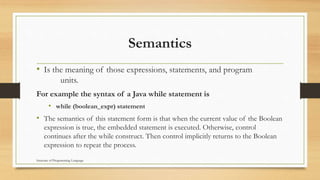
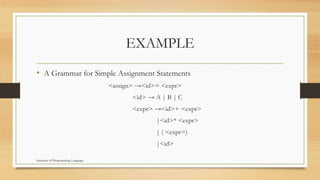
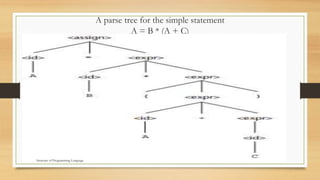
This document describes syntax and semantics in programming languages. It defines syntax as the form of expressions, statements, and program units, while semantics refers to their meaning. It provides examples of syntax rules for Java statements in Backus-Naur Form (BNF) and describes how BNF is used to formally define a programming language's syntax through rules and derivations. It also discusses parse trees for representing the syntactic structure of statements generated from a grammar.