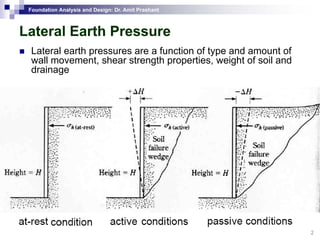
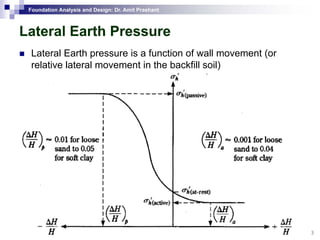
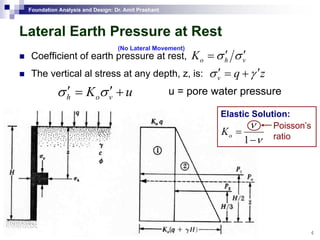
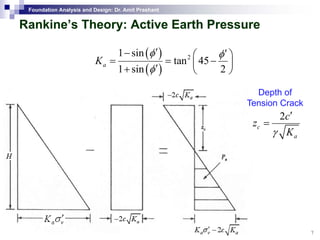
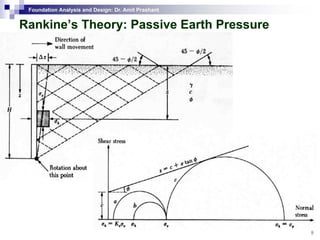
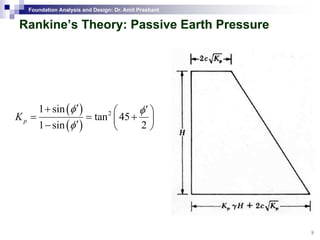
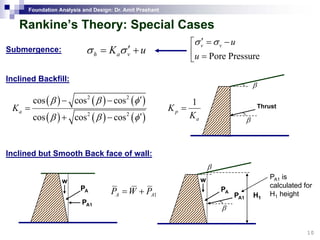
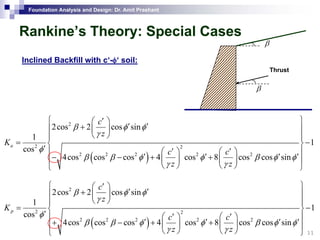
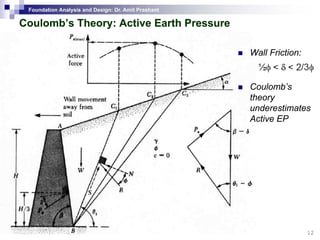
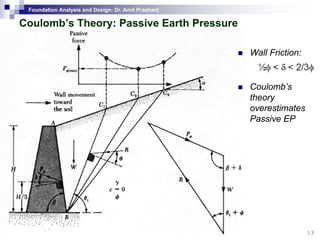
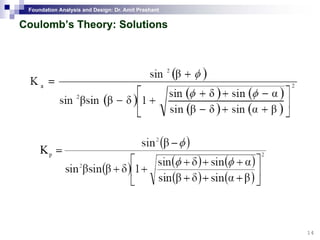
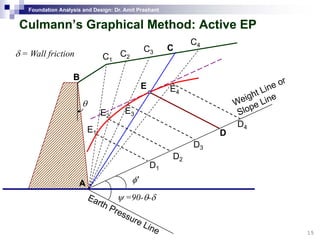
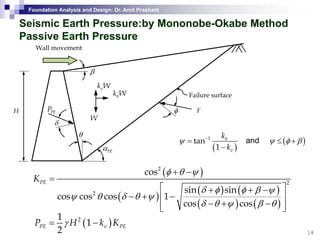
This document discusses lateral earth pressure and methods for calculating active and passive earth pressures on retaining walls. It introduces the concepts of earth pressure at rest, Rankine's theory, and Coulomb's theory for calculating lateral earth pressures. It also describes the Mononobe-Okabe method for calculating seismic earth pressures as a function of factors like soil properties, wall geometry, and ground acceleration. Graphical methods like Culmann's method are also presented for determining active and passive earth pressures.