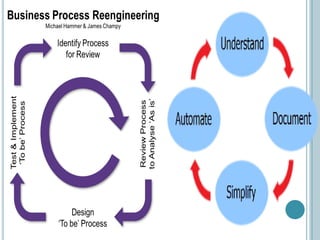
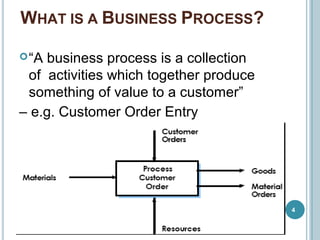
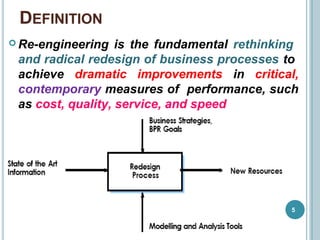
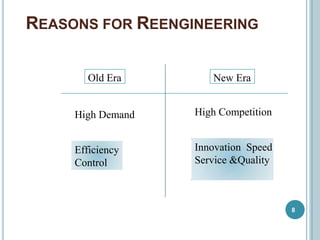
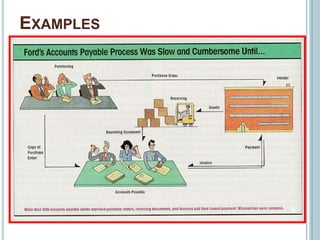
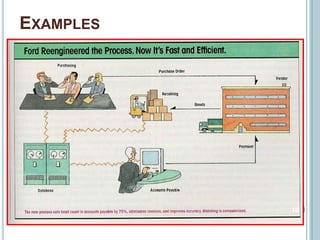
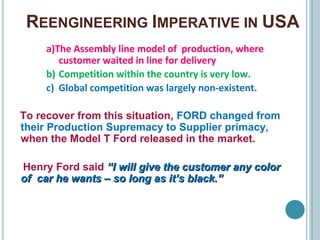
Business Process Re-engineering (BPR) involves fundamentally rethinking and radically redesigning business processes to improve performance in areas such as cost, quality, service, and speed. It differs from reorganization and downsizing, focusing instead on eliminating unnecessary work and empowering employees. The necessity for BPR has been highlighted by examples from companies like Ford and the transformation of manufacturing practices, driven by competitive pressures and customer-focused approaches.