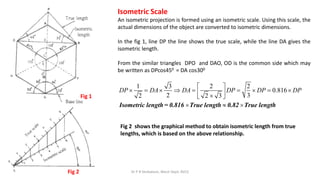
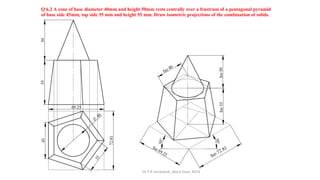
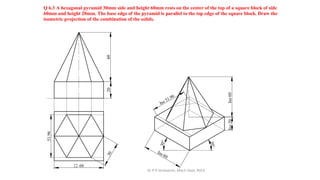
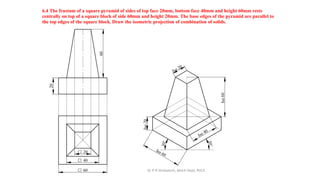
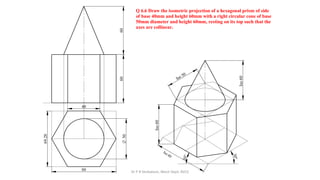
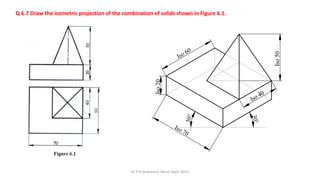
The document is a chapter about isometric projections from a textbook on computer aided engineering graphics. It defines isometric projection as a method to represent 3D objects through drawing where the sides are at 120 degree angles to each other. It discusses isometric scales, lines in isometric projections, and provides examples of drawing isometric projections of combinations of solids like prisms, cylinders, cones, spheres, etc. along with step-by-step solutions and notes.