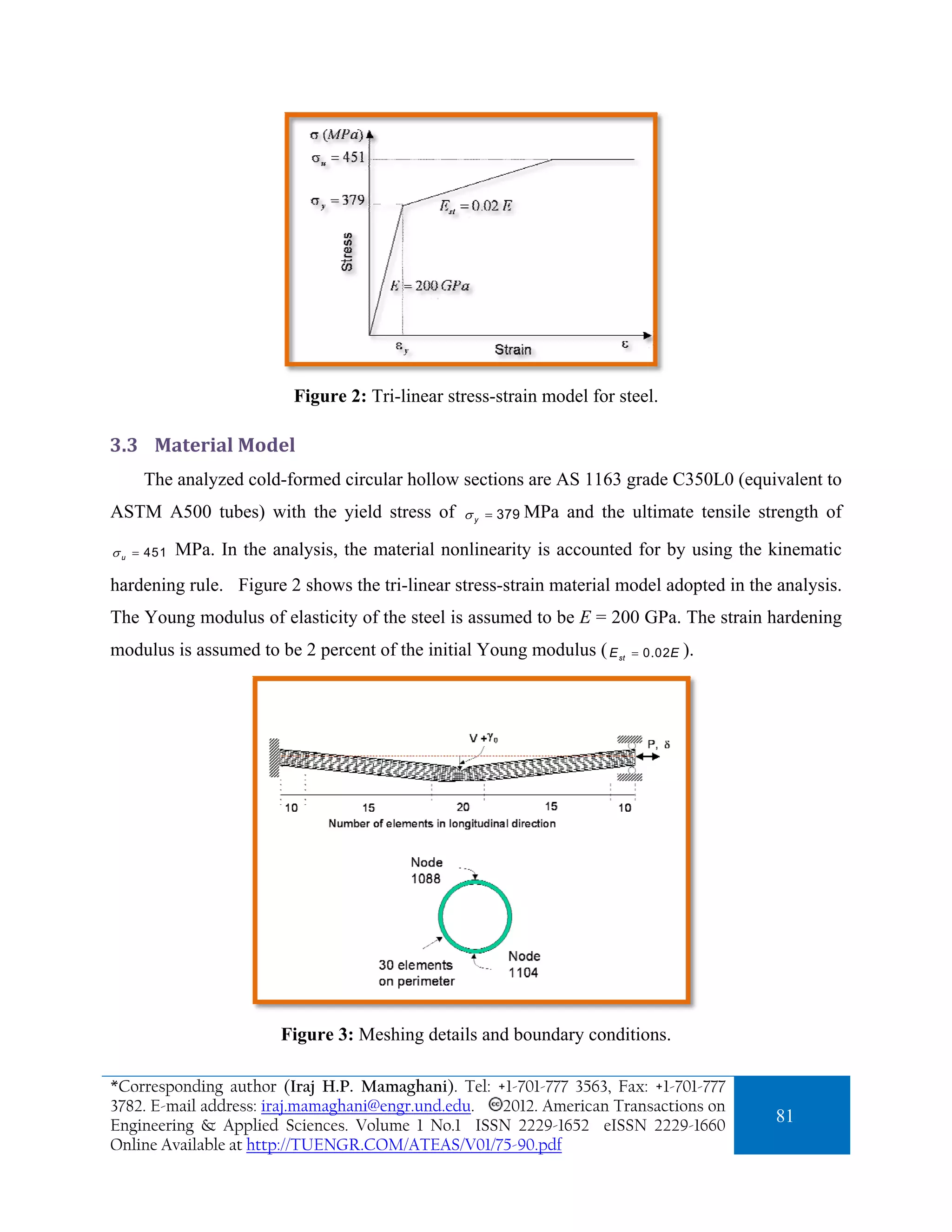
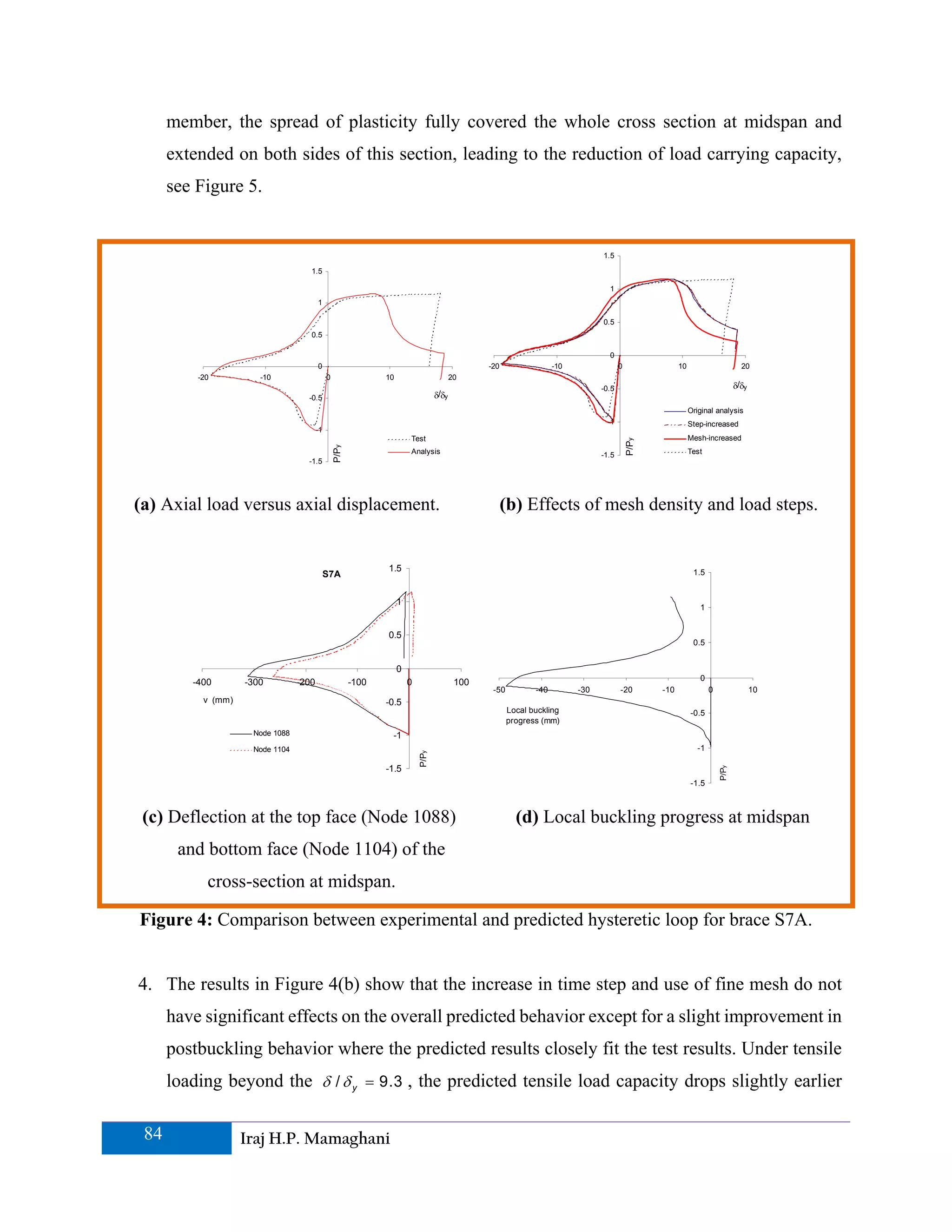
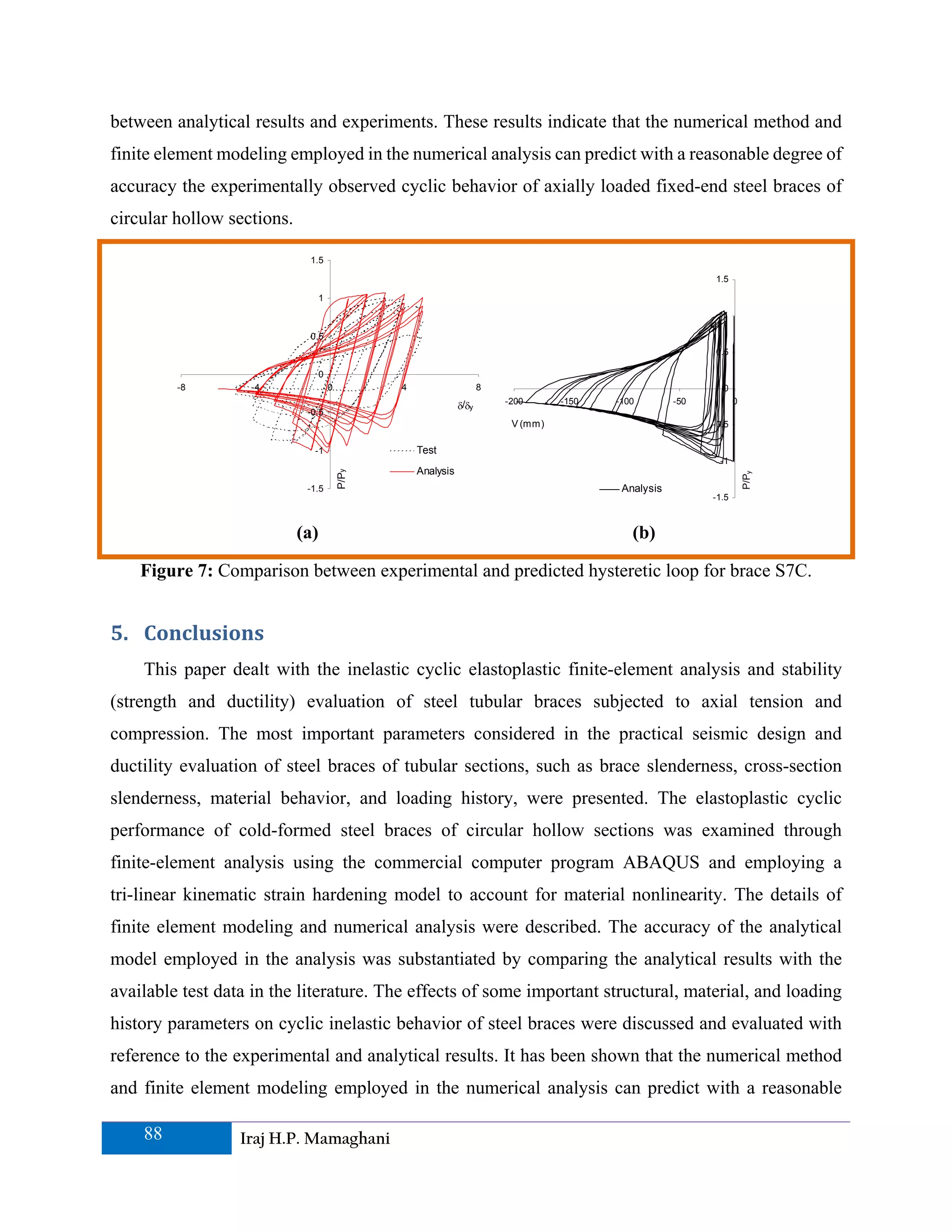
This paper presents a finite element analysis of the cyclic elastoplastic behavior and stability evaluation of steel tubular braces subjected to axial loads. It explores critical design parameters affecting ductility and inelastic behavior under cyclic loading, comparing analytical results with experimental data to ensure accuracy. The study emphasizes the importance of these braces within seismic design, suggesting that both tensile and compressive forces enhance bracing performance during earthquakes.