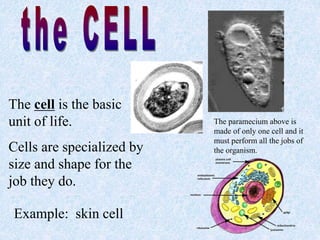
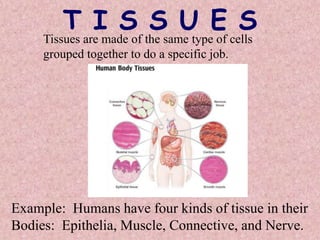
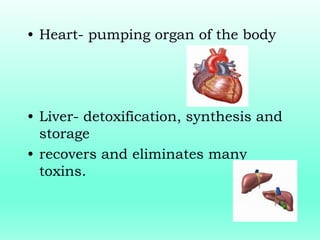
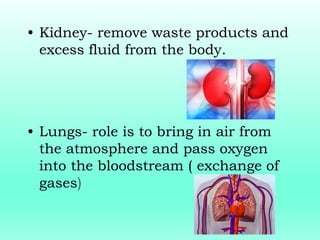
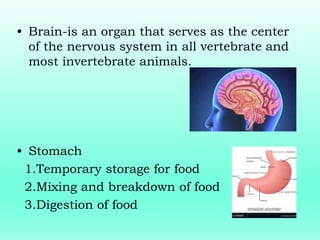
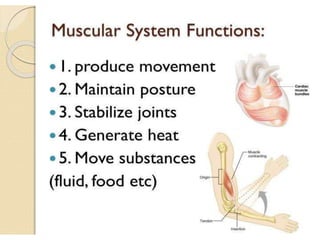
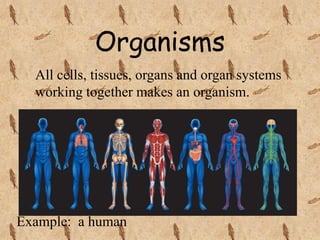
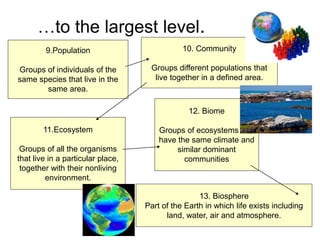
This document outlines the levels of biological organization from cells to the biosphere. It begins by describing unicellular and multicellular organisms and the differences between cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and organisms. It then defines each level in more detail, from cells as the basic unit of life, to tissues as groups of the same cell type, organs as structures made of multiple tissue types, organ systems as groups of organs that work together, organisms as the whole entity, populations as groups of the same species, communities as multiple interacting populations, ecosystems as organisms and their environment, biomes as large climate-defined areas, and finally the biosphere as the portion of Earth that supports life.