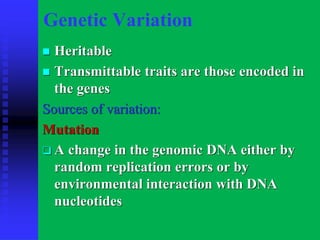
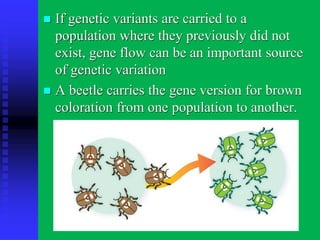
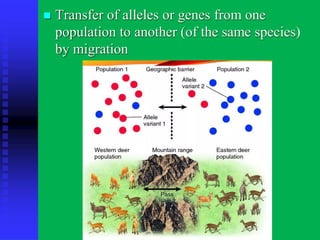
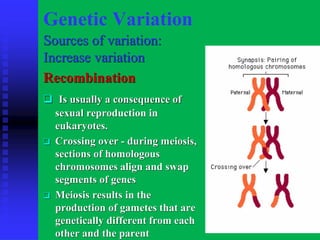
There are three main patterns of evolution: convergent evolution, divergent evolution, and coevolution. Convergent evolution occurs when unrelated species independently evolve similar traits due to adaptation to the same environment. Divergent evolution is when species with a common ancestor evolve differences in traits over time. Coevolution is when two species influence each other's evolution, such as through a predator-prey relationship. Genetic variation within populations is driven by mutation, recombination, gene flow, and genetic drift, and this variation provides the raw material for natural selection to act upon as populations adapt to their environments over generations.