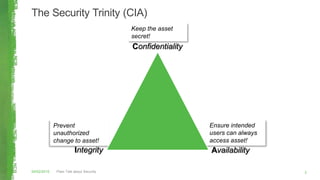
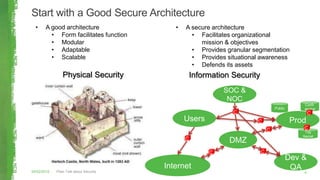
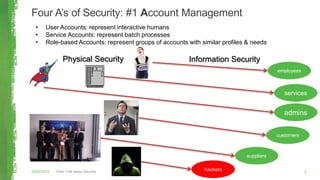
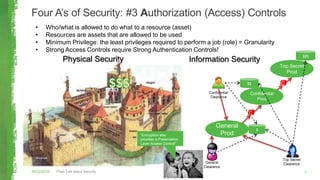
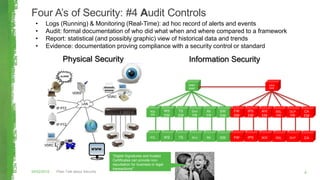
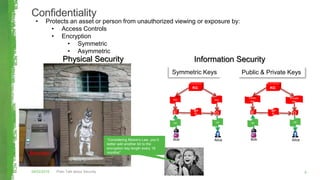
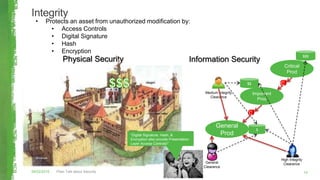
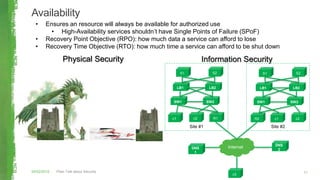
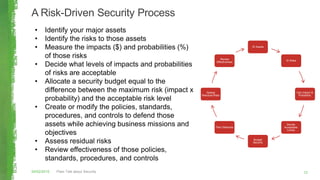
The document discusses key concepts in information security including the security trinity of confidentiality, integrity, and availability. It outlines the four As of security - account management, authentication controls, authorization/access controls, and audit controls. The document then explains how various security controls protect confidentiality, integrity, and availability. It concludes with outlining a risk-driven security process of identifying assets, risks, impacts, and controls to defend assets within an organization's security budget and objectives.