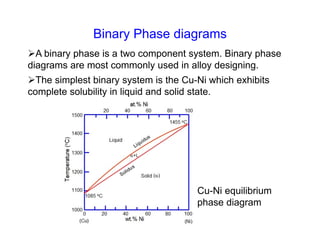
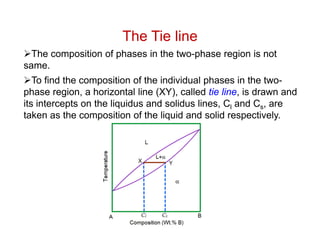
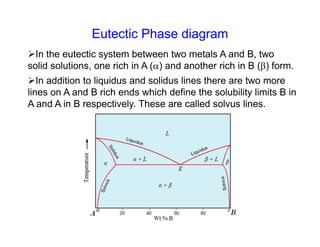
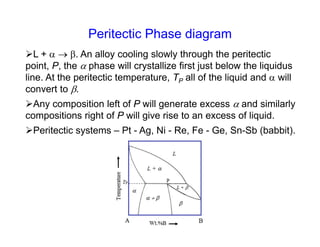
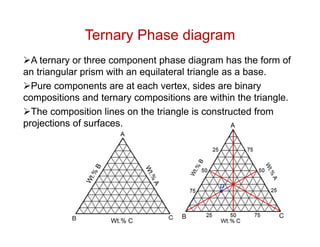
Phase diagrams provide information about the equilibrium conditions and transformations between different phases in a material system. They describe how the phases of a material vary with changes in temperature, pressure, and composition.
This document discusses key concepts related to phase diagrams including phases, the Gibbs phase rule, one-component and binary phase diagrams, eutectic and peritectic reactions, intermediate phases, ternary diagrams, and lever rule. It provides examples of phase diagrams for common material systems like water, Cu-Ni, Pb-Sn, Mg-Pb, and Cu-Zn. Cooling curves are also explained to illustrate phase transformations.