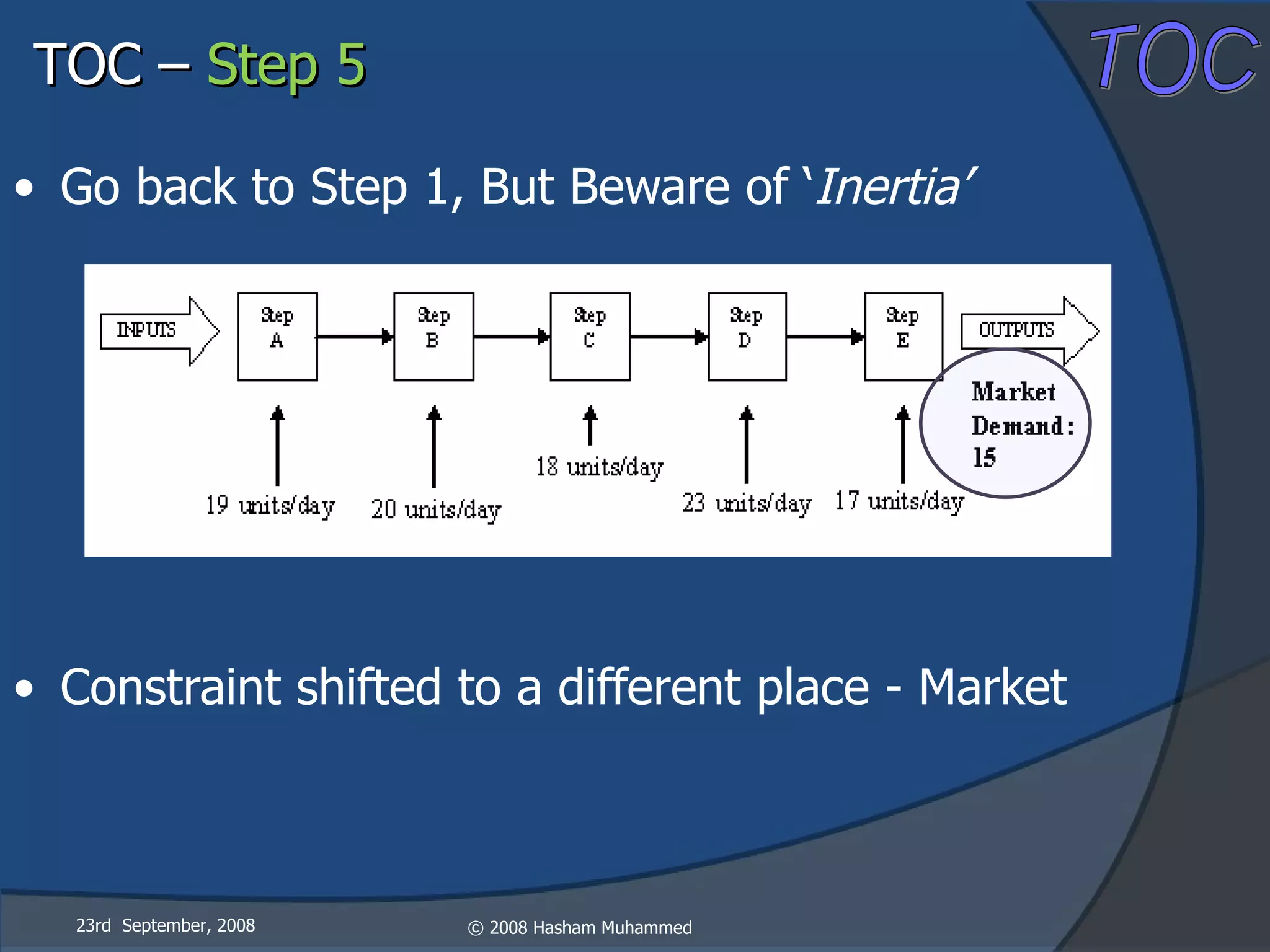
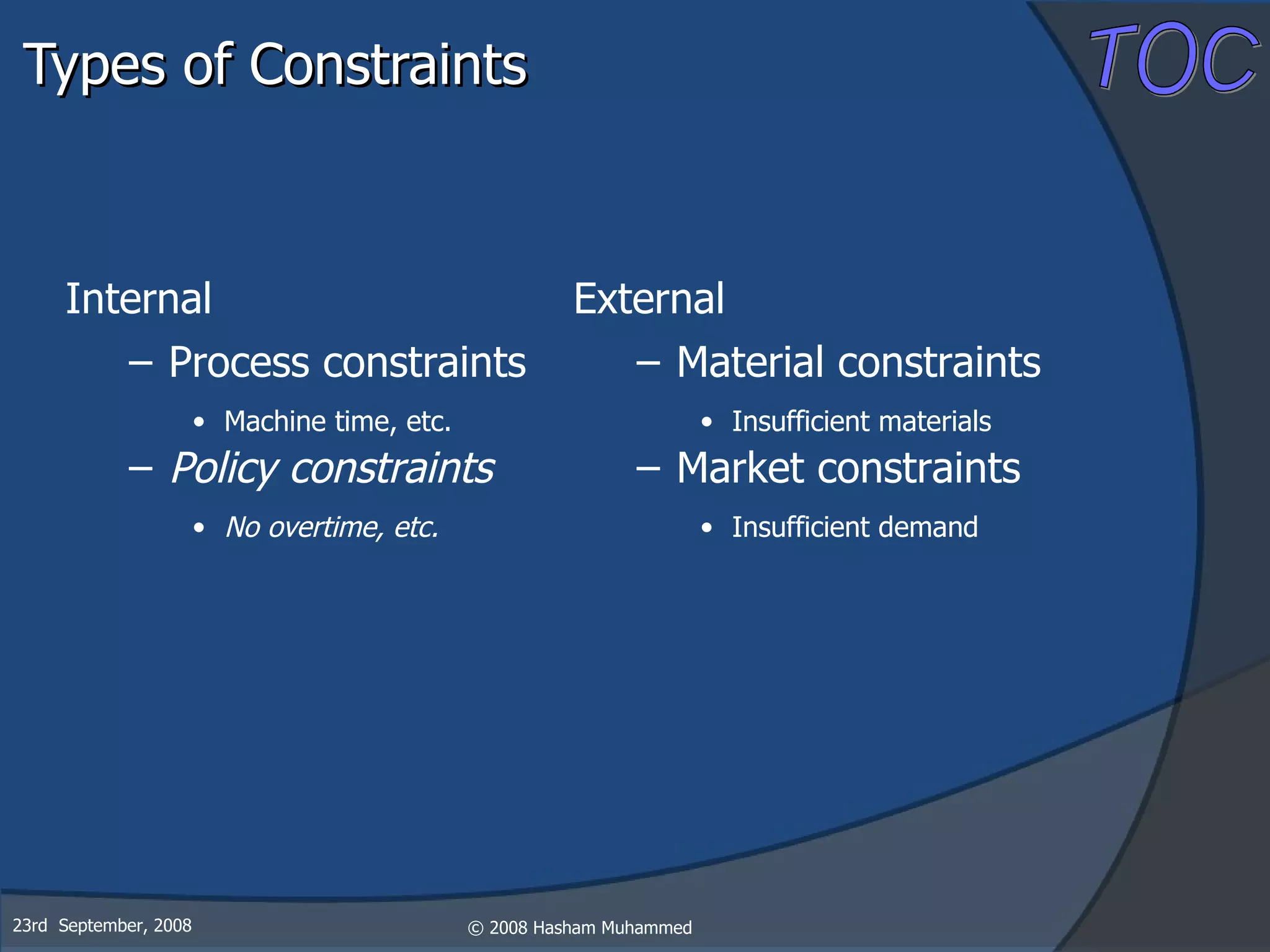
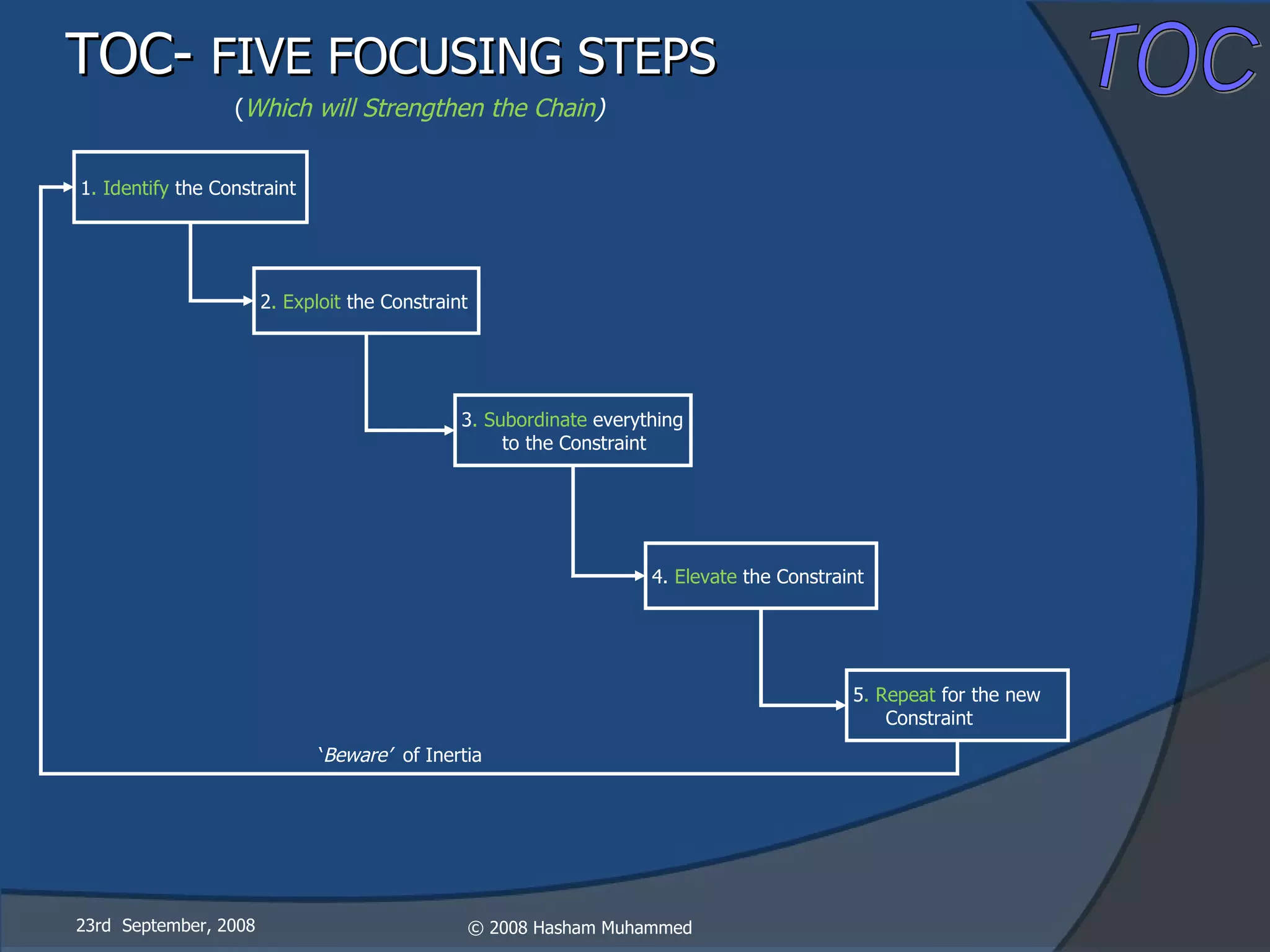
This document presents the Theory of Constraints (TOC), emphasizing its management principles and the importance of understanding system constraints to achieve organizational goals. It outlines a five-step focusing process to identify and address constraints within a system, noting that there is only one constraint at any given time. The key takeaway is that improvement is continuous and leadership is vital in driving changes within the system.
![Introduction to Theory of Constraints Presented by Hasham Muhammed [email_address] 23rd September, 2008](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/IntroductiontoTOC-123288045465-phpapp01/75/Introduction-To-Theory-of-Constraints-1-2048.jpg)