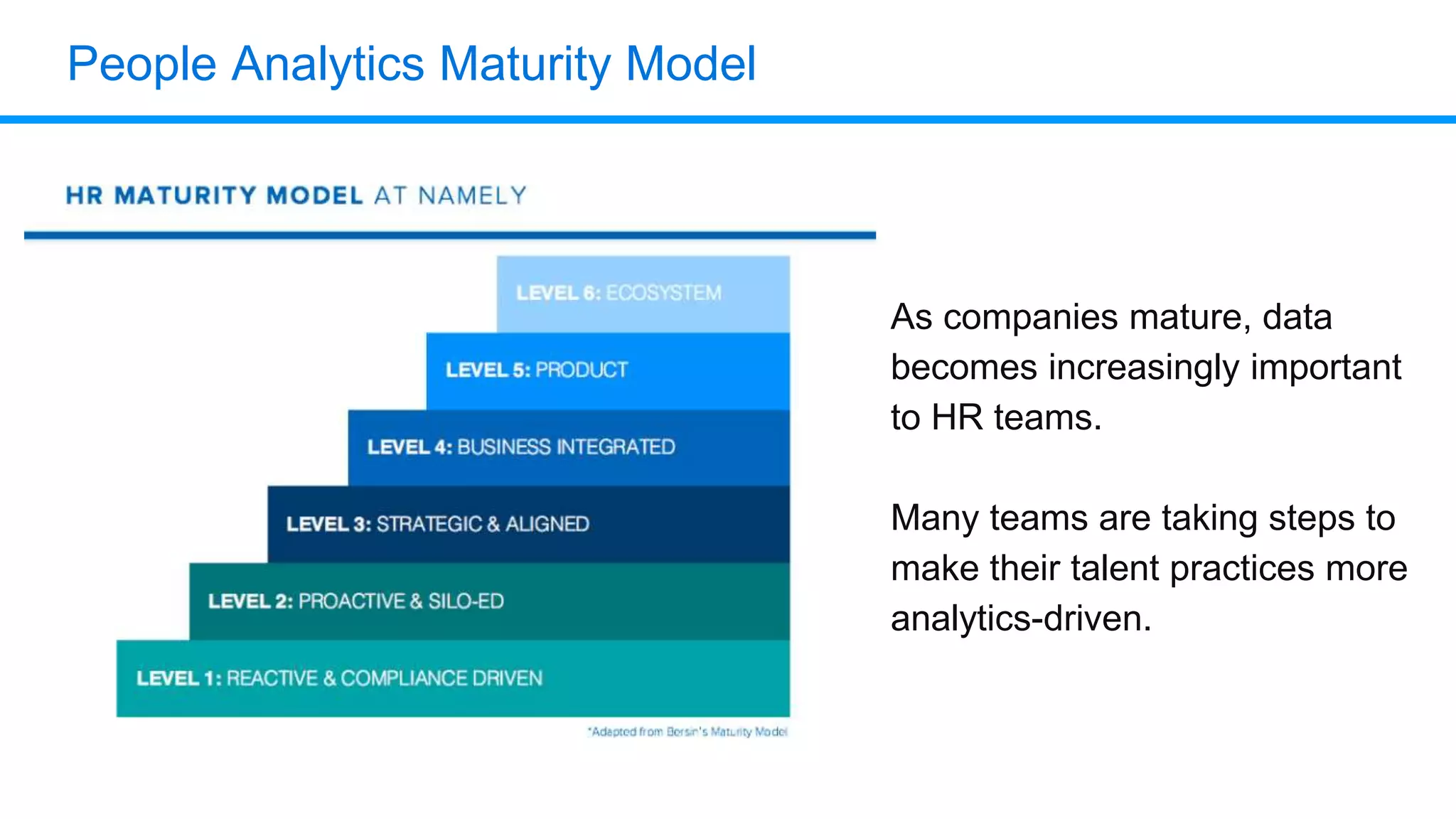
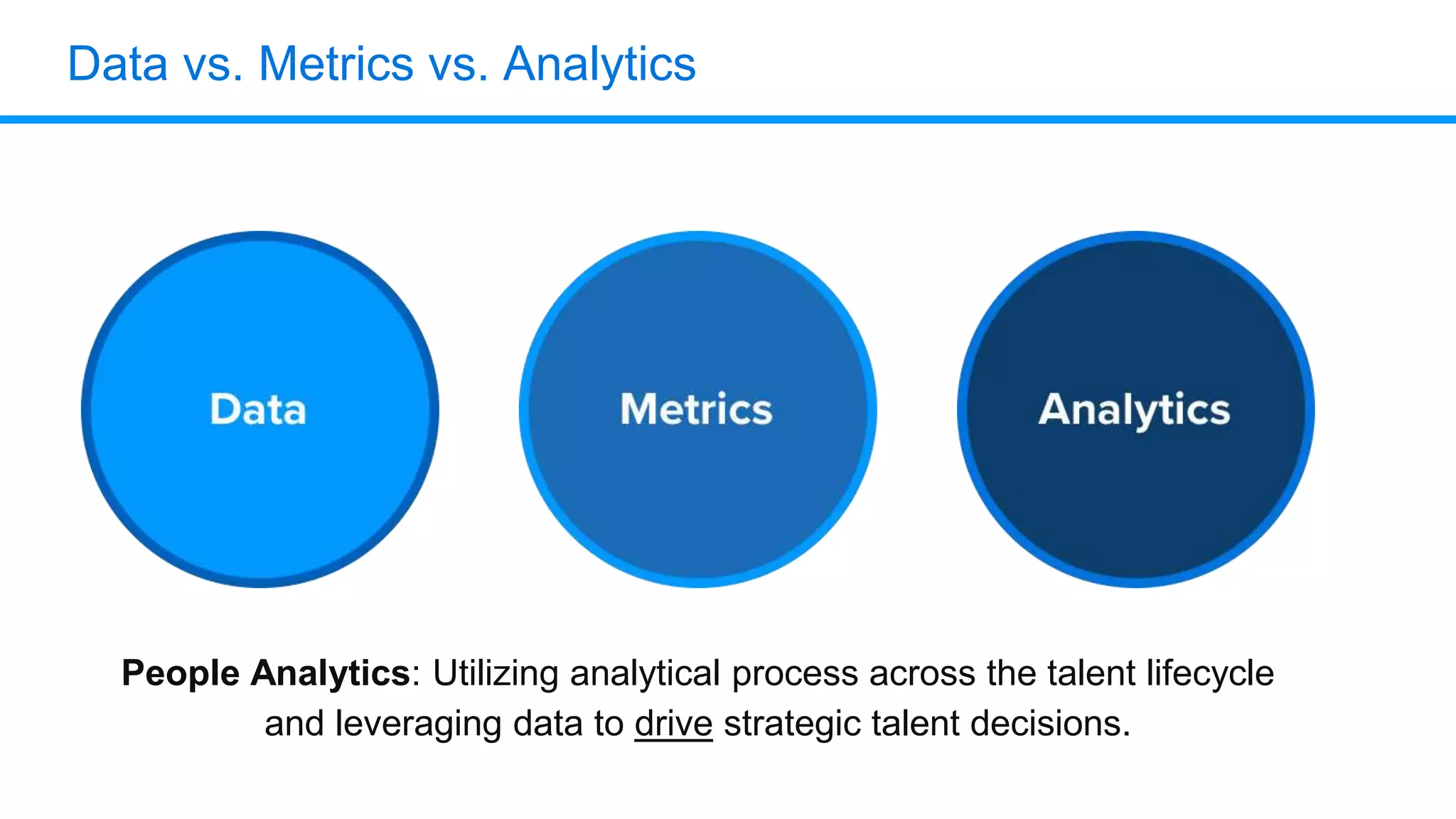
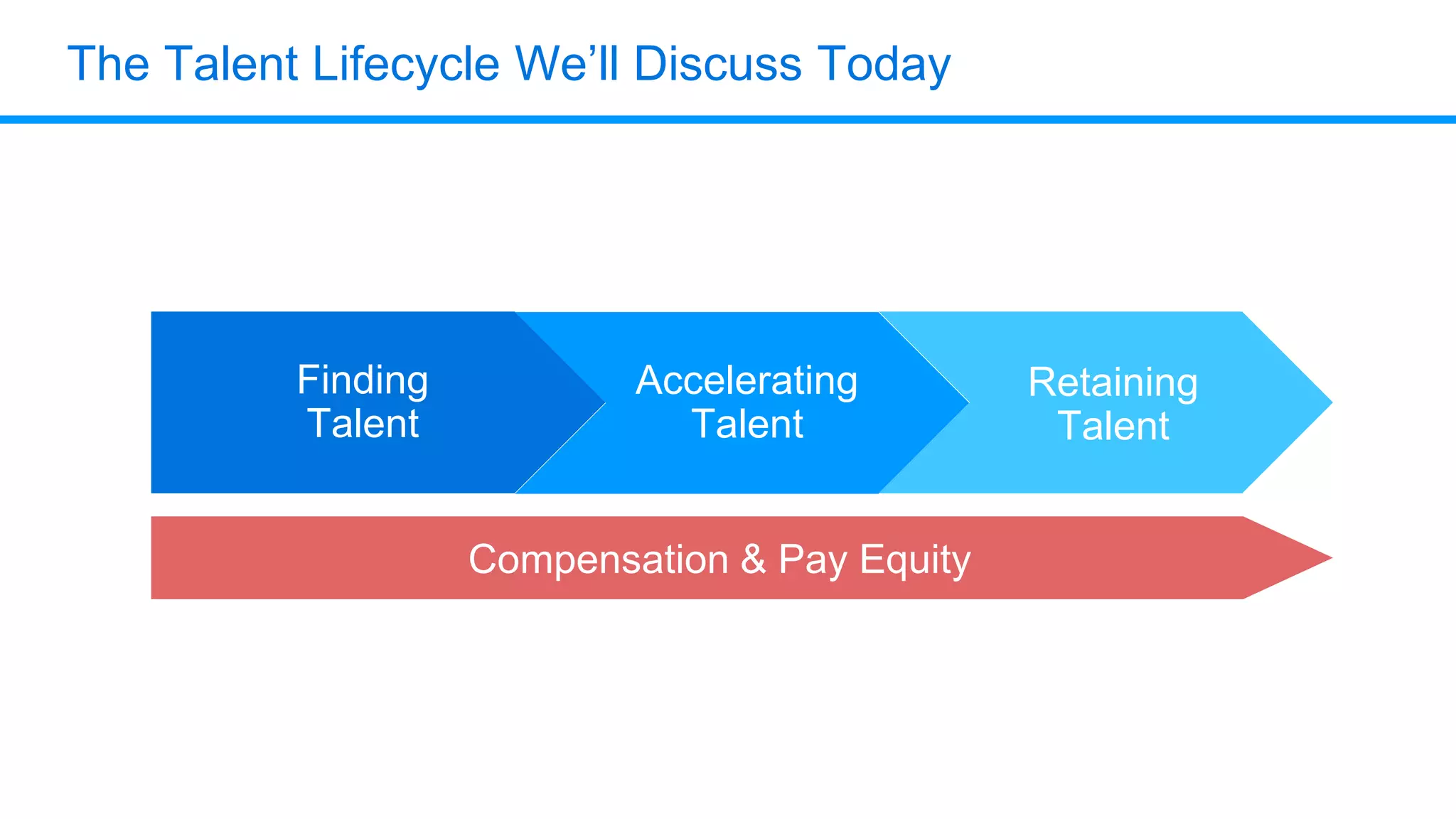
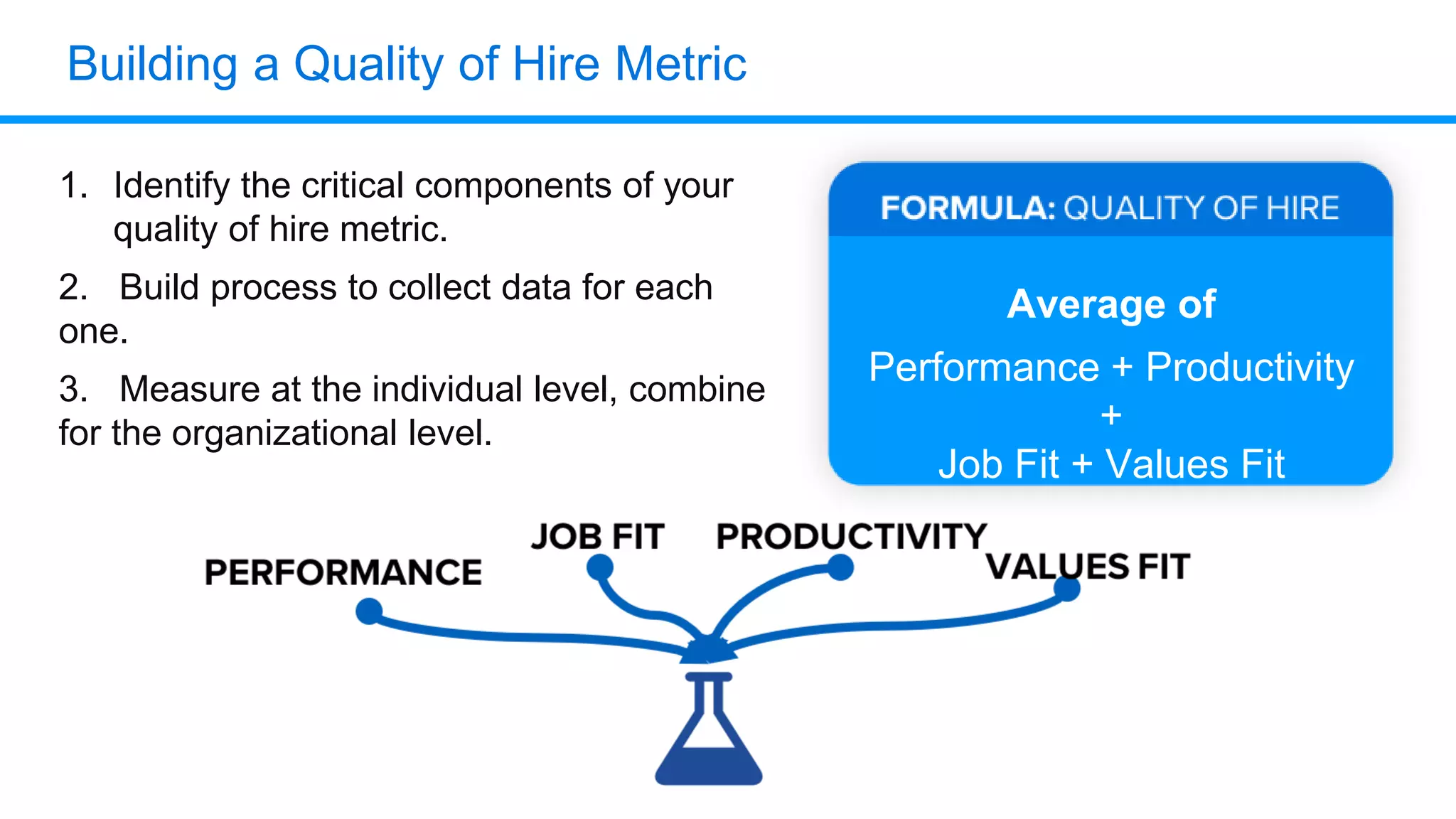
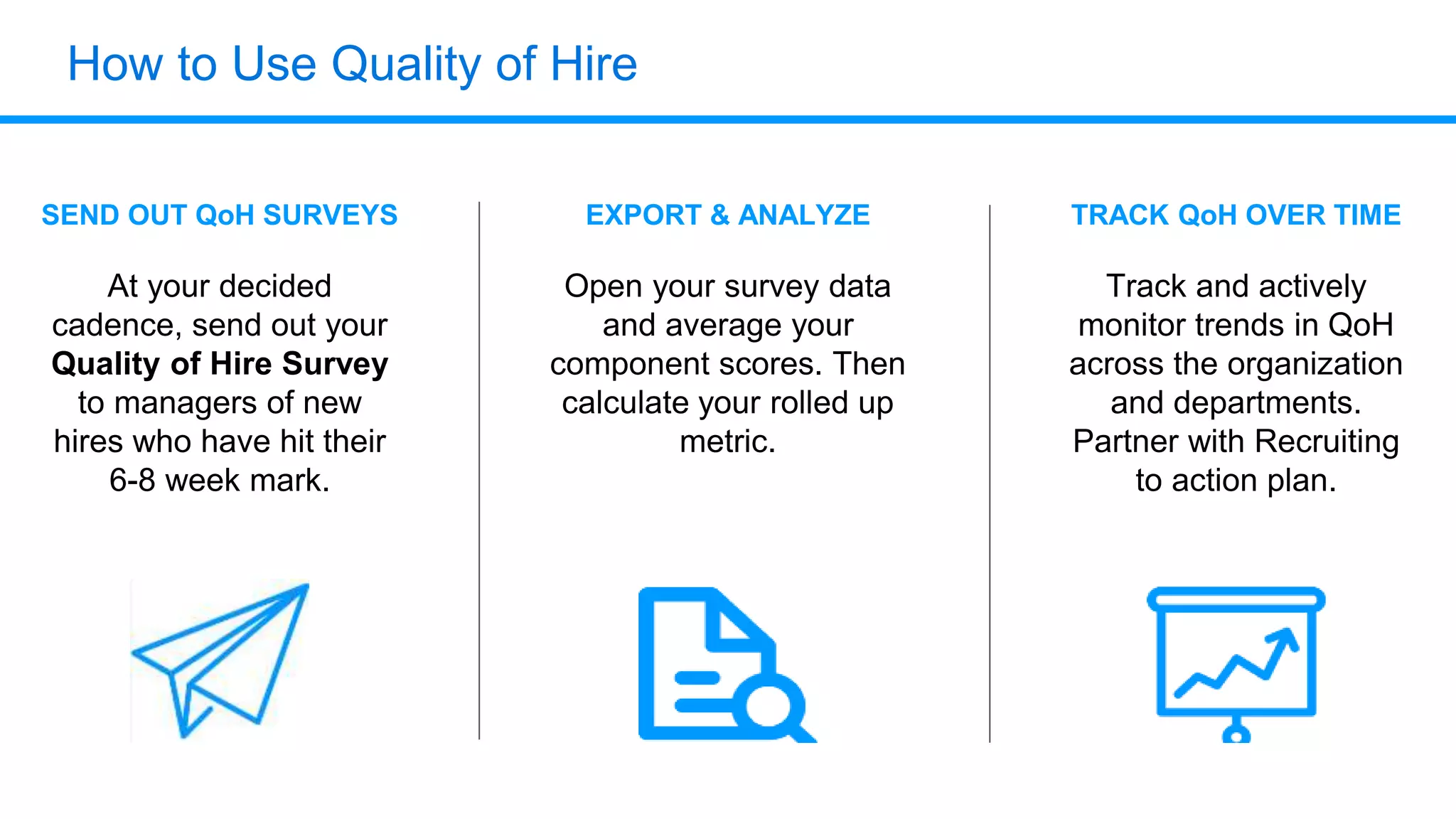
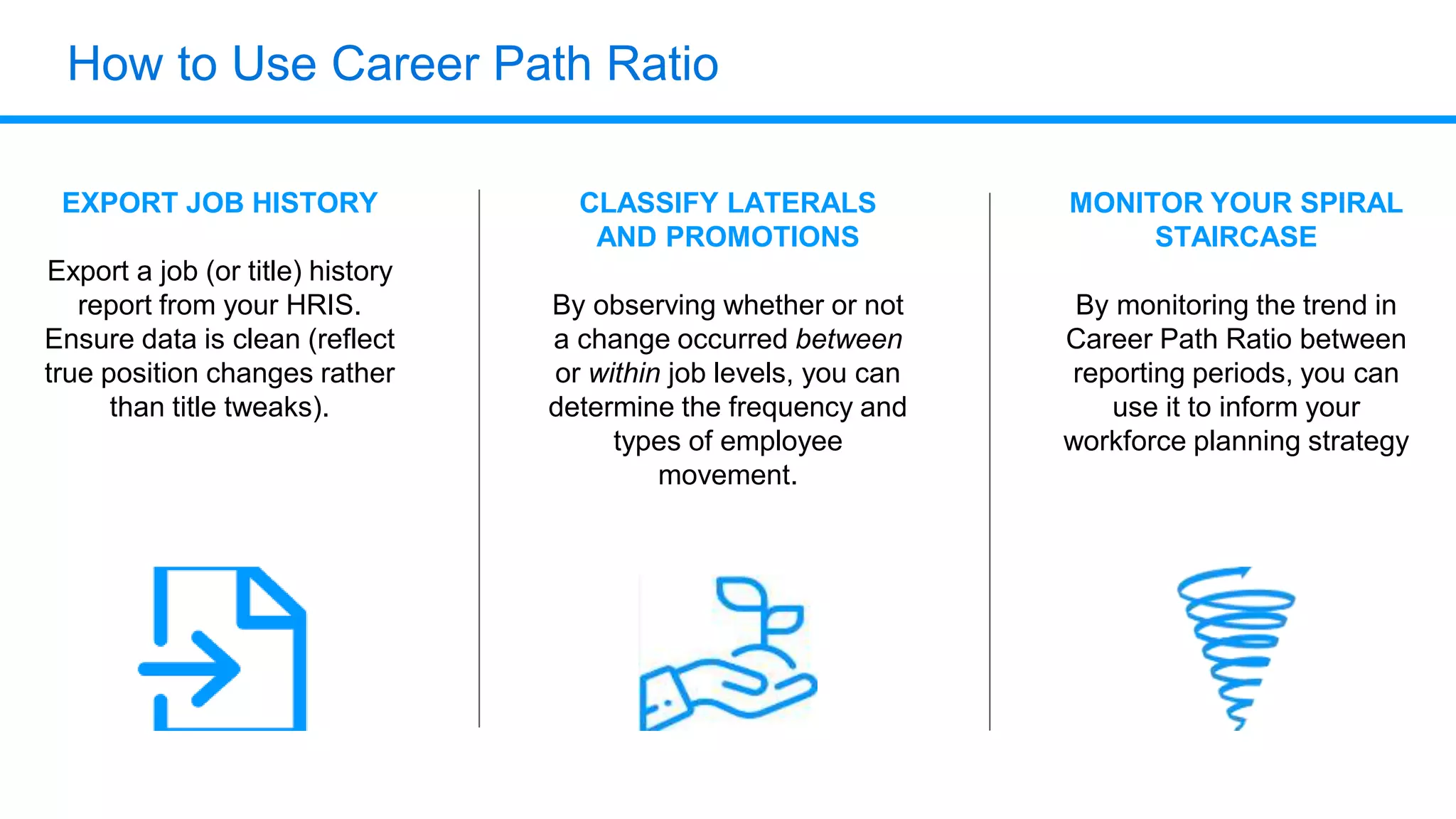
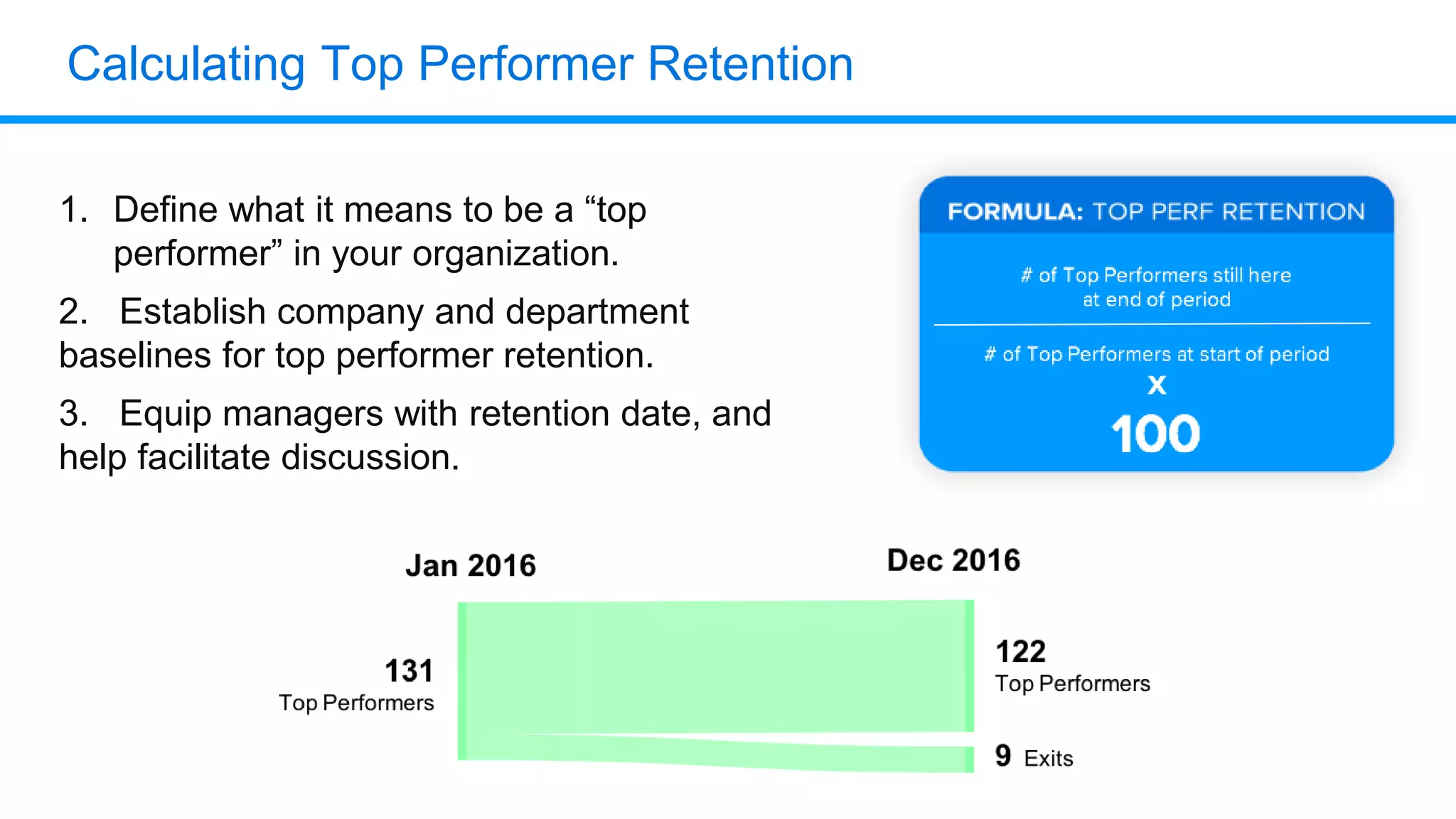
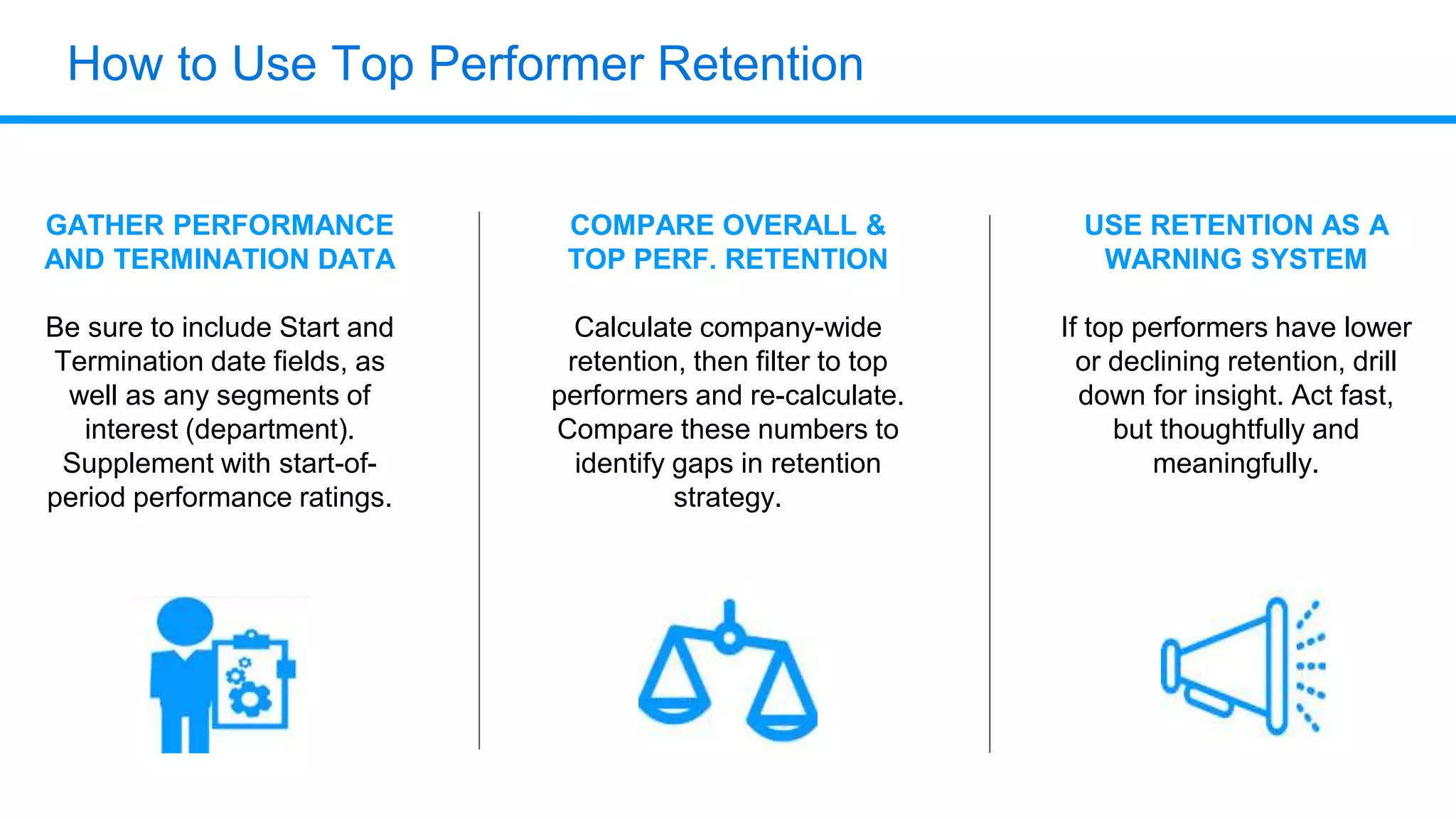
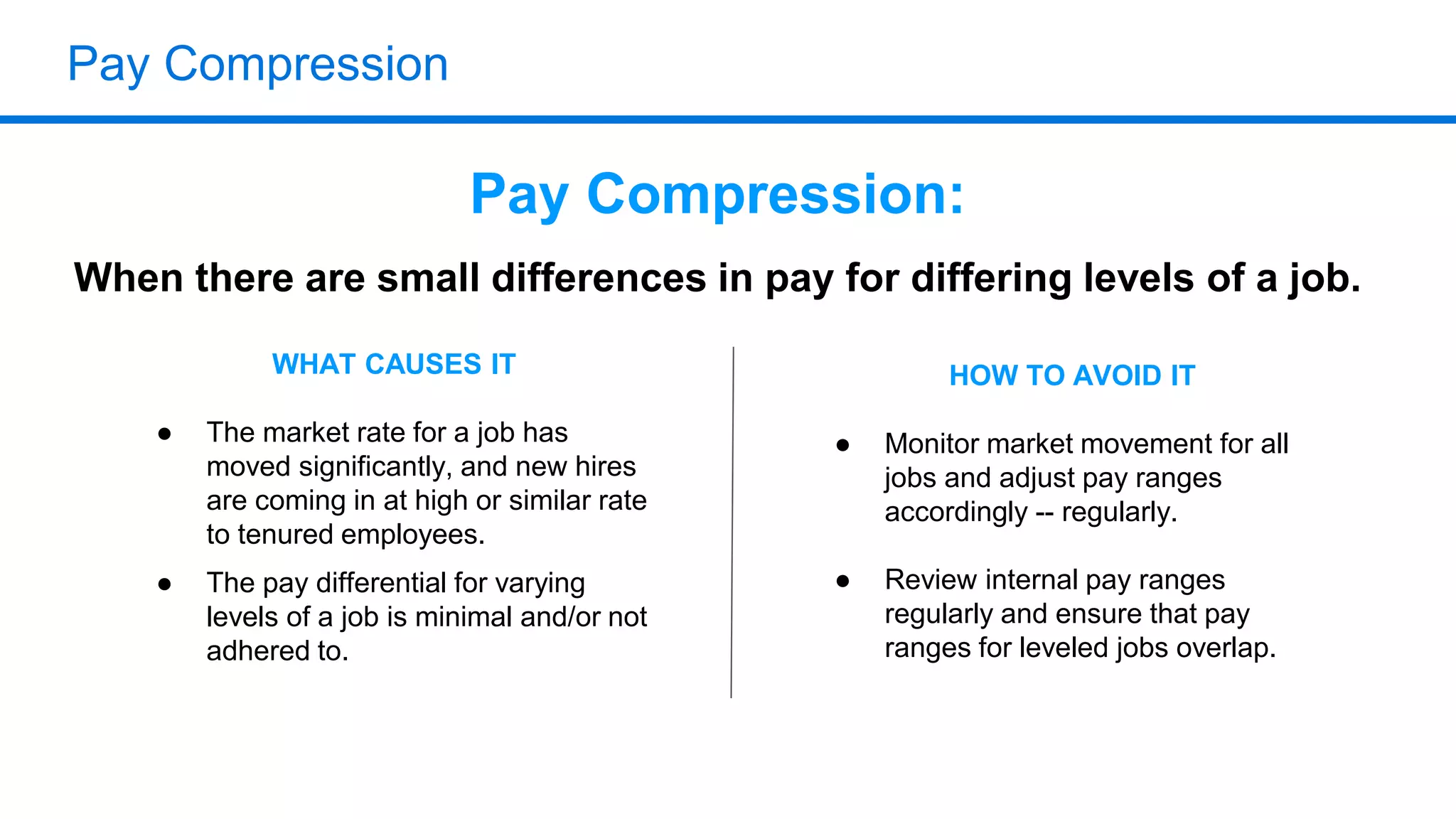
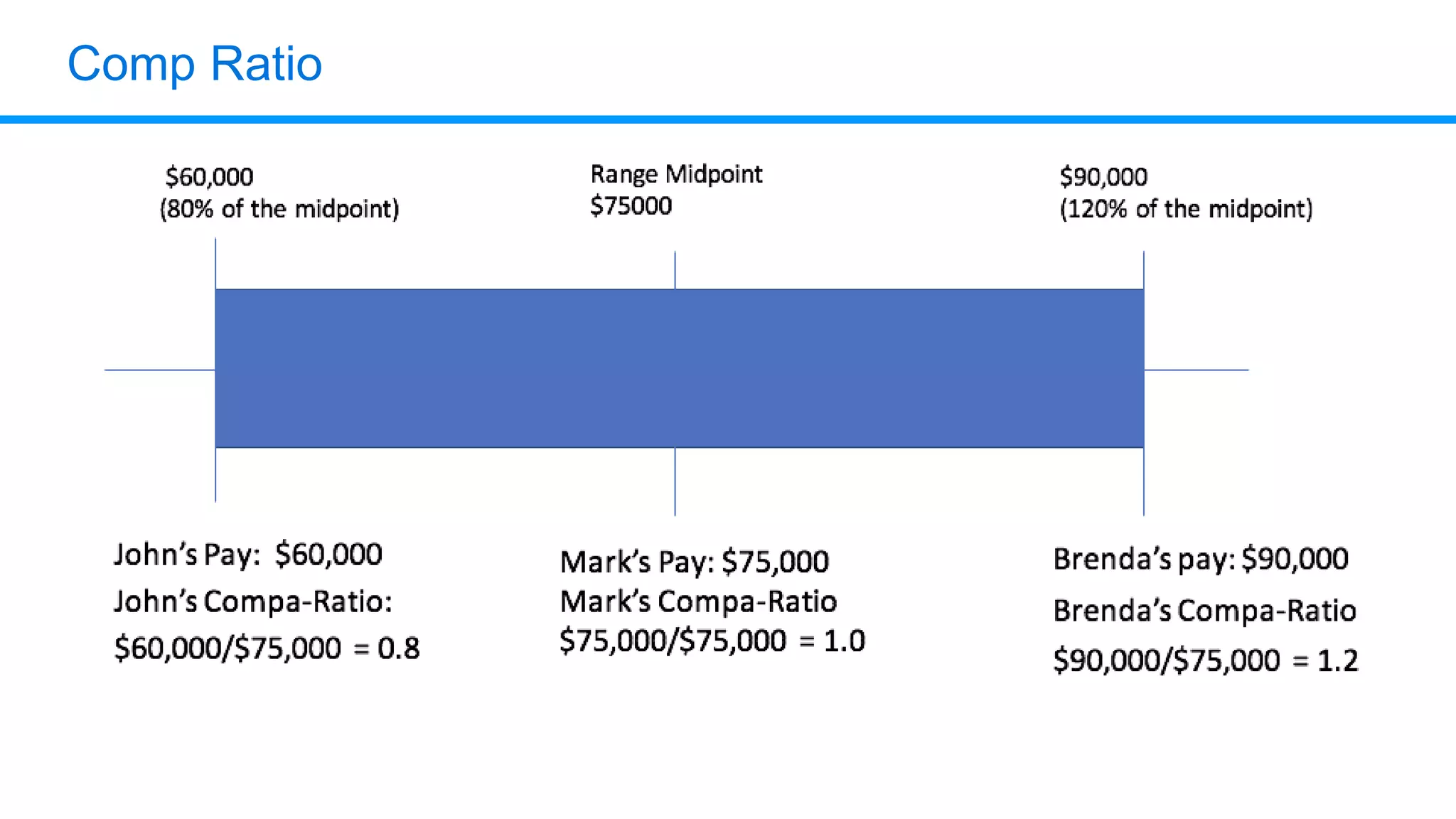
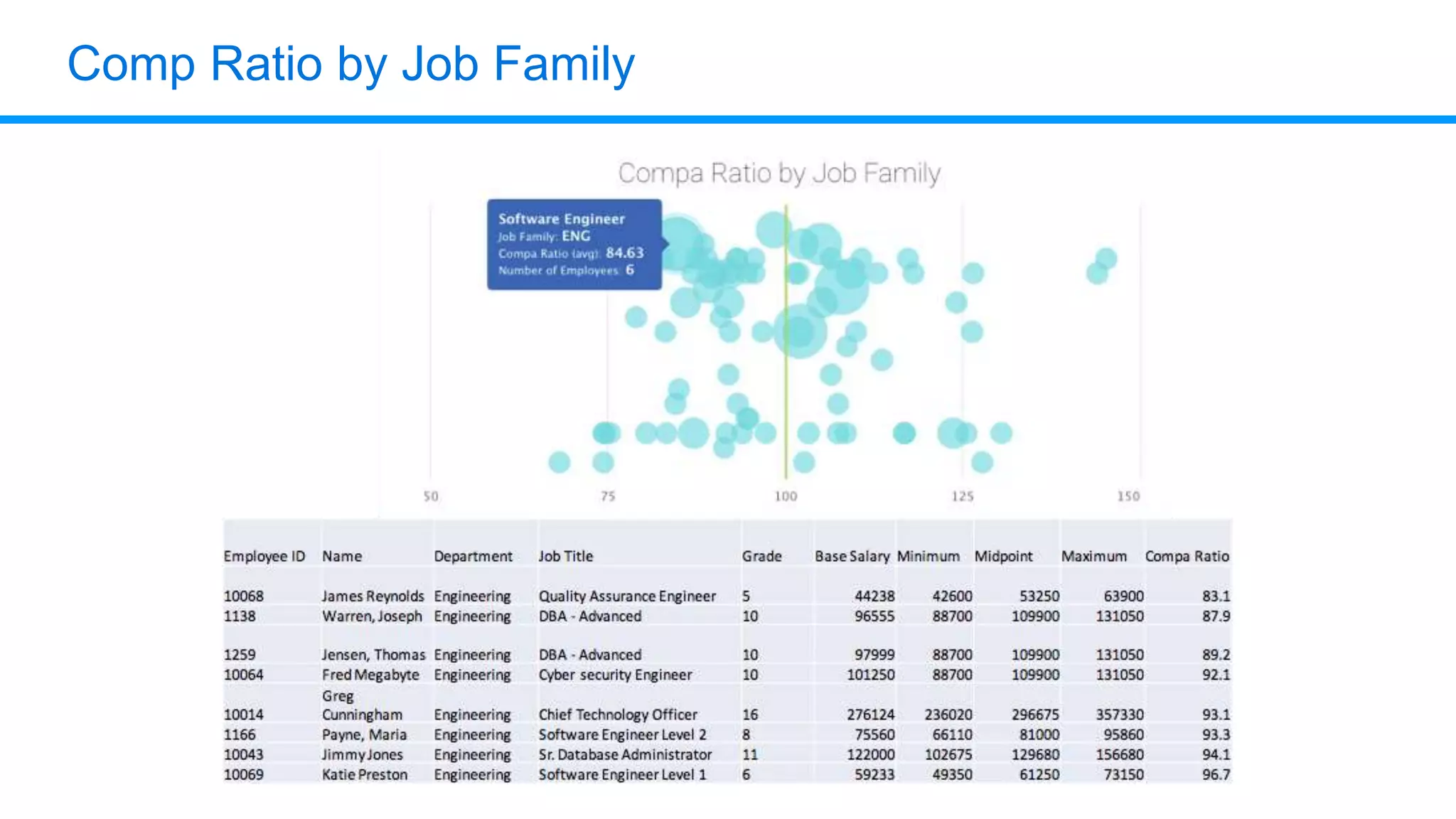
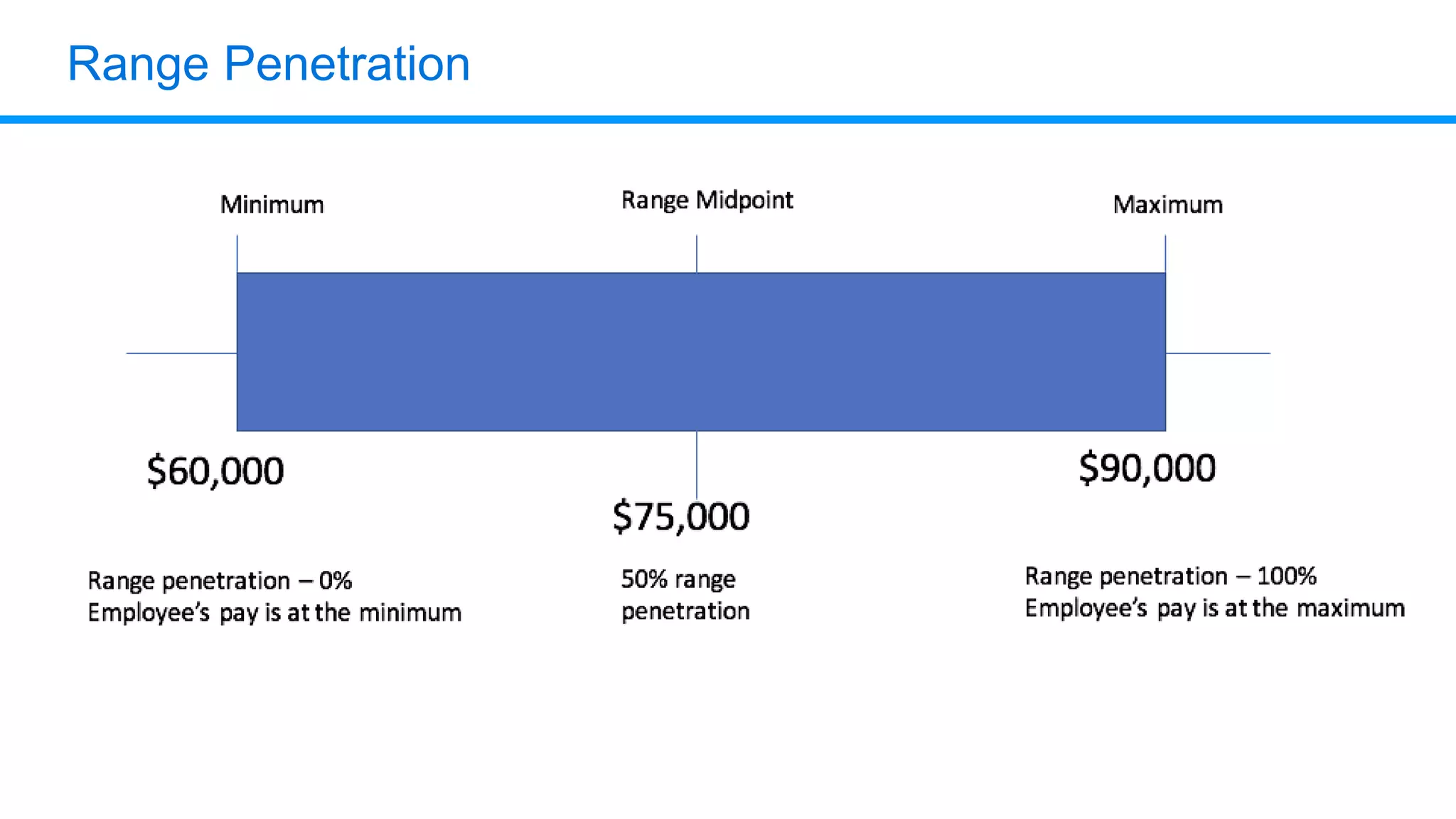
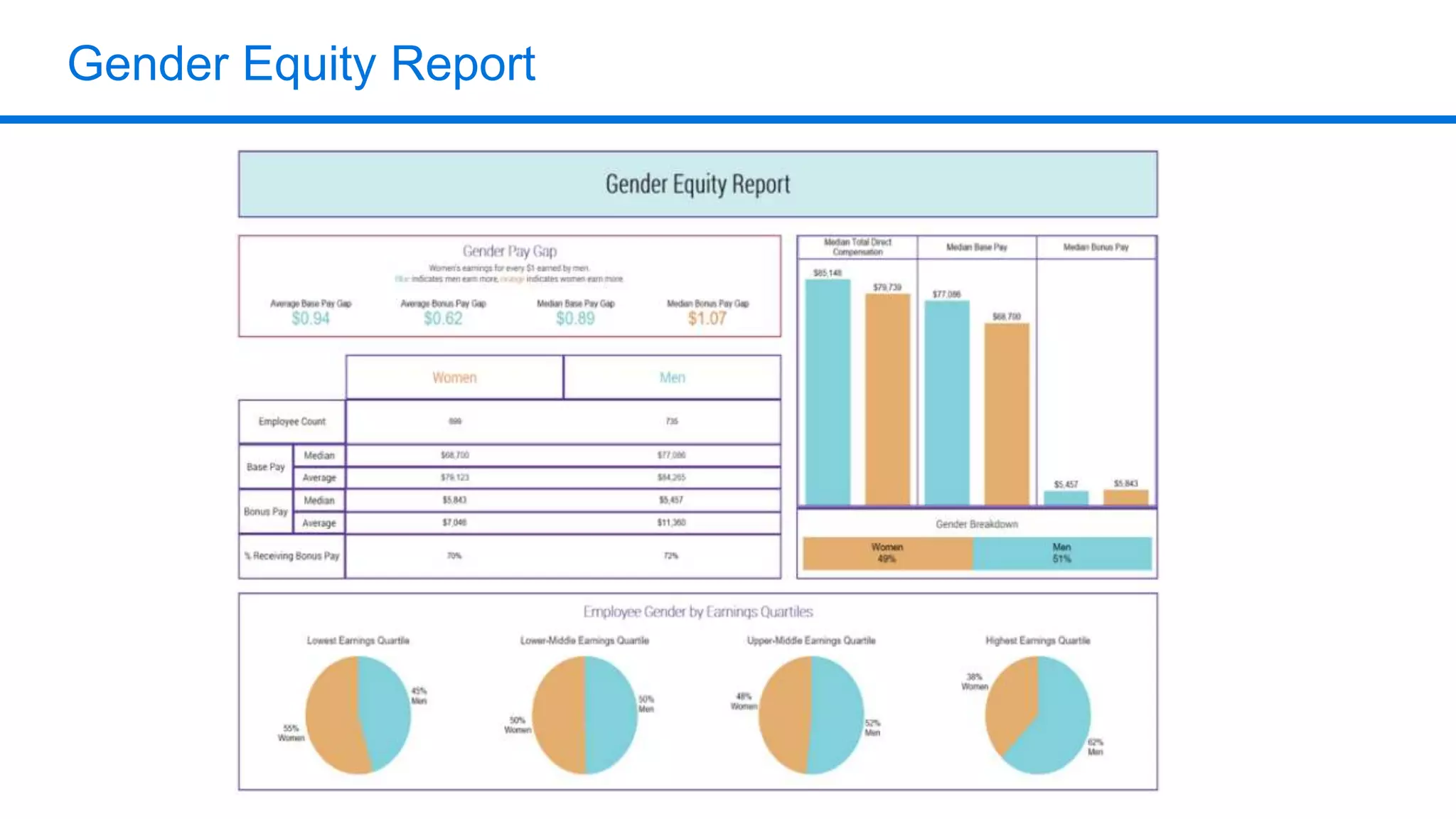
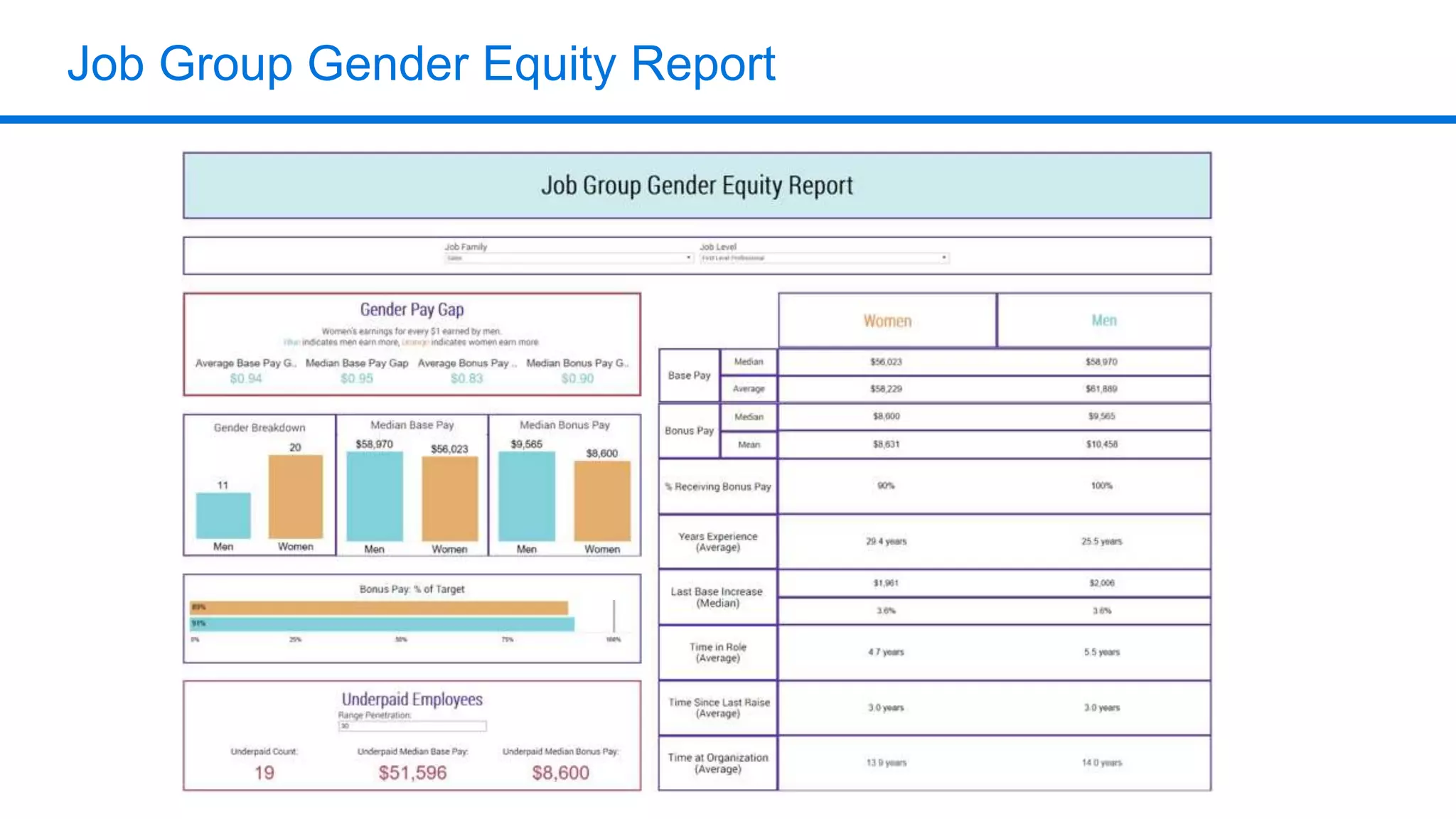
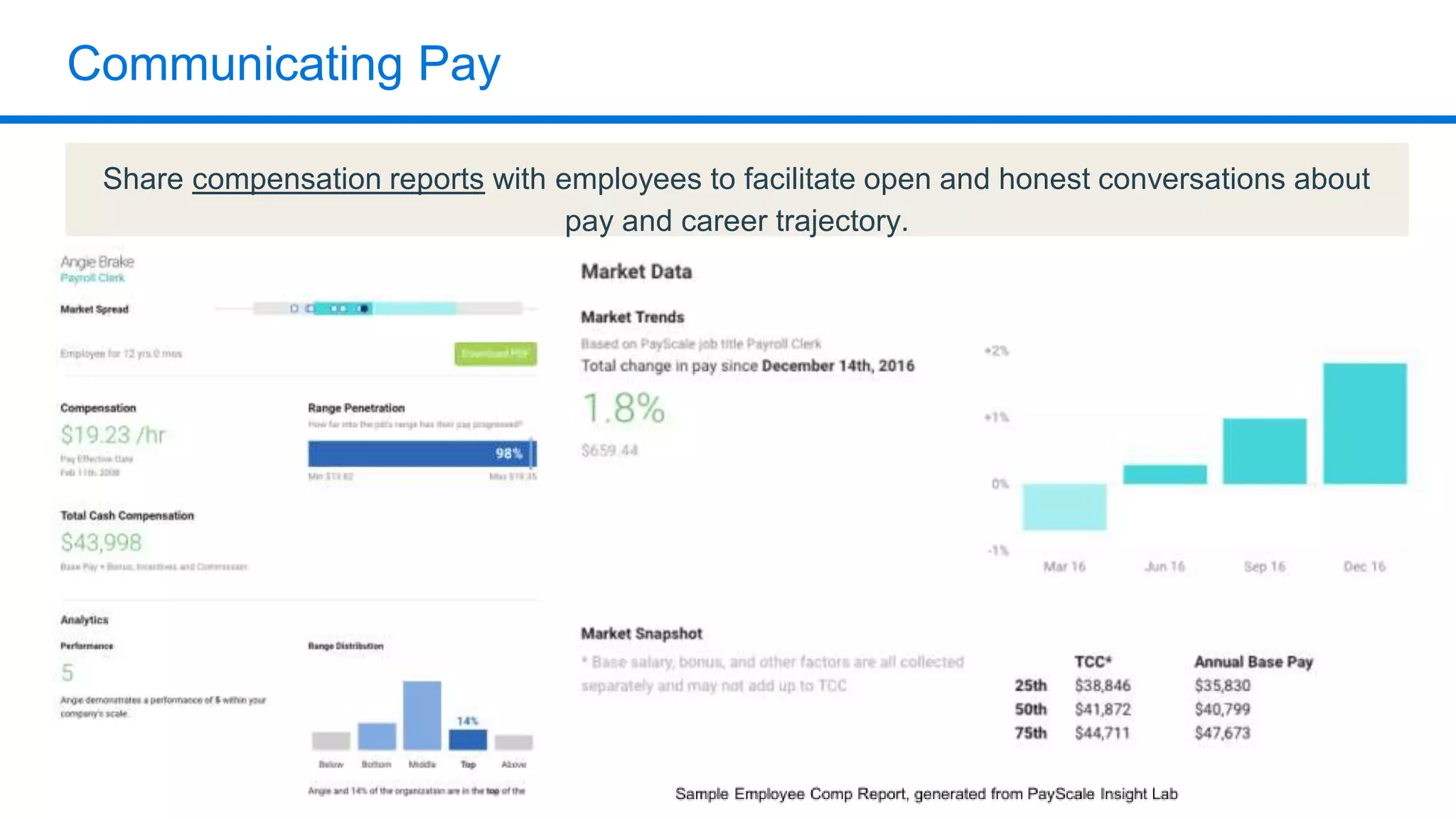
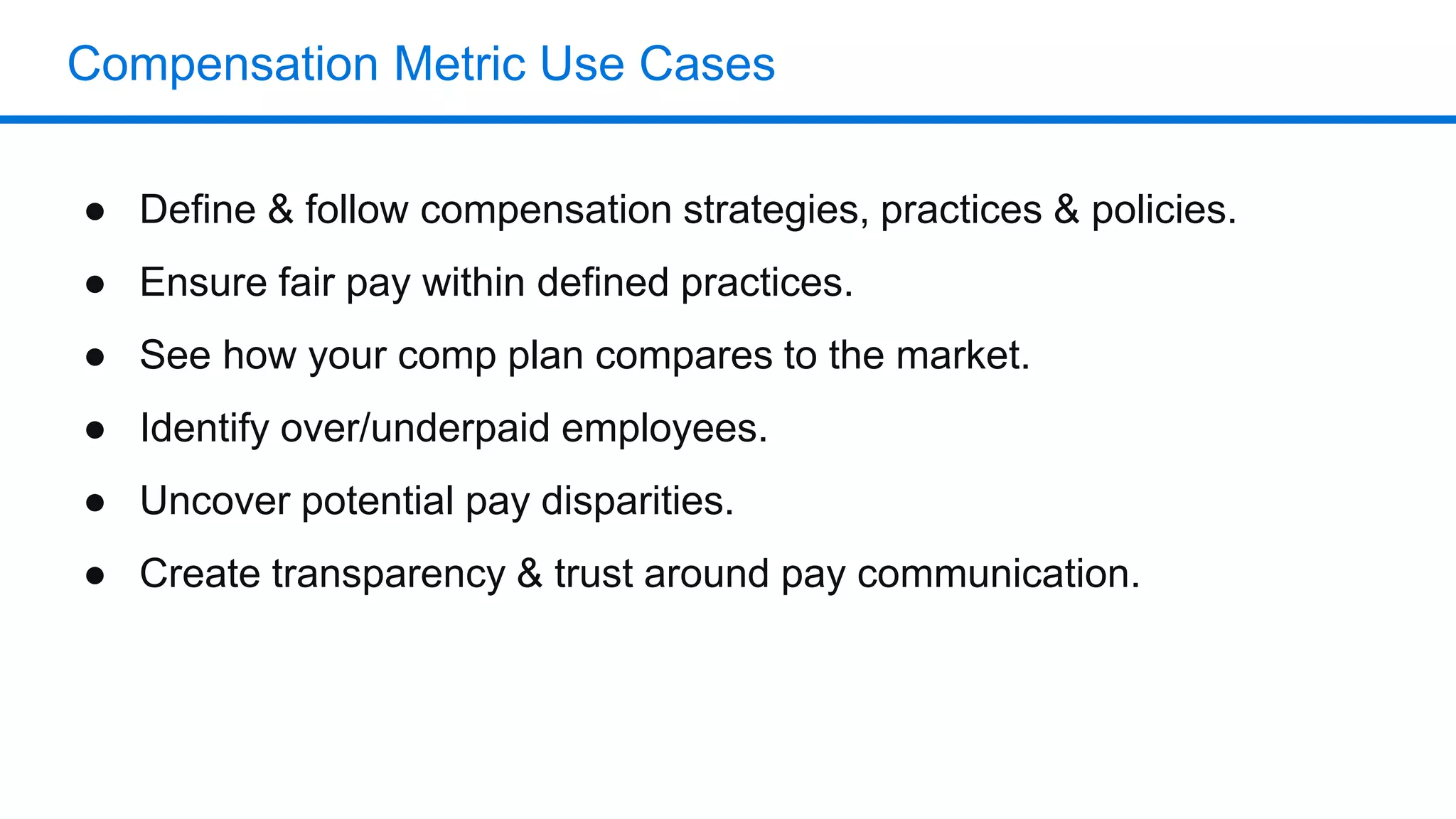
The document outlines six key HR metrics to measure in 2019, focusing on the importance of data and analytics in talent management, including quality of hire, career path ratio, and top performer retention rate. It emphasizes the need for effective data collection and analysis to drive strategic workforce planning and compensation practices, while addressing issues like pay equity and market underpayment. Practical advice is provided for monitoring these metrics to improve HR outcomes and enhance organizational performance.