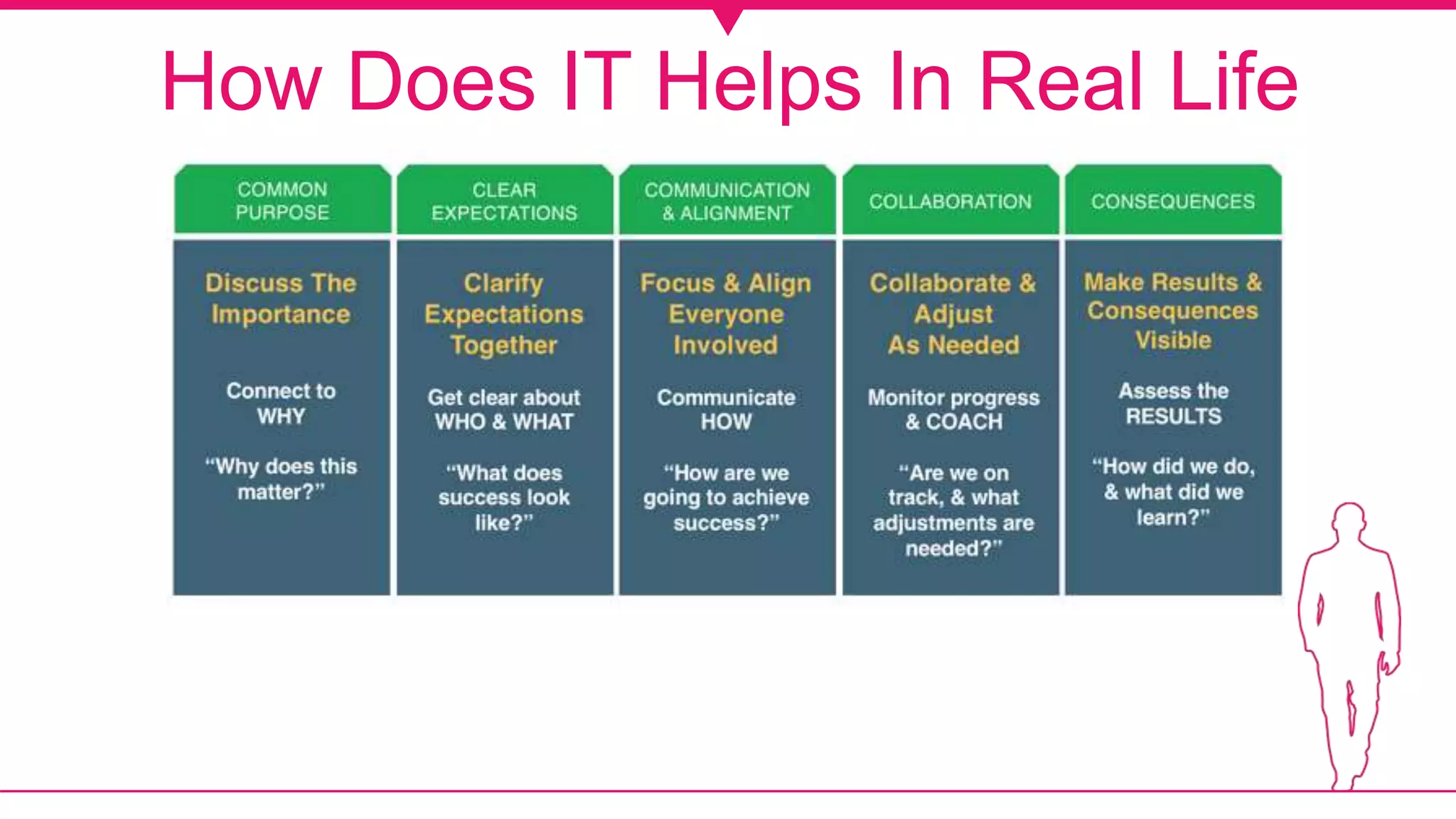
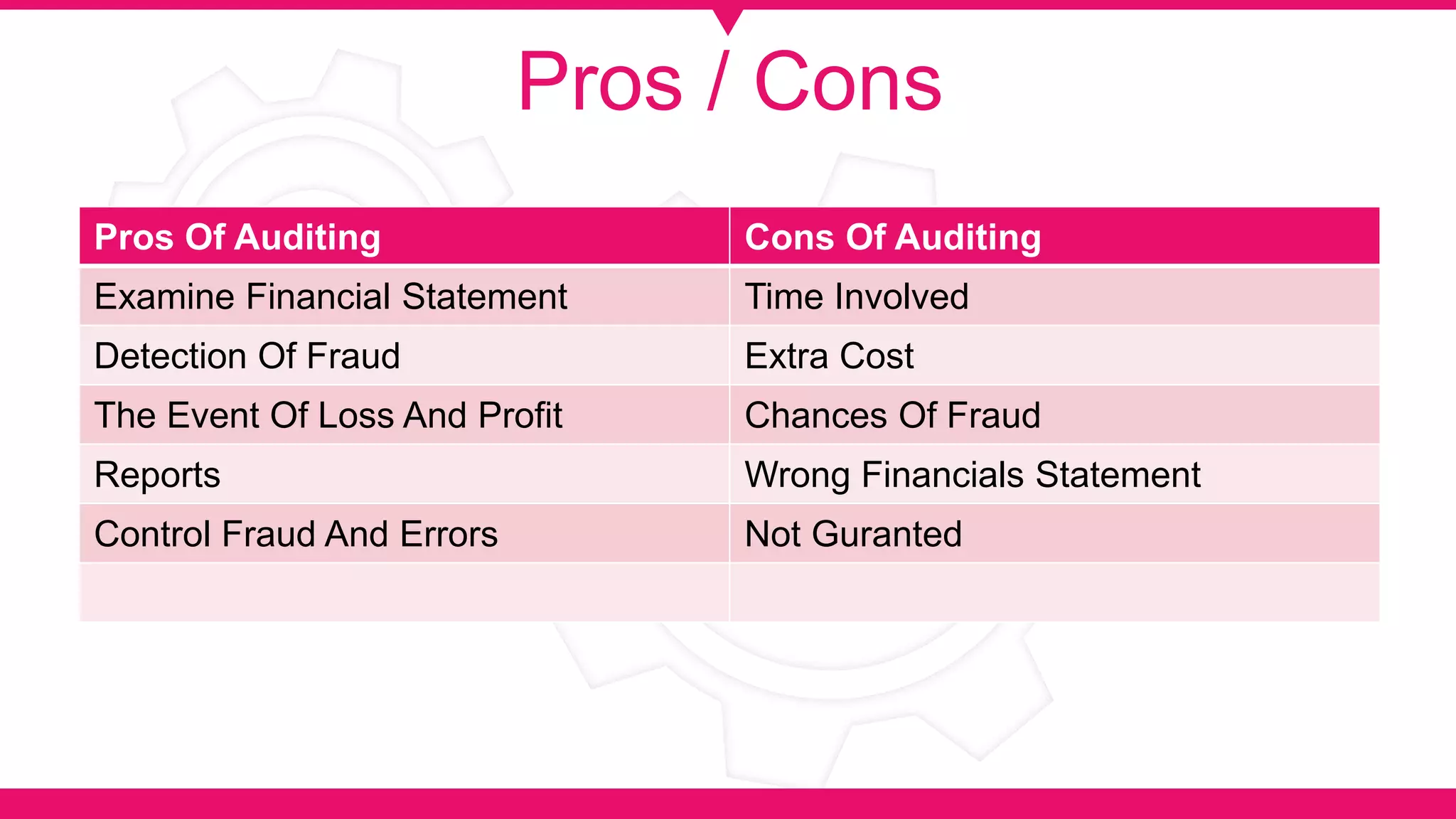
The document discusses the concept of accountability, emphasizing the obligation of organizations or individuals to account for their actions and accept responsibility for failures. It explains different types of auditing, including internal and external audits, detailing their purposes, processes, and the common errors that can occur. The text also outlines the pros and cons of auditing in terms of financial accuracy and operational efficiency.