Embed presentation
Download to read offline


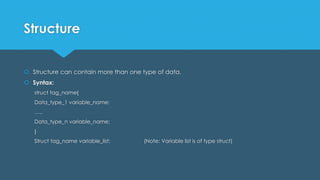

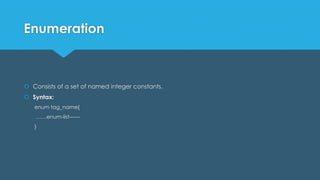

This document discusses derived data types in C including structures, unions, and enumerations. Structures allow grouping different data types together under one name. Unions share the same memory location for different variable types. Enumerations define a set of named integer constants.




