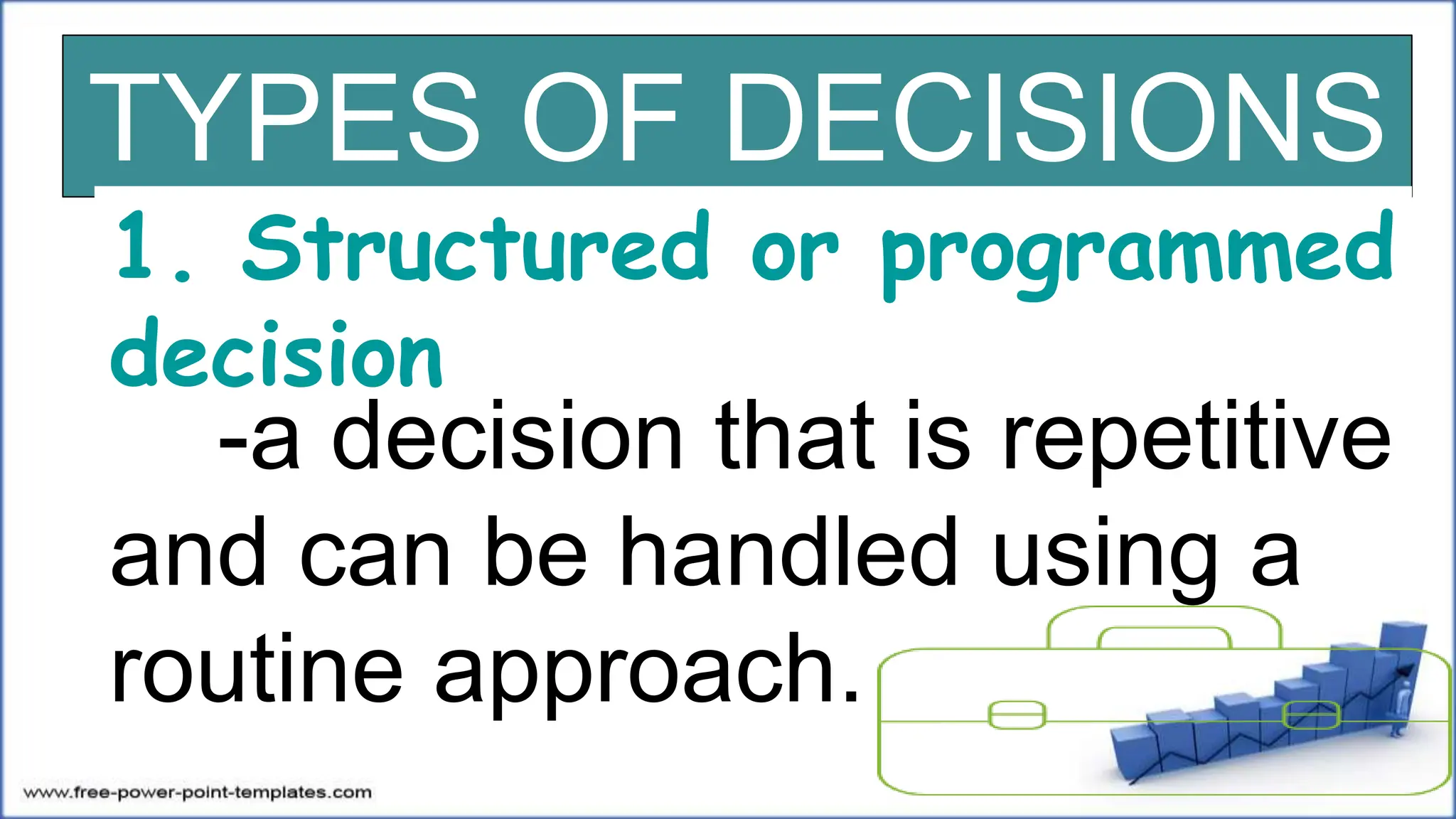
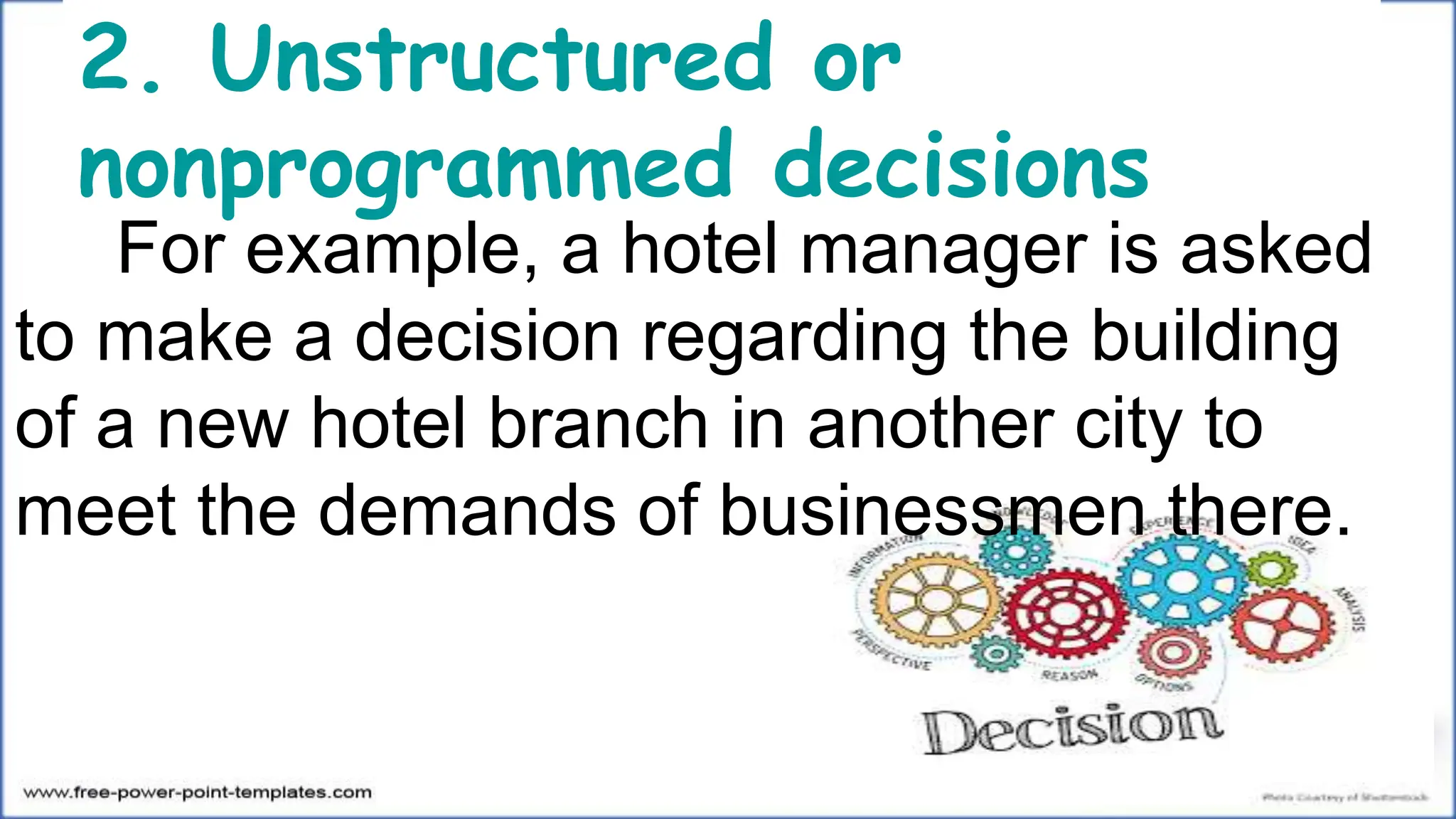
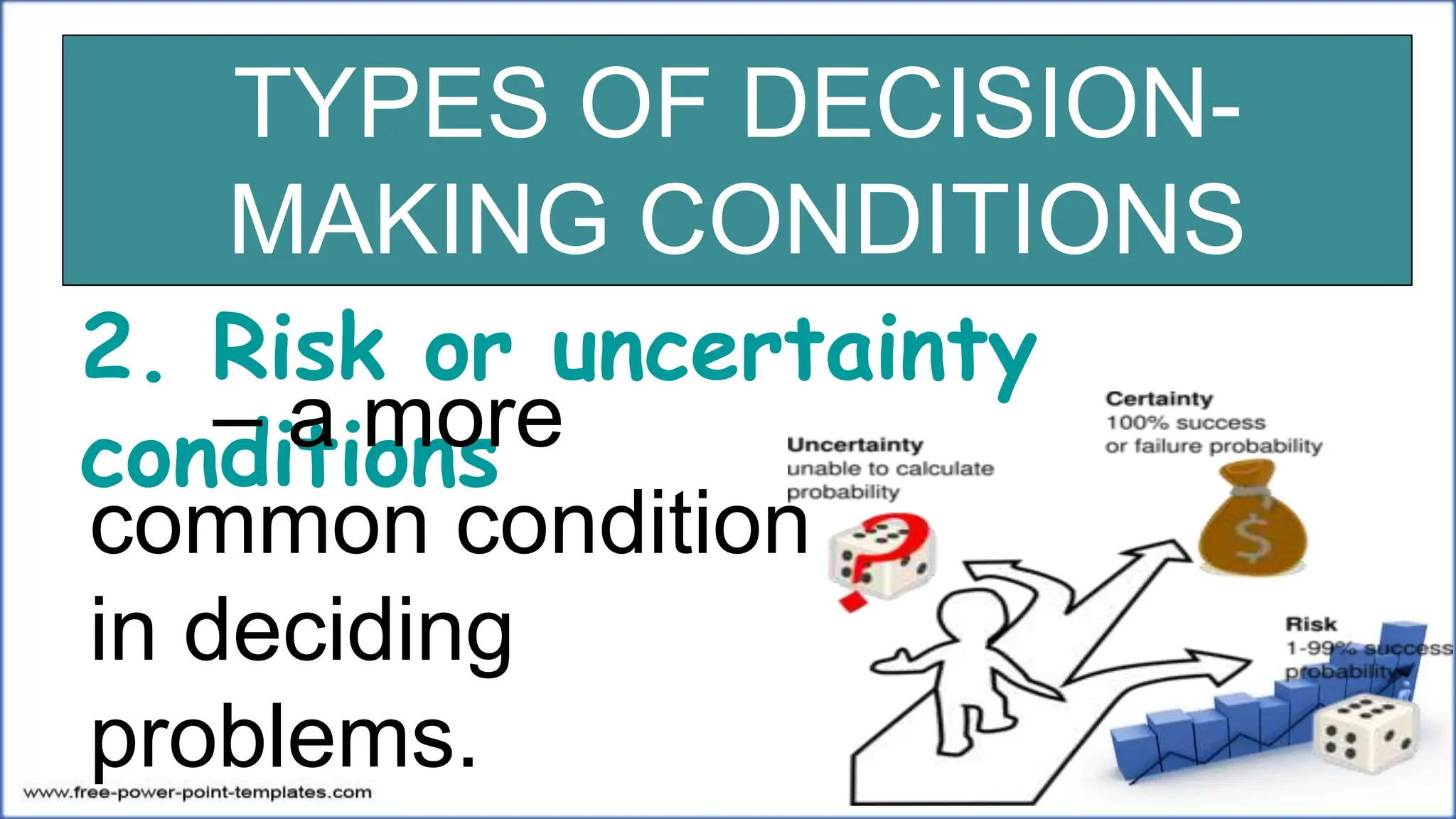
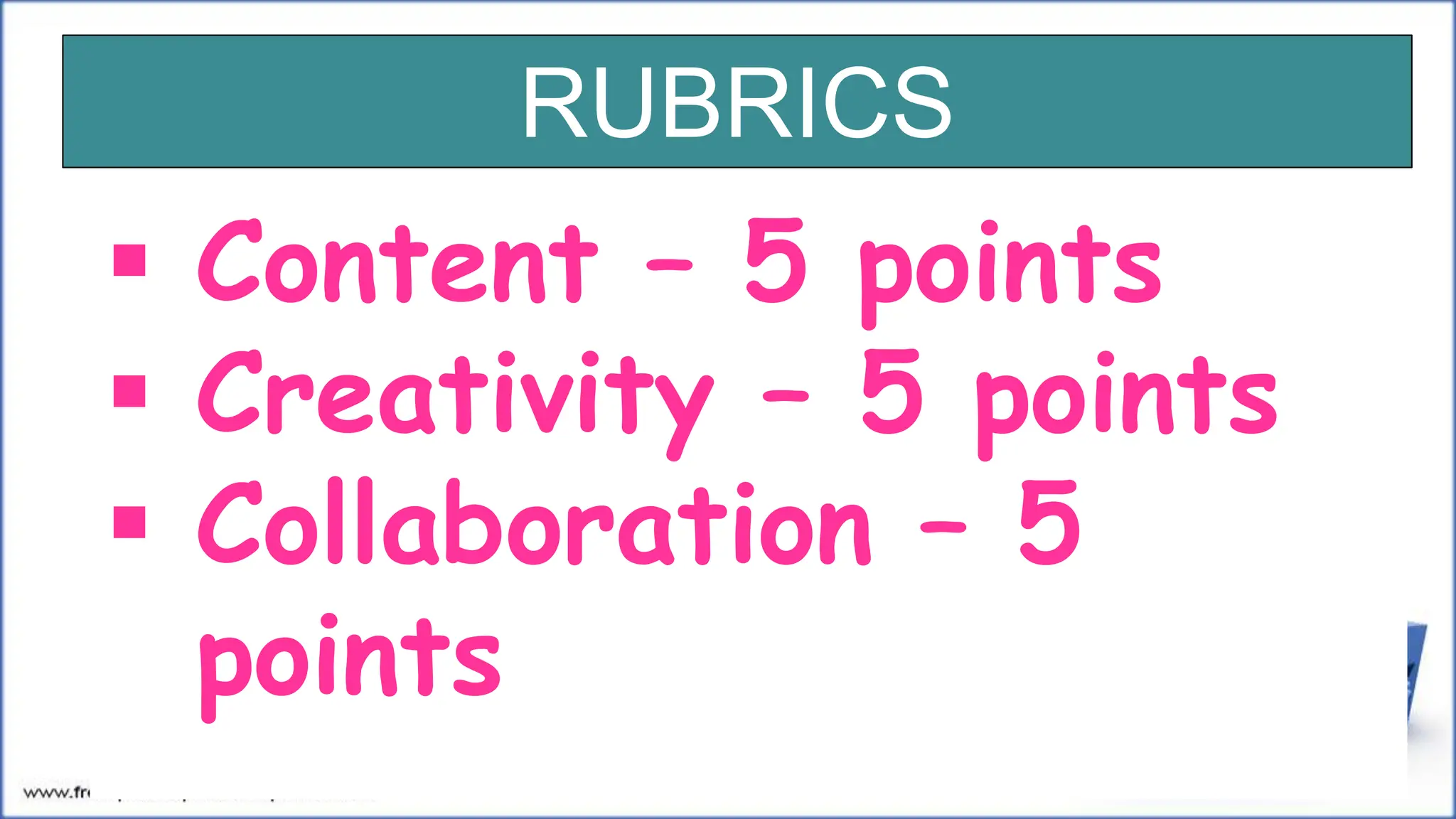
This document discusses decision making, including defining it as a process starting with problem identification and ending with evaluating implemented solutions. It outlines two types of decisions - structured/programmed decisions which are routine, and unstructured/nonprogrammed decisions which have incomplete information. It also describes two decision making conditions - certainty, where all alternatives' results are known, and risk/uncertainty. The document concludes by outlining eight steps in the decision making process and providing examples for each concept.