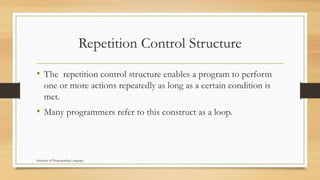
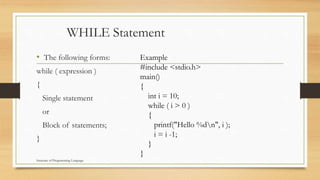
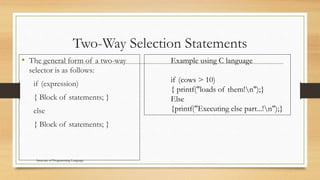
This document discusses various control structures in programming languages including sequence, selection, and repetition structures. It provides examples of each structure in C language. Sequence structures execute statements in order. Selection structures like if-else and switch direct program flow based on conditions. Repetition structures like for, while, and do-while loops repeatedly execute statements as long as a condition is true. Unconditional branching uses goto to transfer control to another part of the program.










![N-WAY, OR MULTIPLE SELECTION
SWITCH
• This allows control to
flow through more
than one selectable
code segment on a
single execution.
General form is
switch( expression )
{
case constant-expression1: statements1;
[case constant-expression2: statements2;]
[case constant-expression3: statements3;]
[default : statements4;]
}
Structure of Programming Language](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9-170718152248/85/9-control-statement-12-320.jpg)