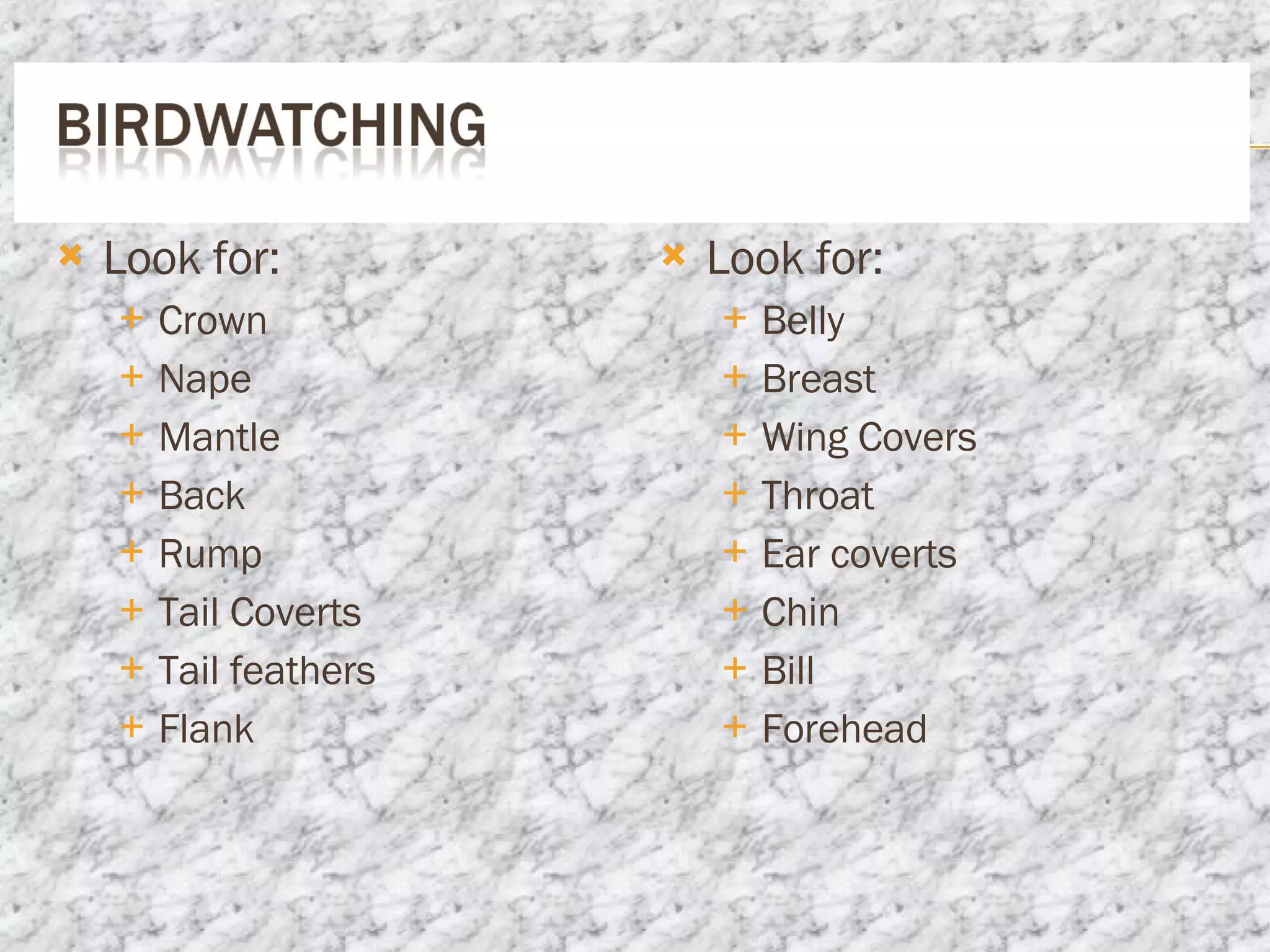
To identify birds, an ornithologist must observe their behaviors, physical features, habitats, and nests. The document outlines 5 steps for bird identification: 1) Determine if the bird lives on land or water, 2) Study the bird's habitat, 3) Examine characteristics of its nest, 4) Consider its size and shape, and 5) Analyze details of its bill such as length, width, and structure to determine if it eats plants or other animals. Close observation of many physical attributes is needed to properly identify each type of bird.