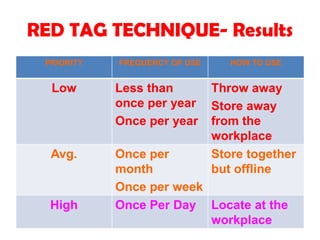
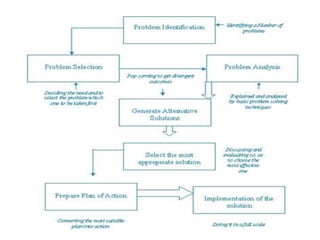
The document discusses 5S and quality circles as tools for total quality management. 5S refers to a system for organizing and standardizing a workplace. It involves sorting, setting in order, shining, standardizing, and sustaining these practices. When implemented through a quality circle, which is a group-based problem solving technique, 5S can lead to benefits like increased productivity, quality and safety while decreasing waste and costs. An example is provided of a community college reprographics shop that saw improved customer service and space optimization from applying 5S through a quality circle.